29 Superior Laryngeal Block
Placement
Anatomy
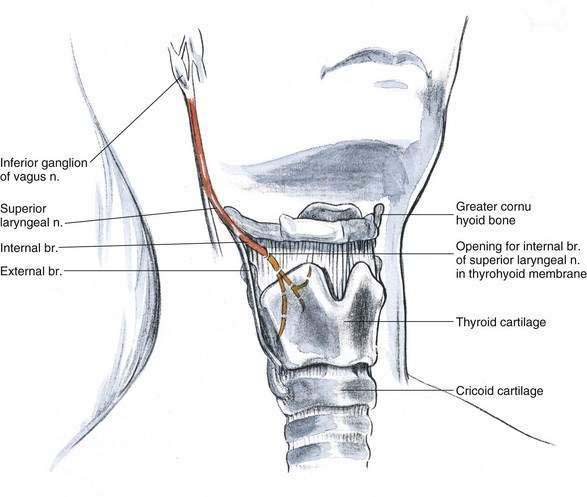
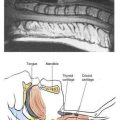
The superior laryngeal nerve is a branch of the vagus nerve. After it leaves the main vagal trunk, it courses through the neck and passes medially, caudal to the greater cornu of the hyoid bone, at which point it divides into an internal branch and an external branch. The internal branch is the nerve of interest in superior laryngeal nerve block, and it is blocked where it enters the thyrohyoid membrane just inferior to the caudal aspect of the hyoid bone (Fig. 29-1).
Position
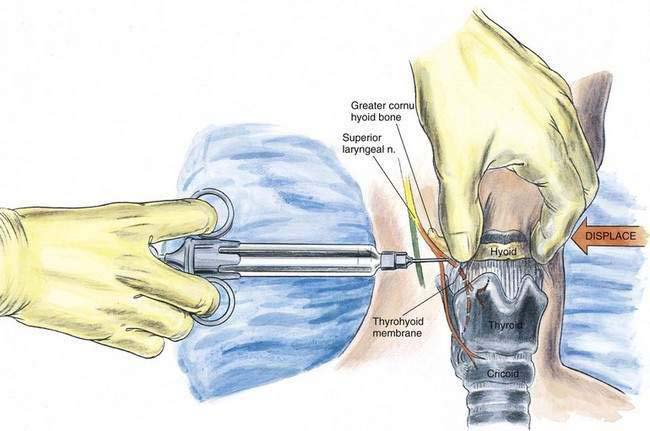
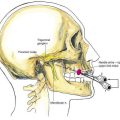
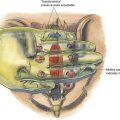
The patient is placed supine with the neck extended. The anesthesiologist should displace the hyoid bone toward the side to be blocked by grasping it between the index finger and the thumb (Fig. 29-2). A 25-gauge, short needle is then inserted to make contact with the greater cornu of the hyoid. The needle is “walked off” the caudal edge of the hyoid and advanced 2 to 3 mm so that the needle tip rests between the thyrohyoid membrane laterally and the laryngeal mucosa medially. Two to 3 mL of the drug is then injected; an additional 1 mL is injected while the needle is withdrawn.