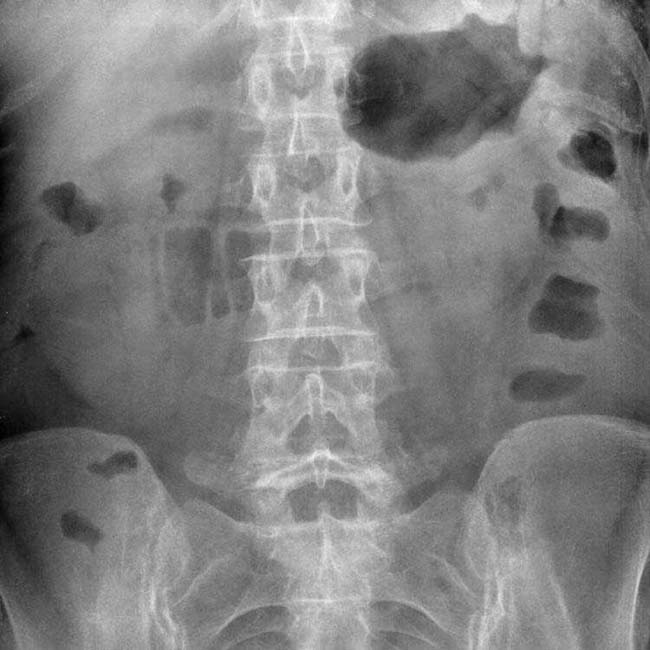
Air-fluid levels on upright or decubitus radiograph
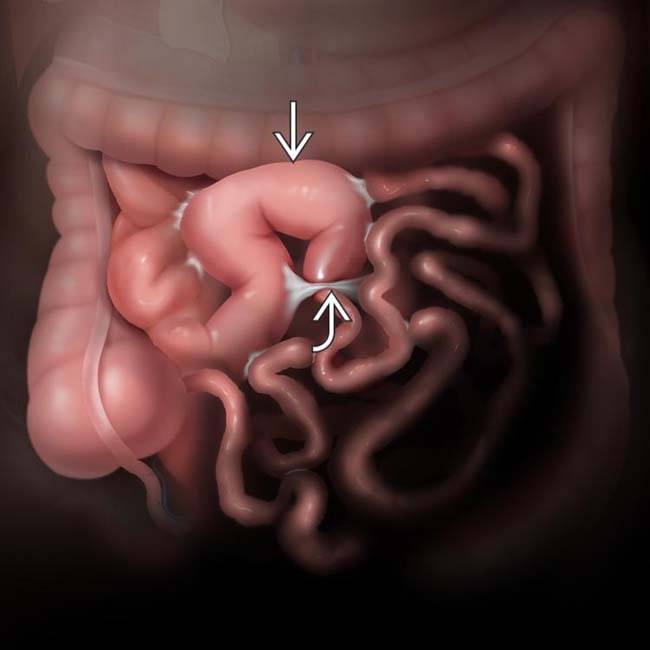
• Transition zone between dilated and collapsed bowel is critical to define presence, site, and cause of obstruction
• Small bowel feces sign: Gas bubbles mixed with particulate matter in dilated loops just proximal to site of obstruction
 , as well as the adhesive band
, as well as the adhesive band  .
.
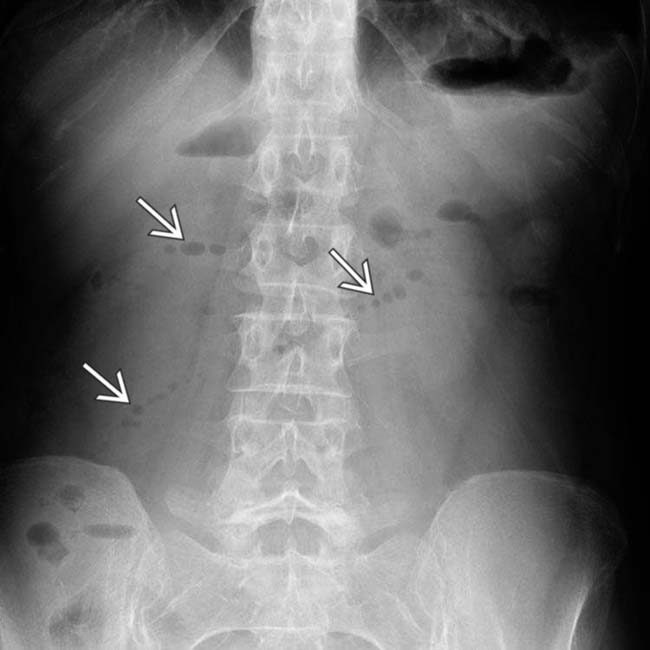
 , indicating gas within fluid-distended, obstructed segments of SB.
, indicating gas within fluid-distended, obstructed segments of SB.
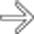
 , but massive dilation of proximal SB segments
, but massive dilation of proximal SB segments  with only small bubbles of intraluminal air
with only small bubbles of intraluminal air  , accounting for the string-of-pearls sign. An adhesive SBO was confirmed at surgery.
