Valsalva Retinopathy
Clinical Features:
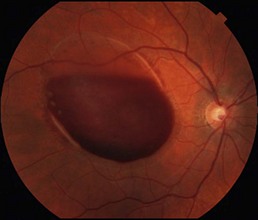
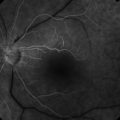
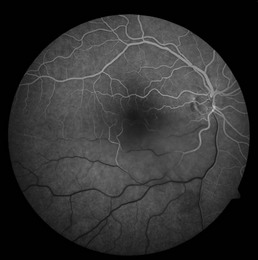
Preretinal hemorrhage accumulates in the sub-internal limiting membrane space, typically overlying the macula (Fig. 19.3.1). With rest, the red blood cells layer such that there is a serous component superiorly.
OCT Features:
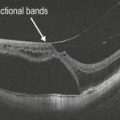
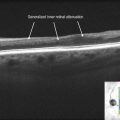
The superior serous component forms a hyporeflective cavity (Fig. 19.3.2), whereas the inferior hemorrhagic component forms a hyper-reflective cavity that blocks the underlying structures (Fig. 19.3.3). OCT can confirm the specific location of the hemorrhage, such as in the sub-internal limiting membrane space (Fig. 19.3.4). OCT is also helpful to monitor the progression and resolution of hemorrhage over time (Fig. 19.3.5).
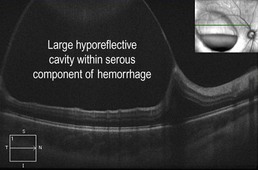
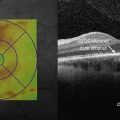
Figure 19.3.2 Horizontal line scan OCT through the superior serous component (corresponding to Figure 1) shows a large hyporeflective cavity. (Modified from Goldman, D.R. & Baumal, C.R. Natural history of valsalva retinopathy in an adolescent. Journal of Pediatric Ophthalmology and Strabismus, in press.)
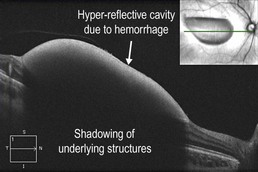
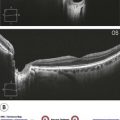
Figure 19.3.3 Horizontal line scan OCT through the inferior hemorrhagic component (corresponding to Figure 19.3.1) shows a large hyper-reflective cavity. (Modified from Goldman, D.R. & Baumal, C.R. Natural history of valsalva retinopathy in an adolescent. Journal of Pediatric Ophthalmology and Strabismus, in press.)
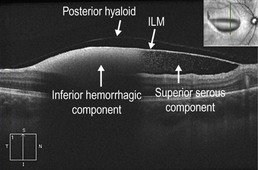
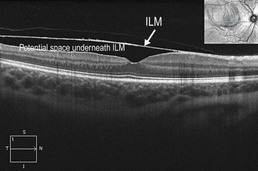
Figure 19.3.4 Vertical line scan OCT shows both the superior serous and inferior hemorrhagic components. Individual red blood cells can be seen disbursed within the serous component. The pre-macular hemorrhage is located underneath the internal limiting membrane. The posterior hyaloid face can also be seen. ILM, internal limiting membrane. (Modified from Goldman, D.R. & Baumal, C.R. Natural history of valsalva retinopathy in an adolescent. Journal of Pediatric Ophthalmology and Strabismus, in press.)