Mediastinal mass, tumor, or lymphadenopathy
• Imaging findings suggesting SVC obstruction
 Dilated collateral veins (internal jugular veins, intercostal veins, azygous vein, lateral thoracic, etc.)
Dilated collateral veins (internal jugular veins, intercostal veins, azygous vein, lateral thoracic, etc.)
 Dilated collateral veins (internal jugular veins, intercostal veins, azygous vein, lateral thoracic, etc.)
Dilated collateral veins (internal jugular veins, intercostal veins, azygous vein, lateral thoracic, etc.)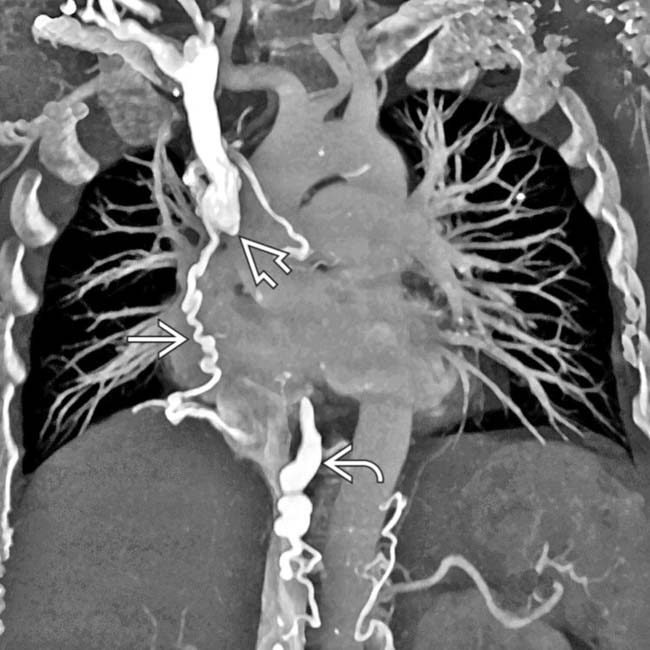
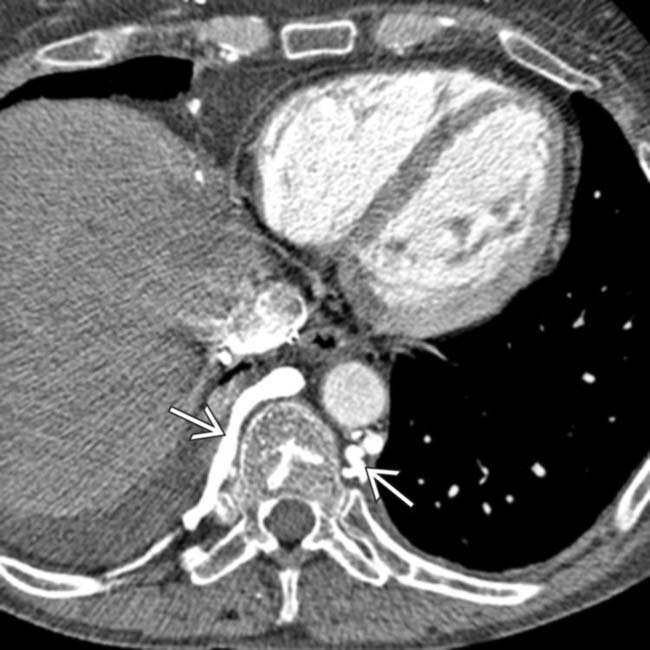
 , with collateral flow through an enlarged azygous vein
, with collateral flow through an enlarged azygous vein  as well as various mediastinal collateral veins
as well as various mediastinal collateral veins 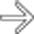 .