, accounting for the string-of-pearls sign. An adhesive SBO was confirmed at surgery.IMAGING
General Features
CT Findings
• Small bowel feces sign: Gas bubbles mixed with particulate matter in dilated loops just proximal to site of obstruction
• Extrinsic lesions
 Hernia
Hernia
 Hernia
Hernia
• Intraluminal lesions: Gallstones, foreign bodies, bezoars, Ascaris
PATHOLOGY
General Features
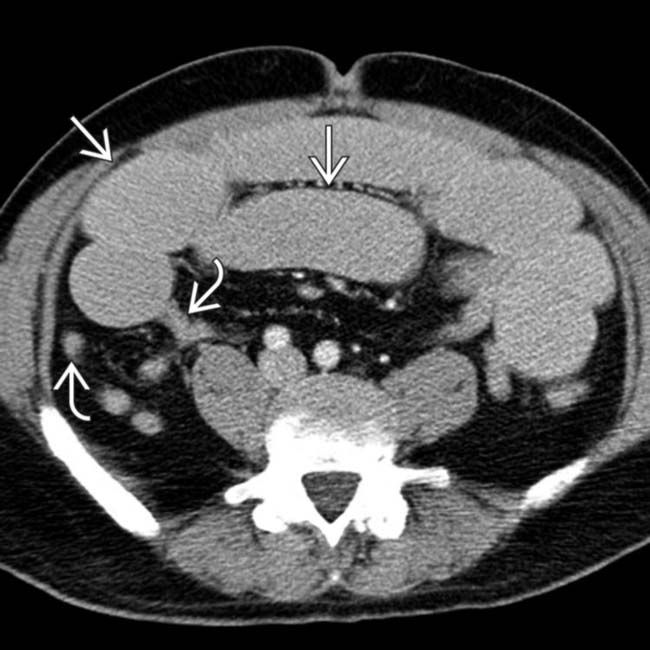
 and decompressed bowel
and decompressed bowel  distal to the transition site.
distal to the transition site.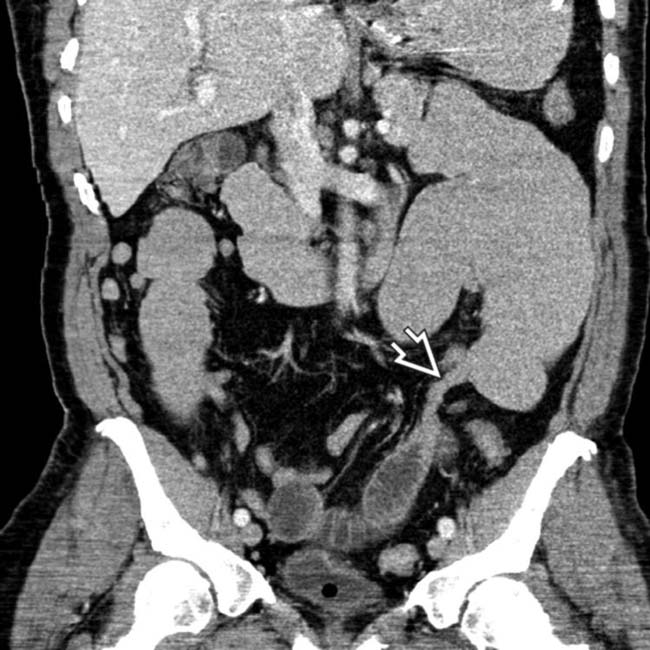
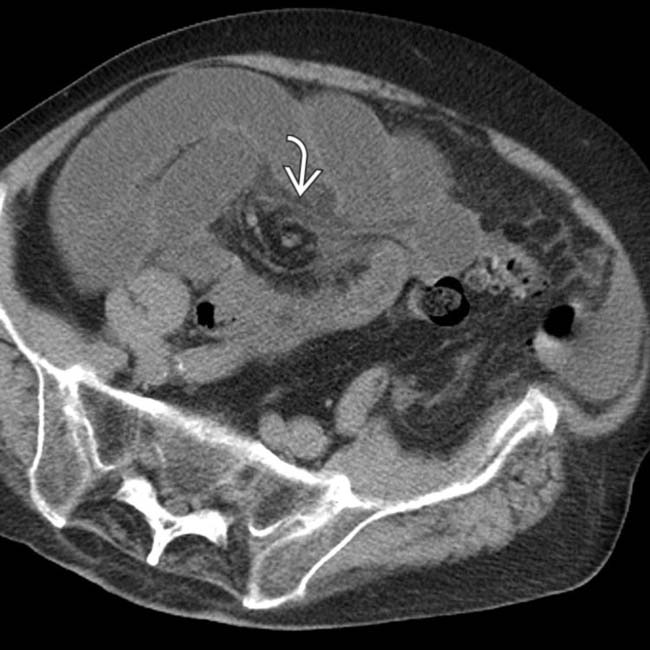
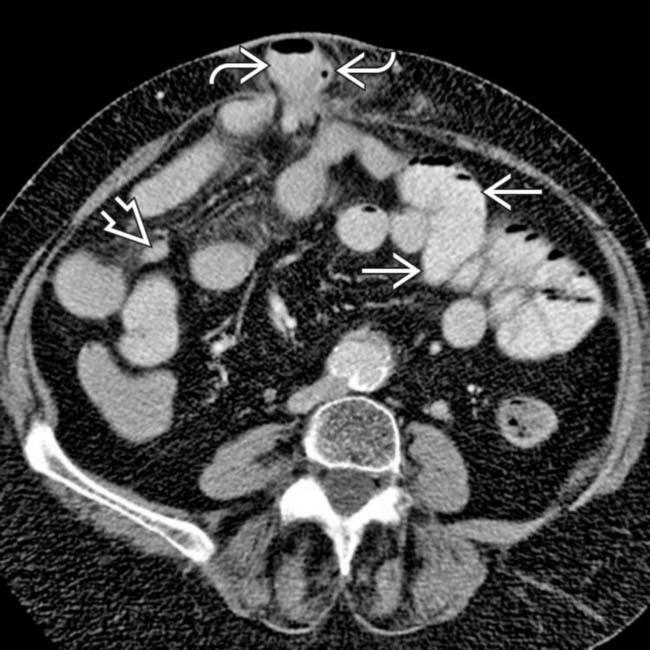
 from dilated to collapsed SB. No mass, hernia, or other specific cause was identified, leading to the inference that this was an adhesive SBO, subsequently confirmed at surgery.
