Sympathetic Ophthalmia
Clinical Features:
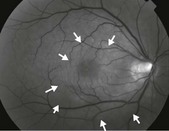
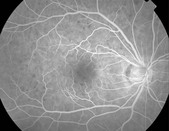
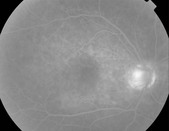
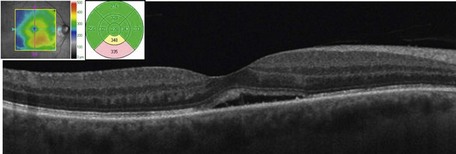
Clinically, patients present with a bilateral severe, unremitting granulomatous panuveitis. There may be associated hypotony, small depigmented nodules at the level of the retinal pigment epithelium (Dalen–Fuch’s nodules), choroidal thickening, and serous retinal detachments (Fig. 17.5.1). Signs of prior injury or surgery in one eye are present.
OCT Features:
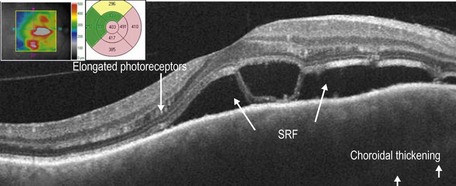
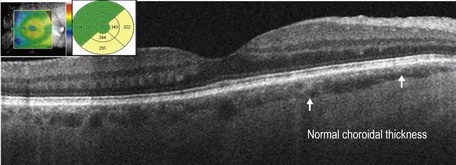
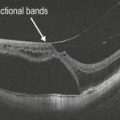
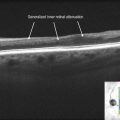
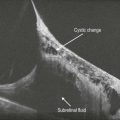
OCT findings include posterior choroidal thickening and accumulation of turbid subretinal fluid with deposition of fibrin and/or fibrinous bands in the subretinal fluid (Fig. 17.5.2). Macular edema may also be seen. In later stages of sympathetic ophthalmia, there is retinal and retinal pigment epithelium atrophy and thinning with transmission defects noted (Fig. 17.5.3).