Chapter 23 The eye
Inflammation of the eye
Inflammation may be a result of an allergic reaction, infection or irritation due to dust or particles. Simple irritation of the eye can be treated with an eye lotion or drops, usually containing either extract of witch hazel (see Chapter 22), or the herb eyebright.
Eyebright, euphrasia officinalis L. and E. rostkoviana hayne (euphrasiae herba)
Therapeutic uses and available evidence
Extract of Euphrasia is a traditional remedy for disorders of the eye such as conjunctivitis. Practically no clinical studies have been carried out, but single-dose eye drops containing extracts of the herb were evaluated in a clinical prospective cohort trial for conjunctivitis, and efficacy and tolerability were deemed ‘good to very good’ by both patients and physicians (Stoss et al 2000). Overall, the evidence for beneficial effects is very limited.
Distilled witch hazel, aqua hamamelidis
Distilled witch hazel is prepared by macerating the dormant and partially dried twigs of Hamamelis virginiana L.,(Hamamelidaceae). It is often used in eye drops and eye lotions to soothe the eye and clear redness (for further details, see witch hazel, Chapter 22, Skin).
Glaucoma
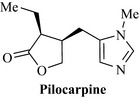
Pilocarpine 
Pilocarpine (Fig. 23.1) is an alkaloid obtained from Jaborandi leaf (Pilocarpus microphyllus Stapf. and other species of Pilocarpus, Rutaceae). Pilocarpine is a sympathomimetic agent, causing salivation, tachycardia and other effects if taken systemically. Its main use is in ophthalmic preparations as a miotic, in open-angle glaucoma and to contract the pupil after the use of atropine (BNF). It is a prescription-only medicine in most countries.
Anterior uveitis
Stoss M., Michels C., Peter E., Beutke R., Gorter R.W. Prospective cohort trial of Euphrasia single-dose eye drops in conjunctivitis. J. Altern. Complement. Med.. 2000;6:499.
British National Formulary. Published biannually by the BMJ Group and the Pharmaceutical Press. See also http://bnf.org/bnf/index.htm