from dilated to collapsed SB. No mass, hernia, or other specific cause was identified, leading to the inference that this was an adhesive SBO, subsequently confirmed at surgery.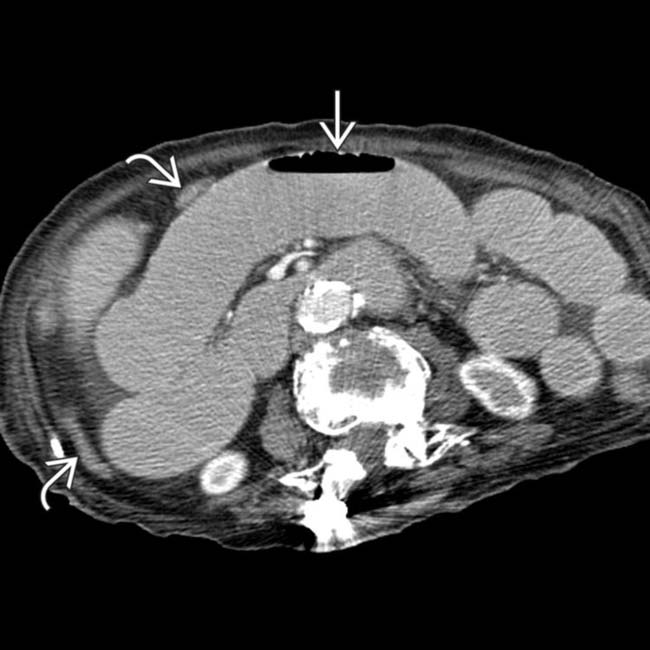
 , while distal SB and colon are decompressed
, while distal SB and colon are decompressed 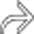 .
.
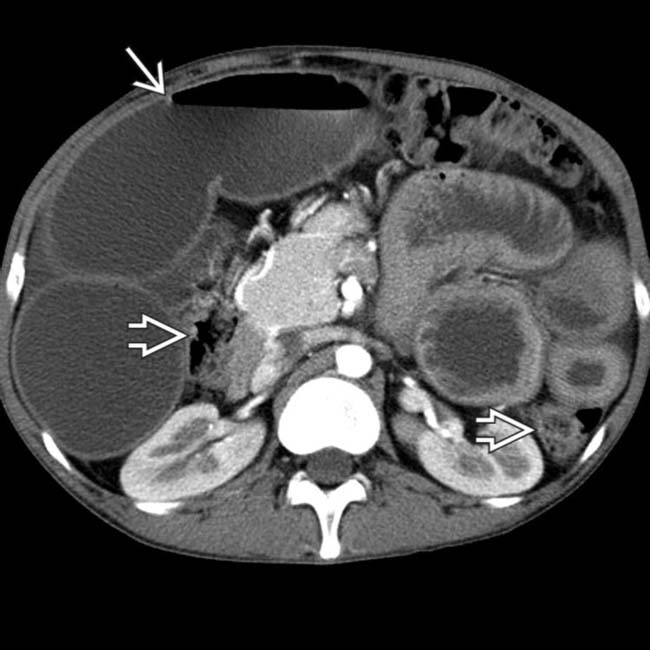
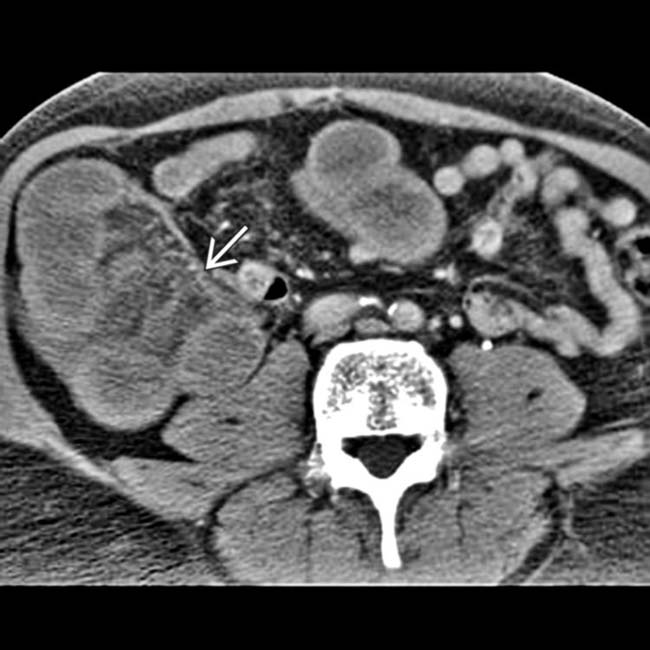
 entering a right femoral hernia.
