Cilioretinal Artery Occlusion
Clinical Features:
There is localized retinal whitening due to inner retinal edema corresponding to the distribution of the cilioretinal artery (Fig. 15.3.1), which is only present in 20–30% of individuals.
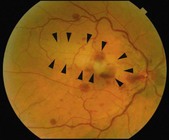
Figure 15.3.1 Color fundus photograph shows localized retinal whitening in the superior macula (arrowheads) corresponding to the distribution of the cilioretinal artery. There are also intraretinal hemorrhages, disc edema, and dilated and tortuous veins due to the concomitant presence of a central retinal vein occlusion.
OCT Features:
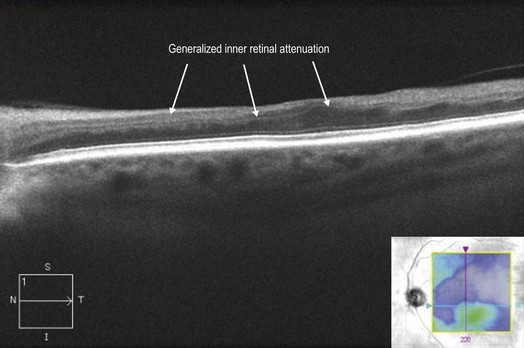
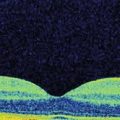
Localized inner retinal hyper-reflectivity, similar to that seen in branch retinal artery occlusion, but localized to the distribution of the cilioretinal artery is seen acutely (Fig. 15.3.2). Later, OCT will show thinning of the retina in the region supplied by the cilioretinal artery, which is best appreciated by a retinal thickness segmentation map (Fig. 15.3.3).
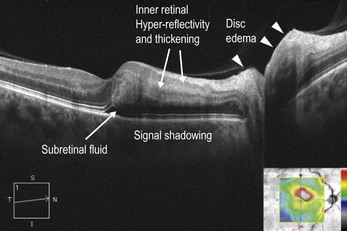
Figure 15.3.2 OCT (corresponding to Figure 15.3.1) in the acute setting of a CiRAO shows inner retinal hyper-reflectivity and thickening of the inner retinal layers with underlying shadowing. There is a tiny pocket of subretinal fluid. There is also associated disc edema (arrowheads) due to the concomitant CRAO.