.
 in the left medial segment of the liver (hot quadrate sign) and collateral veins
in the left medial segment of the liver (hot quadrate sign) and collateral veins  over the surface of the liver.
over the surface of the liver.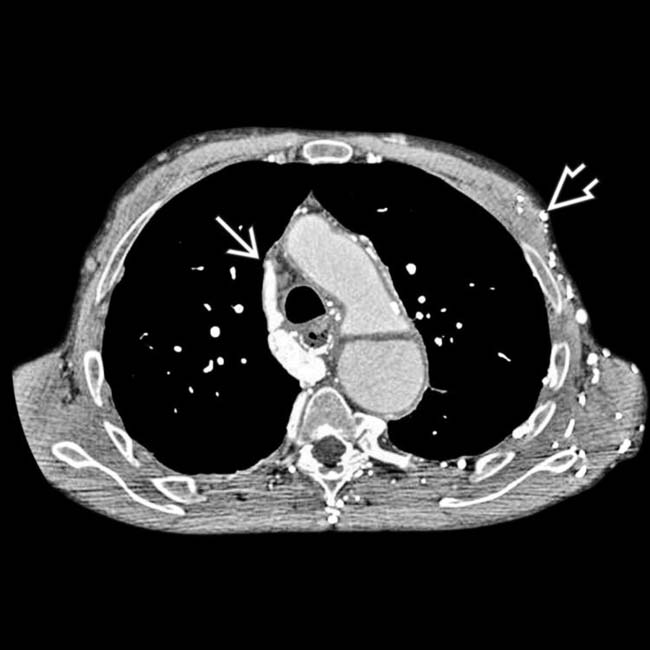
 with extensive collateral veins
with extensive collateral veins  over the chest and abdominal walls.
over the chest and abdominal walls.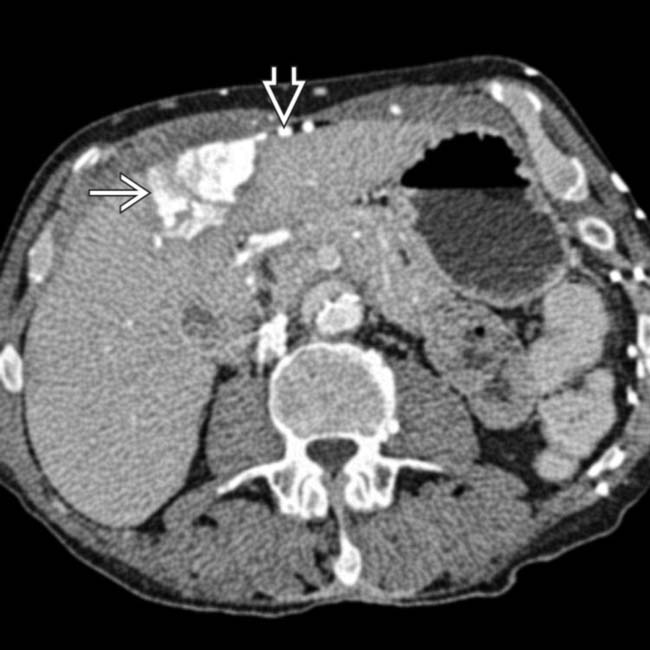
 due to opacification of liver parenchyma alongside the intra- and perihepatic collaterals
due to opacification of liver parenchyma alongside the intra- and perihepatic collaterals  . The liver perfusion abnormality was not seen on portal venous phase images (not shown).
. The liver perfusion abnormality was not seen on portal venous phase images (not shown).CLINICAL ISSUES
Presentation
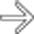
 . A subsequent CECT of the chest documented SVC obstruction related to the patient’s indwelling catheter.
. A subsequent CECT of the chest documented SVC obstruction related to the patient’s indwelling catheter.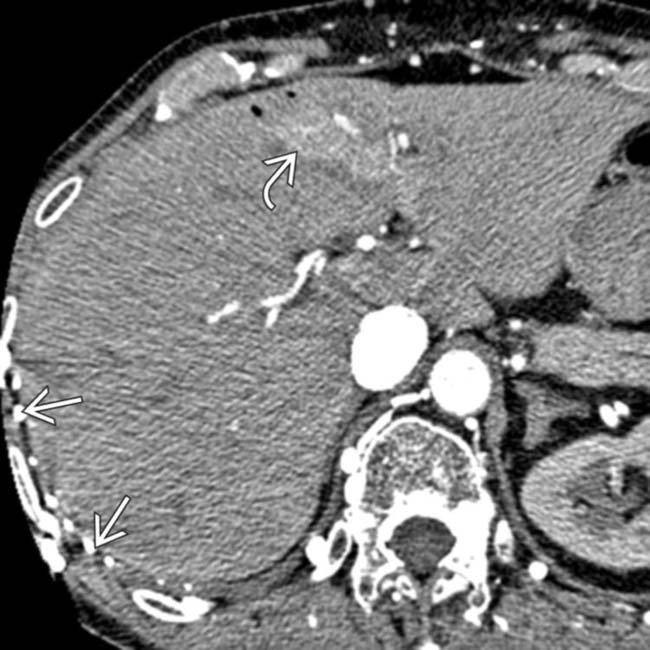
 along the right chest wall, as well as the early enhancement of the liver in the region of the falciform ligament
along the right chest wall, as well as the early enhancement of the liver in the region of the falciform ligament  from venous collaterals.