entering a right femoral hernia.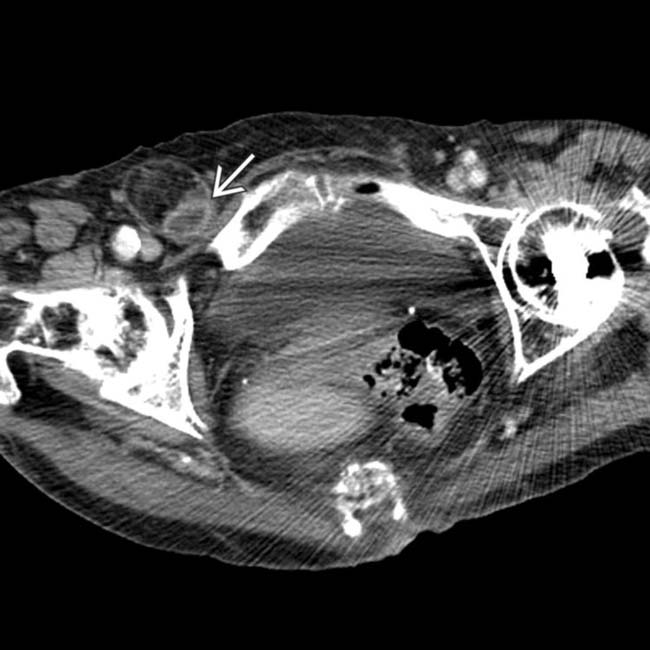
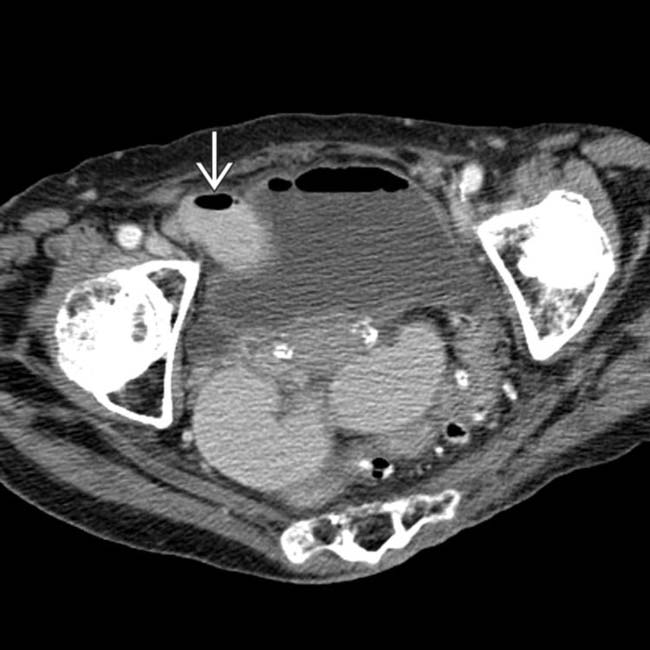
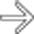 trapped within the femoral hernia, establishing this as the transition point and etiology of the SBO.
trapped within the femoral hernia, establishing this as the transition point and etiology of the SBO.
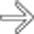 enters the right femoral hernia
enters the right femoral hernia  . Hernias are the 2nd most common etiology for SBO, though much less common than adhesive SBO.
. Hernias are the 2nd most common etiology for SBO, though much less common than adhesive SBO.
 and SB segments that are matted together
and SB segments that are matted together  without definable mesenteric fat between SB segments.
without definable mesenteric fat between SB segments.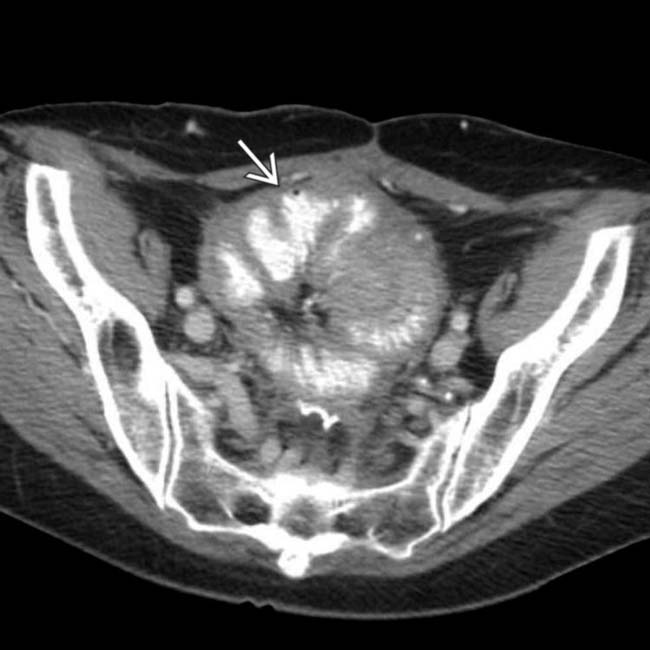
 due to serosal implants of recurrent ovarian carcinoma. Almost 1/2 of all women with ovarian carcinoma will develop symptoms of SBO.
