20 Trigeminal (Gasserian) Ganglion Block
Placement
Anatomy
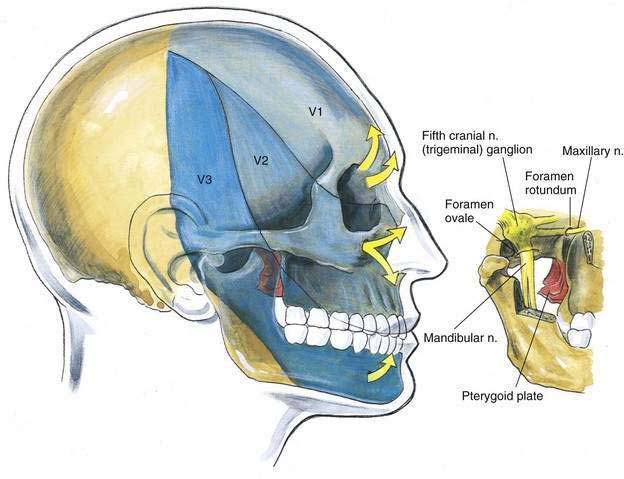
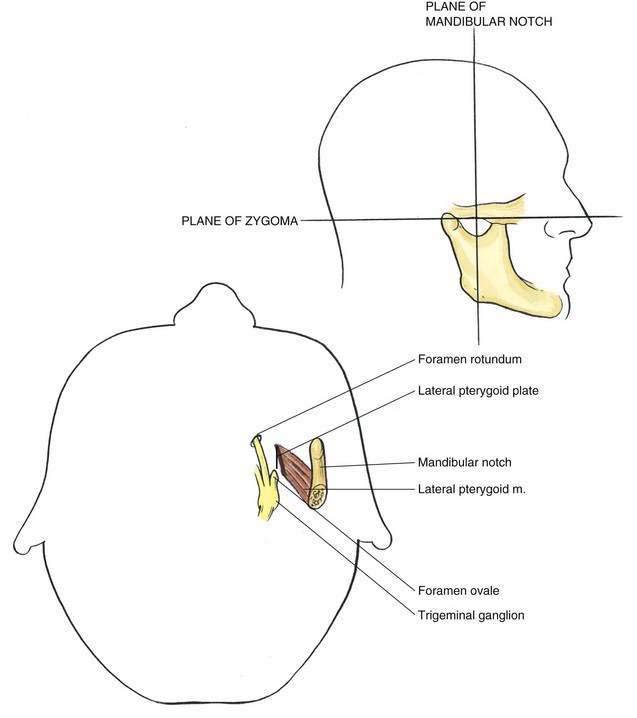
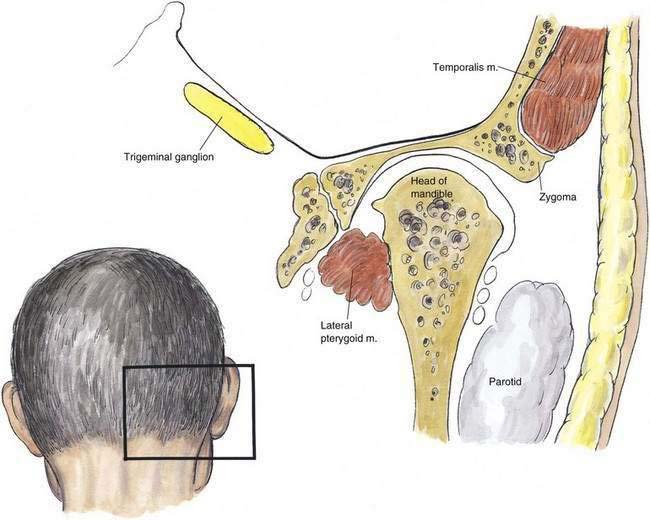
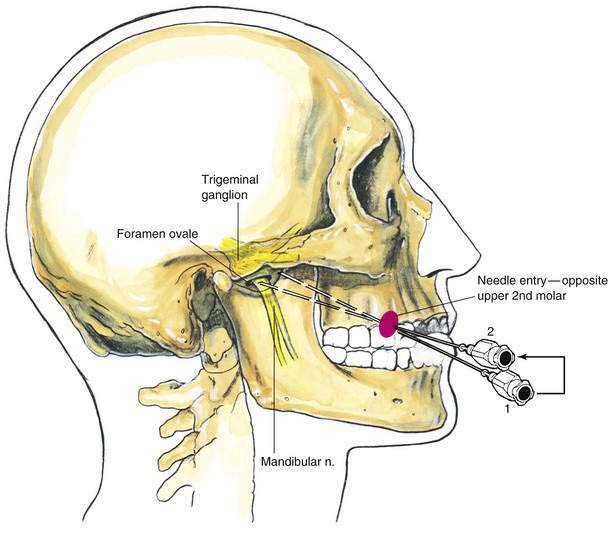
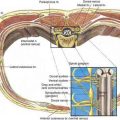
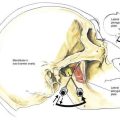
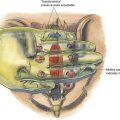
The trigeminal ganglion is located intracranially and measures approximately 1 × 2 cm. In its intracranial location, it lies lateral to the internal carotid artery and cavernous sinus and slightly posterior and superior to the foramen ovale, through which the mandibular nerve leaves the cranium (Fig. 20-1). From the trigeminal ganglion, the fifth cranial nerve divides into its three principal divisions: the ophthalmic, maxillary, and mandibular nerves. These nerves provide sensation to the region of the eye and forehead, upper jaw (midface), and lower jaw, respectively (see Fig. 20-1). The mandibular division carries motor fibers to the muscles of mastication, but otherwise these nerves are wholly sensory. The trigeminal ganglion is partially contained within a reflection of dura mater, Meckel’s cave. Figures 20-2 and 20-3 show that the foramen ovale is approximately in the horizontal plane of the zygoma, and in the frontal plane is roughly at the level of the mandibular notch. The foramen ovale is slightly less than 1 cm in diameter and is situated immediately dorsolateral to the pterygoid process.
