CHAPTER 9 Thorax
Heart and great vessels
Principles of cardiac surgery
Contraindications for surgery
Correction of a defect alone may be contraindicated in the presence of the following:
Preoperative preparation
Postoperative complications
Renal failure
Due to ATN, resulting from renal hypoperfusion. Haemofiltration/haemodialysis may be required.
Congenital heart disease
Acyanotic
Acquired valvular heart disease
Ischaemic heart disease
Aetiology
Male sex, smoking, family history, hypertension, hyperlipidaemia, diabetes, obesity, myxoedema.
Investigations
• ECG: may be normal at rest in up to 75% of patients; S-T depression with angina – exercise ECG usually confirms diagnosis
Pericarditis
Thoracic aorta
Thoracic trauma
Closed injuries
Investigations
Pleura and lungs
Pulmonary infections
Bronchiectasis
Lung tumours
Bronchial carcinoma
Symptoms and signs
Complications
• Thoracic: pleural effusion, recurrent laryngeal nerve palsy (hoarseness), SVC obstruction, Horner’s syndrome (ptosis, meiosis, enophthalmos, anhidrosis) especially with Pancoast’s tumour (invasive cancer of apex of lung).
Investigations
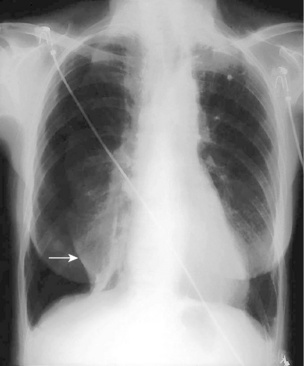
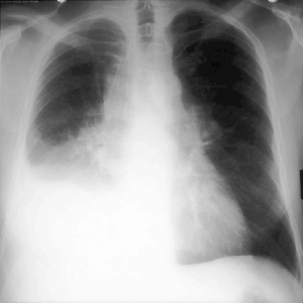
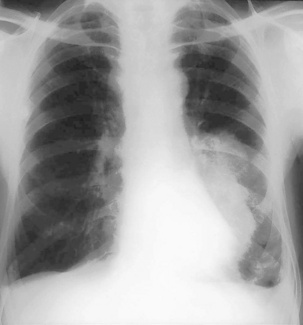
• CXR: PA and lateral (→ Fig. 9.3), mass, raised diaphragm with involvement of phrenic nerve, pleural effusion
Mediastinum
Certain lesions are more likely to occur in characteristic mediastinal sites:
• Anterior mediastinum: dermoid cysts, teratoma, pericardial cysts, bronchogenic cysts, diaphragmatic hernia (foramen of Morgagni), thymoma
• Posterior mediastinum: neurogenic tumours, e.g. dumbbell tumours of neurofibroma, paravertebral mass, e.g. TB abscess, phaeochromocytoma, diaphragmatic hernia, achalasia, hiatus hernia.