due to serosal implants of recurrent ovarian carcinoma. Almost 1/2 of all women with ovarian carcinoma will develop symptoms of SBO.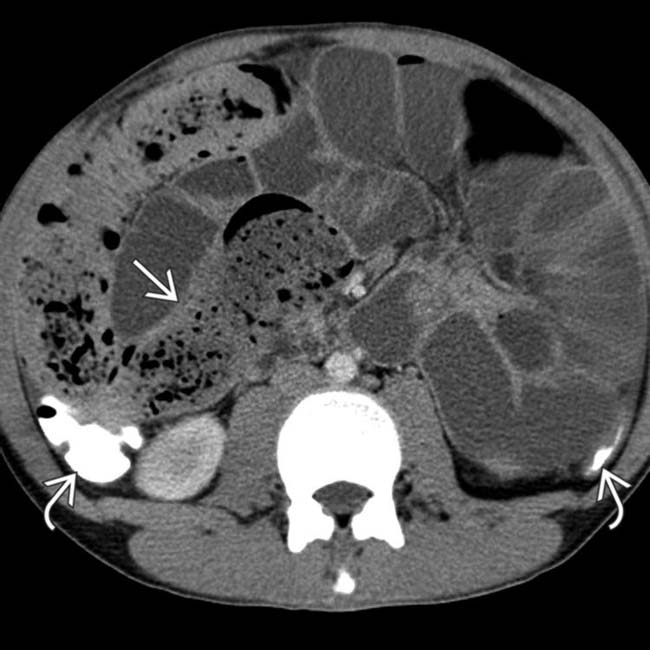
 , the result of prior attempts at colon cleansing by water-soluble contrast enema. The SB is markedly distended with a small bowel feces sign in the distal ileum
, the result of prior attempts at colon cleansing by water-soluble contrast enema. The SB is markedly distended with a small bowel feces sign in the distal ileum  . This is a classic example of DIOS (distal intestinal obstruction syndrome) in a patient with cystic fibrosis.
. This is a classic example of DIOS (distal intestinal obstruction syndrome) in a patient with cystic fibrosis.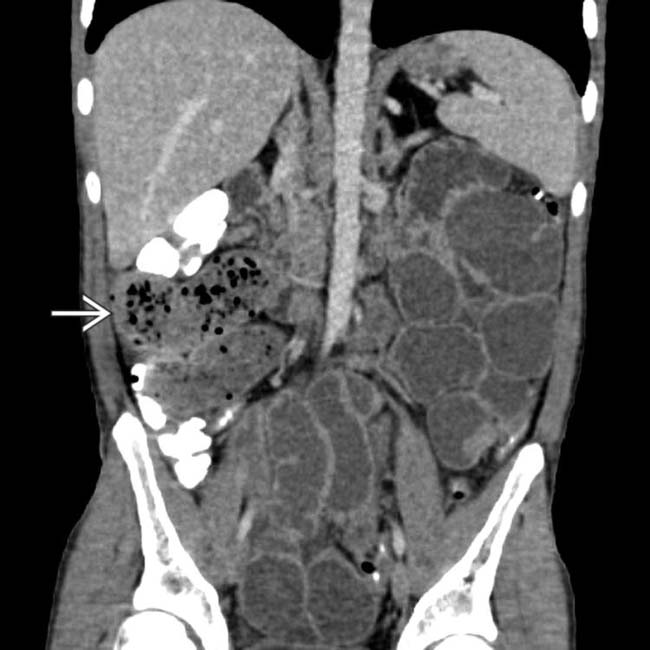
 .
.
 . The colon
. The colon  is decompressed.
is decompressed.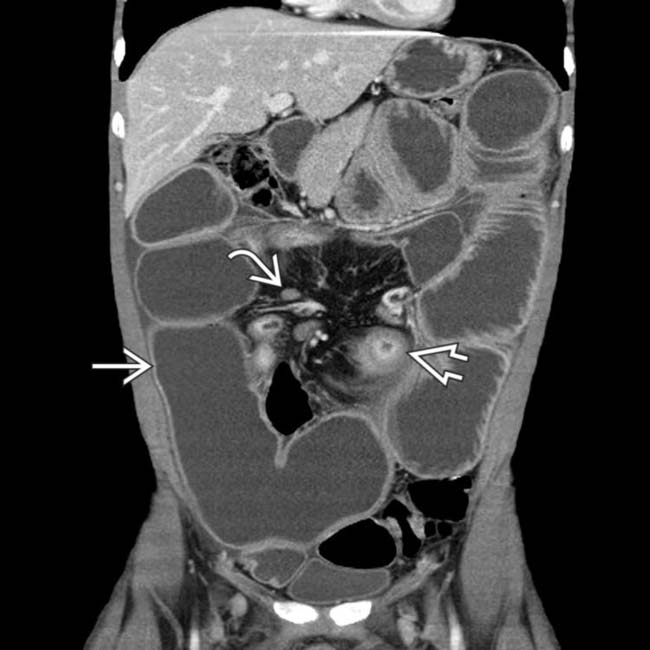
 with the transition point being more distal SB, featuring mucosal hyperenhancement, submucosal edema, and luminal narrowing
with the transition point being more distal SB, featuring mucosal hyperenhancement, submucosal edema, and luminal narrowing  . Mesenteric lymphadenopathy
. Mesenteric lymphadenopathy  is another typical feature of Crohn disease.