Position
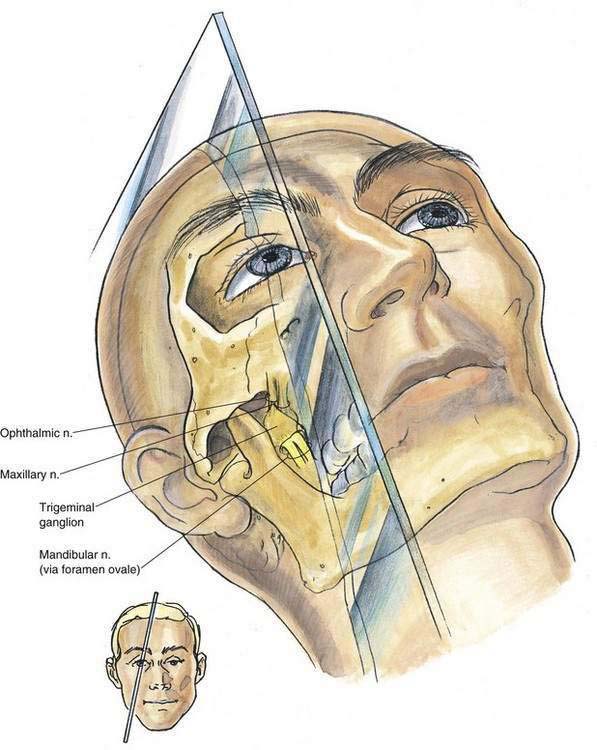
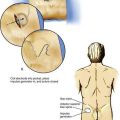
Patients are placed in a supine position and asked to fix their gaze straight ahead, as if they were looking off into the distance. The anesthesiologist should be positioned at the patient’s side, slightly below the level of the shoulder, so that by looking toward the patient’s face, the perspective shown in Figure 20-4 is observed.
Needle Puncture
A skin wheal is raised immediately medial to the masseter muscle, which can be located by asking the patient to clench his or her teeth. (It will most often be located approximately 3 cm lateral to the corner of the mouth.) Through this site, as illustrated in Figure 20-5, a 22-gauge, 10-cm needle is inserted as shown at position 1, aided by fluoroscopic guidance. The plane of insertion should be in line with the pupil, as illustrated in Figure 20-4. This will allow the needle tip to contact the infratemporal surface of the greater wing of the sphenoid bone, immediately anterior to the foramen ovale. This occurs at a depth of 4.5 to 6 cm. Once the needle is firmly positioned against this infratemporal region, it is withdrawn and redirected in a stepwise manner until it enters the foramen ovale at a depth of approximately 6 to 7 cm, or 1 to 1.5 cm past the needle length required to contact the bone initially (position 2).