Chapter 47 Unrelated Donor Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation
Table 47-1 Common Definitions in Human Leukocyte Antigen Genetics
| Term | Definition | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Allele | Unique sequence of an HLA gene defined by molecular methods | DRB1*04:01 allele is a unique sequence defined as DR4 by serologic methods |
| Antigen | Antibody-defined protein | DR4 antigen is a serologically defined protein product of an HLA gene |
| Haplotype | HLA genes inherited as a chromosomal unit | HLA-A1, HLA-B8, HLA-DR3 is a common haplotype among white populations |
| Genotype | Molecularly defined HLA allele or sequence | Genotypically matched donor and recipient are identical for the HLA alleles at a given HLA gene (e.g., HLA-DRB1*04:01) |
| Phenotype | Serologically defined HLA protein or antigen | Phenotypically matched donor and recipient share the same HLA antigen (e.g., HLA-DR4) |
HLA, Human leukocyte antigen.
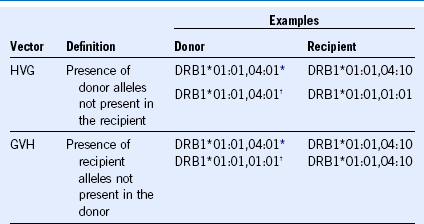
GVH, Graft versus host; HVG, host versus graft.
* These combinations contain bidirectional (both HVG and GVHD) mismatch vectors.
Criteria for an Interpretable Study on the Role of Human Leukocyte Antigen Matching in Cases of Unrelated Donor Transplantation
Table 47-3 Principles of Donor Human Leukocyte Antigen Matching Using High-Resolution DNA Typing Methods
GVHD, Graft-versus-host disease; HLA, human leukocyte antigen.
Human Leukocyte Antigen Selection Criteria for Unrelated Donors
Table 47-4 Importance of HLA Mismatching on Survival After Unrelated Donor Transplantation
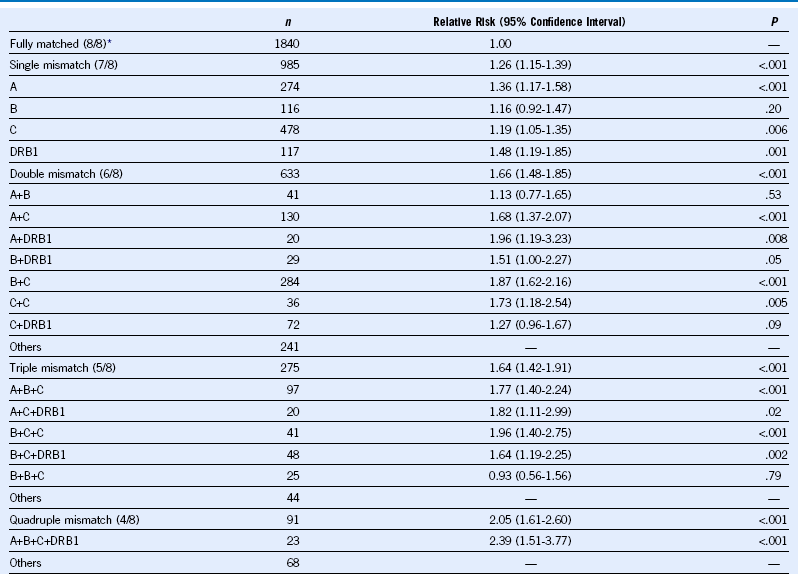
Data from Lee SJ, Klein J, Haagenson M, et al: High-resolution donor-recipient HLA matching contributes to the success of unrelated donor marrow transplantation. Blood 110:4576, 2007.