is another typical feature of Crohn disease.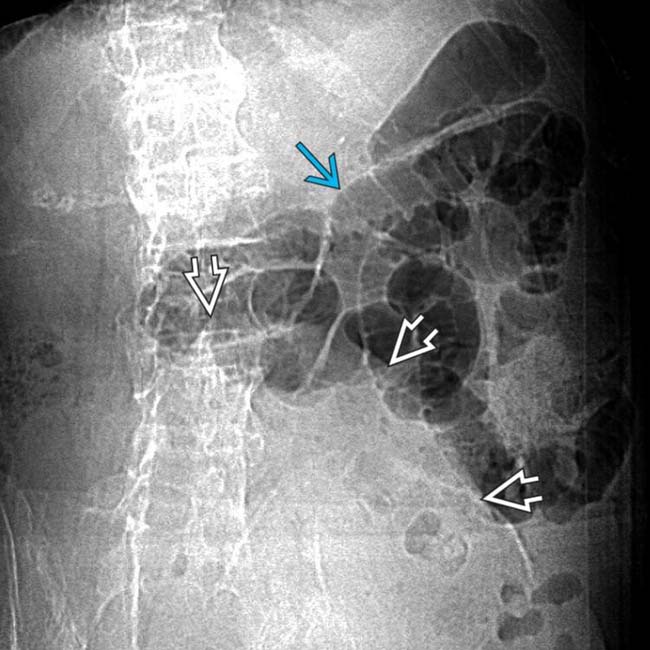
 , but minimal gas in the distal SB and colon. Instead, there is a suggestion of a lower abdominal mass
, but minimal gas in the distal SB and colon. Instead, there is a suggestion of a lower abdominal mass  .
.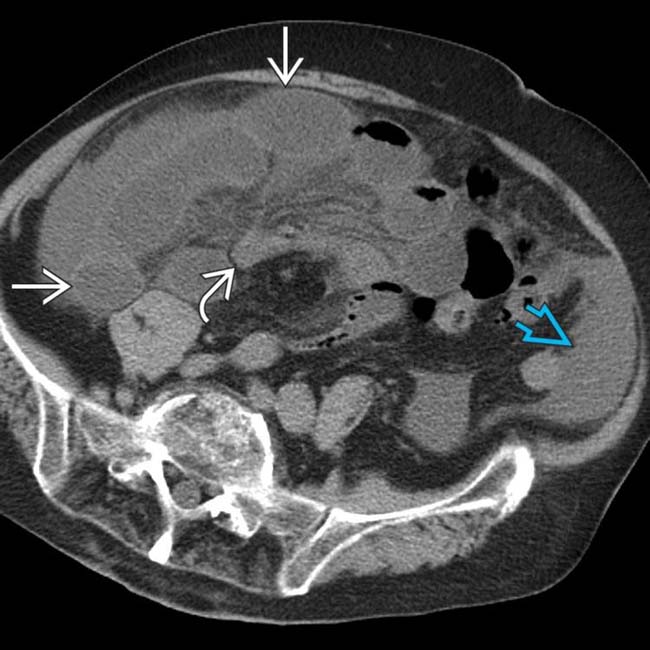
 that are almost entirely fluid-filled with little gas, accounting for the mass seen on the supine film. Mesenteric vessels
that are almost entirely fluid-filled with little gas, accounting for the mass seen on the supine film. Mesenteric vessels  to these segments are engorged and crowded with blurred margins. Ascites is present
to these segments are engorged and crowded with blurred margins. Ascites is present  .
.
 , twisting of the SB mesenteric vessels.
, twisting of the SB mesenteric vessels.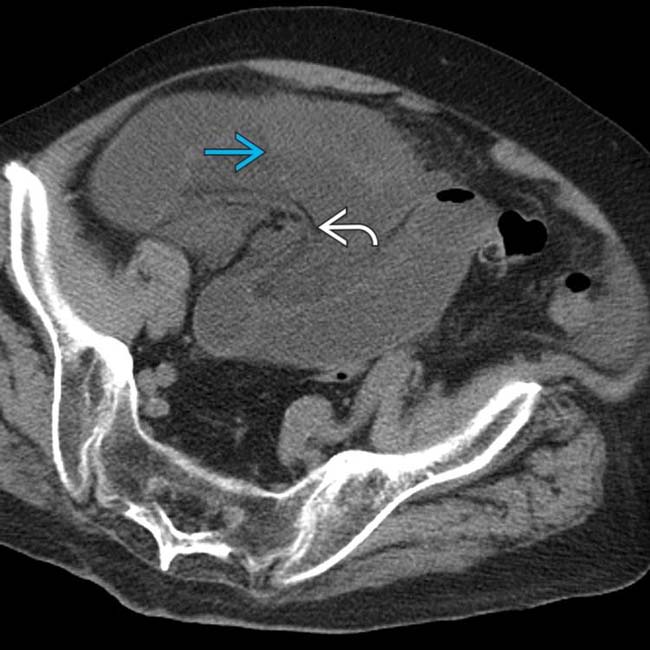
 , owing to infiltration of the SB mesentery and localized ascites between the affected SB loops. The mesenteric vessels
, owing to infiltration of the SB mesentery and localized ascites between the affected SB loops. The mesenteric vessels 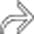 are acutely angulated.
are acutely angulated.
 tethered by their stretched mesenteric vessels.
