Chapter 557 Thyroid Development and Physiology
557.1 Thyroid Hormone Studies
Serum Thyroxine-Binding Globulin
The thyroid hormones are transported in plasma bound to TBG, a glycoprotein synthesized in the liver. Estimation of TBG levels is occasionally necessary because TBG is increased or decreased in a variety of clinical situations, with effects on the level of total thyroxine. TBG binds about 70% of T4 and 50% of T3. TBG levels increase in pregnancy, in the newborn period, and with administration of estrogens (oral contraceptives), perphenazine, or methadone, and they decrease with androgens, anabolic steroids, glucocorticoids, and L-asparaginase. These effects are the results of modulation of hepatic synthesis of TBG. TBG levels may be markedly decreased owing to decreased production with liver disease or loss in the gut with protein-losing enteropathies or urine, as in the congenital nephrotic syndrome. Decreased or increased levels of TBG also occur as genetic traits (Chapter 558).
DeBoer MD, LaFranchi SH. Pediatric thyroid testing issues. Pediatr Endocrinol Rev. 2007;5:570-577.
Brown RS, Huang SA, Fisher DA. The maturation of thyroid function in the perinatal period and during childhood. In: Braverman LE, Utiger RD, editors. Werner & Ingbar’s the thyroid: a fundamental and clinical text. ed 9. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2005:1013-1028.
Fisher DA. Physiological variations in thyroid hormones: physiological and pathophysiological considerations. Clin Chem. 1996;42:135-139.
Kalomenou I, Alevizaki M, Ladopoulos C, et al. Thyroid volume and echostructure in schoolchildren living in an iodine-replete area: relation to age, pubertal stage, and body mass index. Thyroid. 2007;17:875-881.
LaFranchi SH, Haddow JE, Hollowell JG. Is thyroid inadequacy during gestation a risk factor for adverse pregnancy and developmental outcomes? Thyroid. 2005;15:60-71.
Williams Fl, Mires GJ, Barnett C, et al. Transient hypothyroxinemia in preterm infants: the role of cord sera thyroid hormone levels adjusted for prenatal and intrapartum factors. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2005;90:4599-4606.
Brown RS, Huang SA, Fisher DA. The maturation of thyroid function in the perinatal period and during childhood. In: Braverman LE, Utiger RD, editors. Werner & Ingbar’s the thyroid: a fundamental and clinical text. ed 9. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2005:1013-1028.
Caldwell KL, Jones R, Hollowell JG. Urinary iodine concentration: United States National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2001–2002. Thyroid. 2005;15:692-699.
Carrasco N, Kopp P. Thyroid synthesis and secretion. In: Braverman LE, Utiger RD, editors. Werner & Ingbar’s the thyroid: a fundamental and clinical text. ed 9. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2005:37-76.
De Felice M, Di Lauro F. The development of the thyroid gland: what we know and what we would like to know. Curr Opin Endocrinol Metab. 2005;12:4-9.
Friesema ECH, Grueters A, Biebermann H, et al. Association between mutations in a thyroid hormone transporter and severe X-linked psychomotor retardation. Lancet. 2004;364:1435-1437.
Heuer H, Visser TJ. Minireview: pathophysiological importance of thyroid hormone transporters. Endocrinol. 2009;150:1078-1083.
Santisteban P. Development and anatomy of the hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid axis. In: Braverman LE, Utiger RD, editors. Werner & Ingbar’s the thyroid: a fundamental and clinical text. ed 9. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2005:8-25.

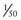 that of T4, but T3 is the physiologically active thyroid hormone.
that of T4, but T3 is the physiologically active thyroid hormone.