from venous collaterals.













































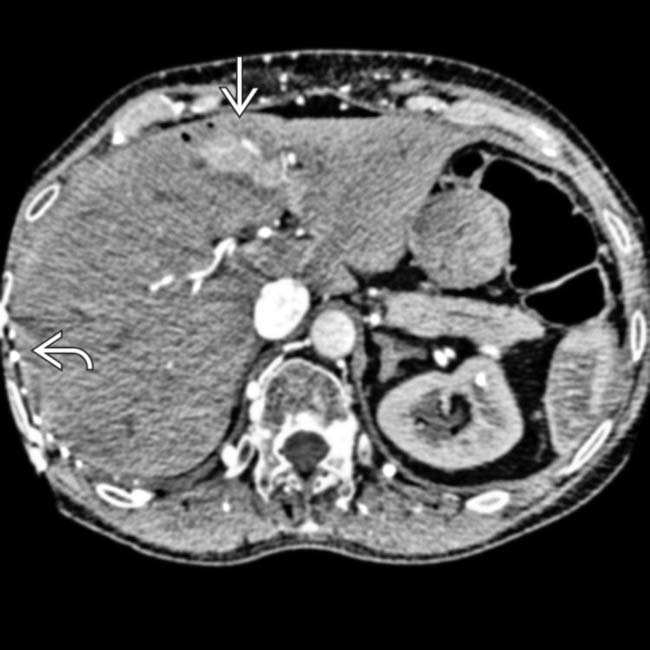
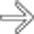
 along the surface of the liver, with opacification of a portion of the medial segment
along the surface of the liver, with opacification of a portion of the medial segment  due to transhepatic collateral venous flow.
due to transhepatic collateral venous flow.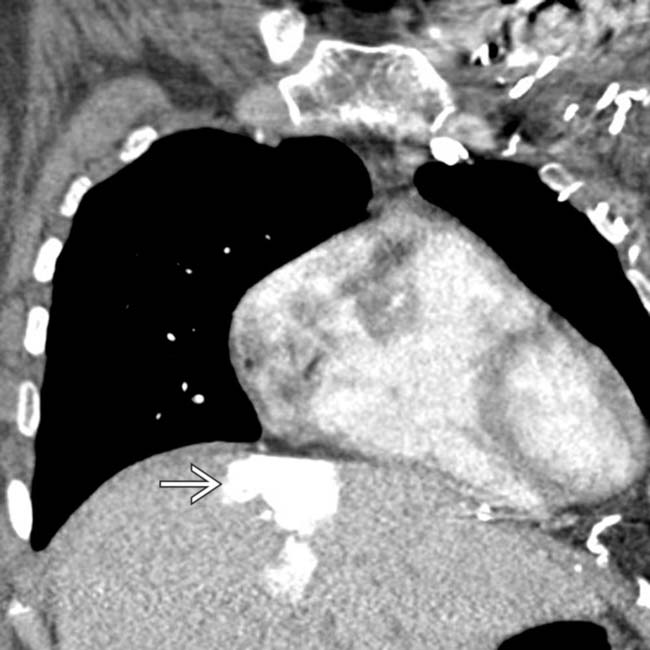
 in the left medial segment of the liver in a patient with SVC obstruction.
in the left medial segment of the liver in a patient with SVC obstruction.