tethered by their stretched mesenteric vessels.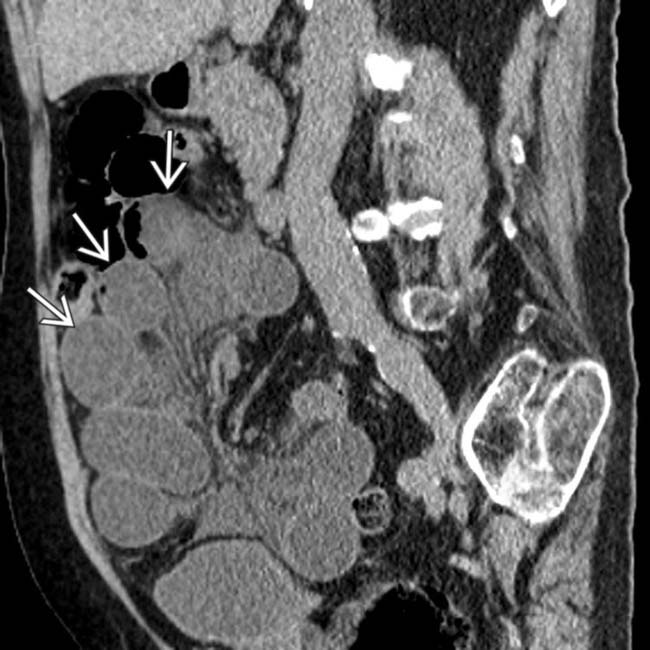
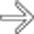 , with the “strings” being the mesenteric vessels and the “balloons” the SB segments within a closed loop SBO. This patient has many classic CT features of a closed loop SBO with ischemia, confirmed at surgery.
, with the “strings” being the mesenteric vessels and the “balloons” the SB segments within a closed loop SBO. This patient has many classic CT features of a closed loop SBO with ischemia, confirmed at surgery.
 and adjacent intraloop ascites
and adjacent intraloop ascites 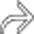 . Bowel wall enhancement suggests the viability of bowel.
. Bowel wall enhancement suggests the viability of bowel.
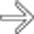 .
.
 .
.
 extending to ventral hernia, incarcerated loops within a hernia sac
extending to ventral hernia, incarcerated loops within a hernia sac  , and decompressed loops
, and decompressed loops  distal to obstruction.
distal to obstruction.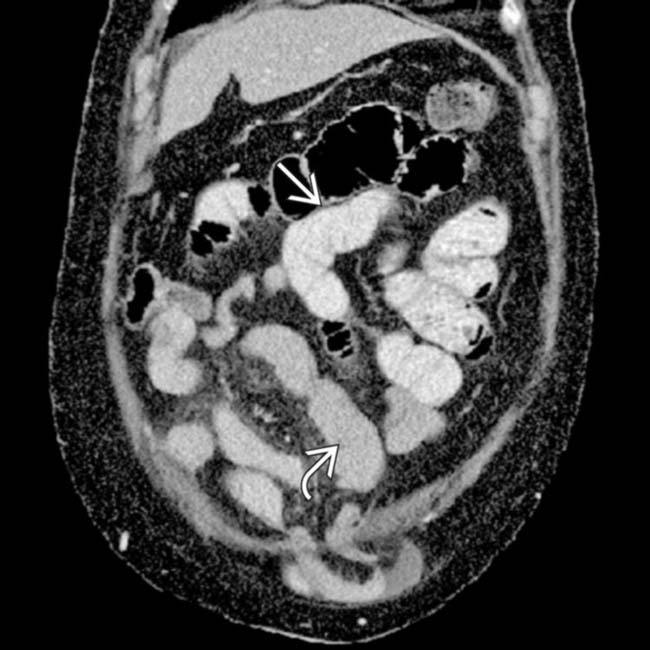
 , less dense in distal obstructed segments
, less dense in distal obstructed segments 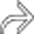 , reflecting slow transit time, and contrast dilution secondary to fluid-filled segments in SBO.
, reflecting slow transit time, and contrast dilution secondary to fluid-filled segments in SBO.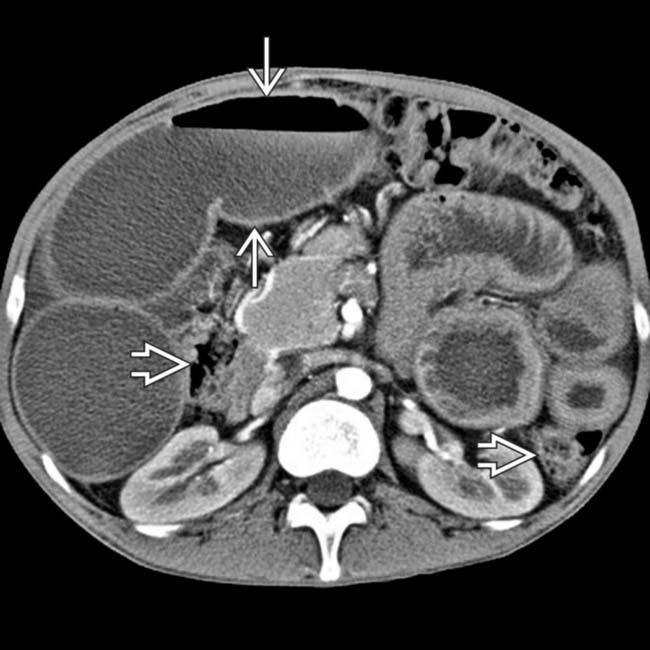
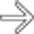 . Note the decompressed colon
. Note the decompressed colon  . At surgery, a chronic stricture was resected.
