Chapter 12 Ultrasound in the Intensive Care Unit
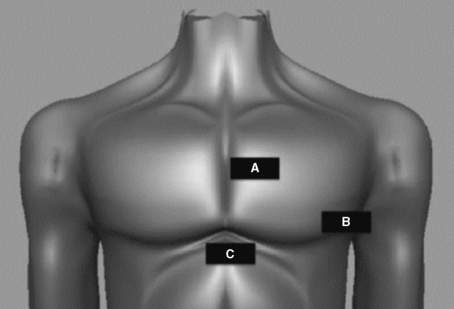
4 Where is the ultrasound transducer placed for cardiac imaging?
Because bone effectively blocks the transmission of ultrasound waves and creates an acoustic shadow on the ultrasound image display, the sonographer must use windows that allow ultrasound waves to avoid the sternum and ribs. The main echocardiographic windows are depicted in Figure 12-1.
5 What questions can be answered by focused transthoracic echocardiography?
 Is the left ventricular systolic function hyperdynamic, normal, depressed, or severely depressed?
Is the left ventricular systolic function hyperdynamic, normal, depressed, or severely depressed?
 Is the right ventricle dilated?
Is the right ventricle dilated?
 Is right ventricular systolic function normal or depressed?
Is right ventricular systolic function normal or depressed?
 Is a pericardial effusion present, and, if so, is there evidence of tamponade?
Is a pericardial effusion present, and, if so, is there evidence of tamponade?
 Do any of the valves appear grossly abnormal on two-dimensional imaging?
Do any of the valves appear grossly abnormal on two-dimensional imaging?
 Does the inferior vena cava (IVC) appear underfilled, normal, or overloaded?
Does the inferior vena cava (IVC) appear underfilled, normal, or overloaded?
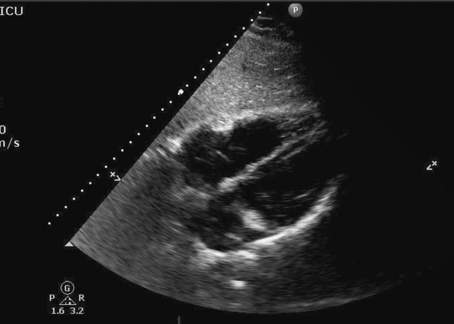
With advanced training, the intensivist can perform comprehensive transthoracic and/or transesophageal examinations. Figure 12-2 is an example of a normal subcostal four-chamber view obtained in the ICU.
9 How does fluid in the pleural space appear on ultrasound?
Pleural effusion and hemothorax, like all free fluid, appear black on the ultrasound display.
10 What is the FAST examination?
 Low-frequency ultrasound examination of the right upper quadrant (for blood between the diaphragm and liver, between liver and kidney, or around the kidney)
Low-frequency ultrasound examination of the right upper quadrant (for blood between the diaphragm and liver, between liver and kidney, or around the kidney)
 Left upper quadrant (for blood between diaphragm and spleen, between spleen and kidney, or around the kidney)
Left upper quadrant (for blood between diaphragm and spleen, between spleen and kidney, or around the kidney)
 Heart and pericardial space (for evidence of cardiac activity and pericardial fluid)
Heart and pericardial space (for evidence of cardiac activity and pericardial fluid)
16 Where can I learn critical care ultrasound techniques?
Key Points Ultrasound in the intensive care unit
1. High frequency provides excellent image resolution with poor depth. Low frequency allows deep imaging at the expense of image resolution.
2. Free fluid appears black on the ultrasound display.
3. Left ventricular systolic function can be accurately estimated by focused echocardiography.
4. Pneumothorax can be ruled out by ultrasound detection of lung sliding in multiple sites over the chest.
5. Ultrasound imaging of full compression of the common femoral vein and popliteal vein can be used to screen for lower-extremity DVT.
1 Blaivas M. Ultrasound in the detection of venous thromboembolism. Crit Care Med. 2007;35(5 Suppl):S224–S234.
2 Feissel M., Michard F., Faller J.P., et al. The respiratory variation in inferior vena cava diameter as a guide to fluid therapy. Intensive Care Med. 2004;30:1834–1837.
3 Lichtenstein D.A., Menu Y. A bedside ultrasound sign ruling out pneumothorax in the critically ill: lung sliding. Chest. 1995;108:1345–1348.
4 Mayo P.H., Beaulieu Y., Doelken P., et al. American College of Chest Physicians/La Société de Réanimation de Langue Française statement on competence in critical care ultrasonography. Chest. 2009;135:1050–1060.
5 Moore C.L., Copel J.A. Point-of-care ultrasonography. N Engl J Med. 2011;364:749–757.
6 Noble V.E., Nelson B. Manual of Emergency and Critical Care Ultrasound, 2nd ed. New York: Cambridge University Press; 2011.