. At surgery, a chronic stricture was resected.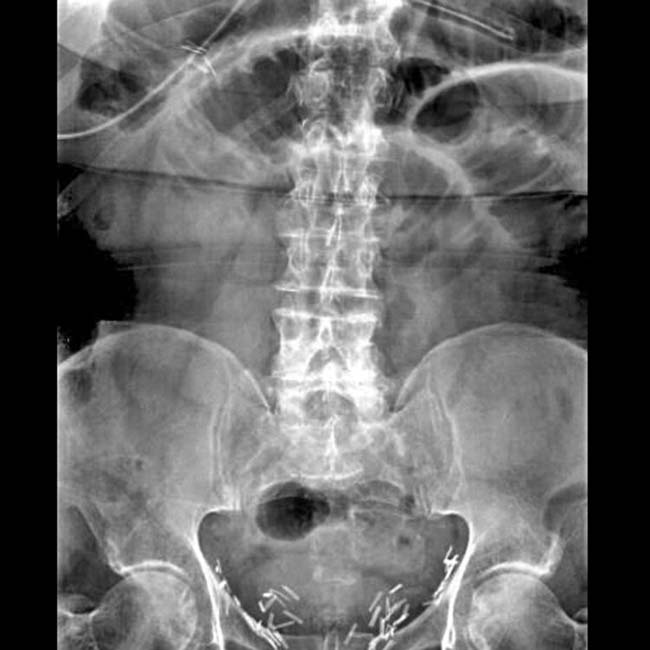
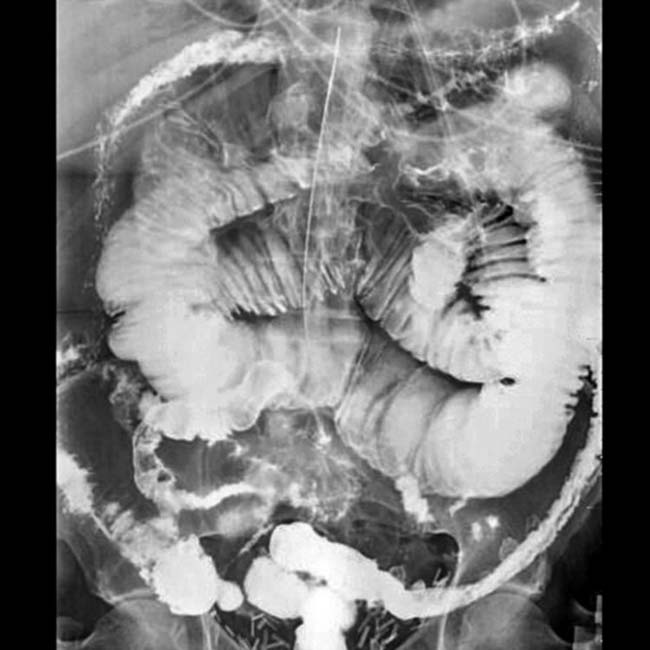
 due to adhesions, which caused SBO.
due to adhesions, which caused SBO.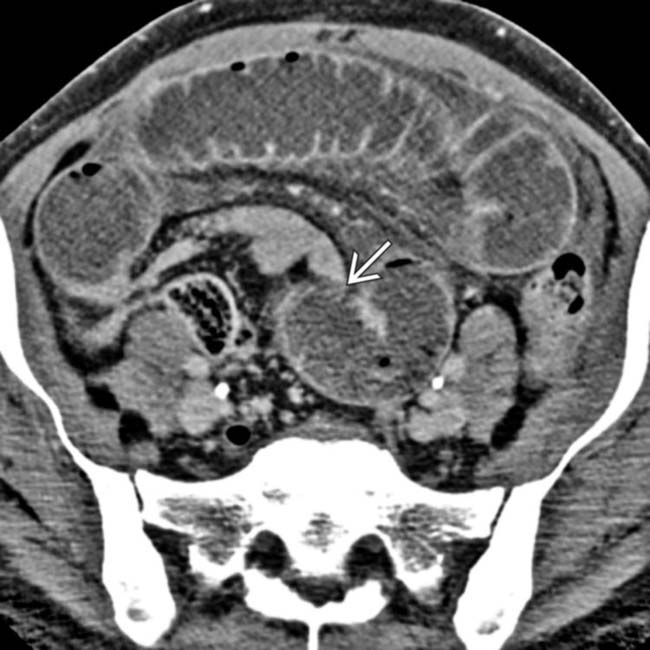
 from dilated to nondilated bowel. This small bowel obstruction was due to adhesions.
from dilated to nondilated bowel. This small bowel obstruction was due to adhesions.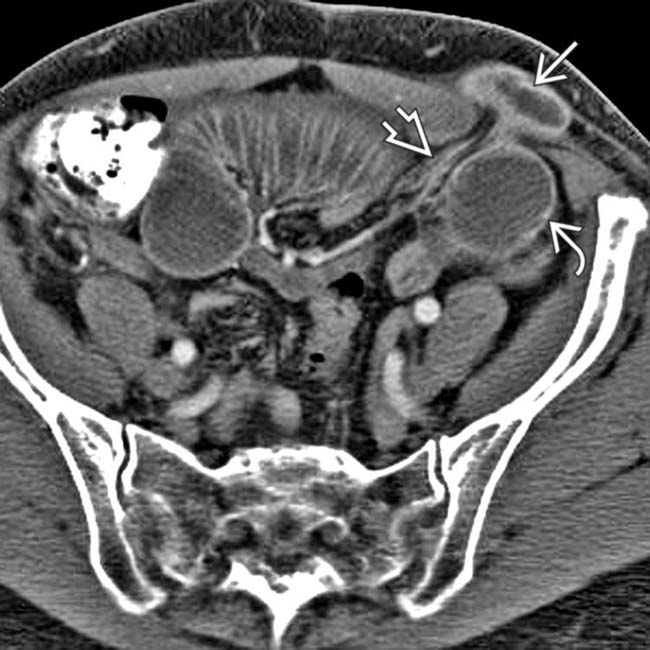
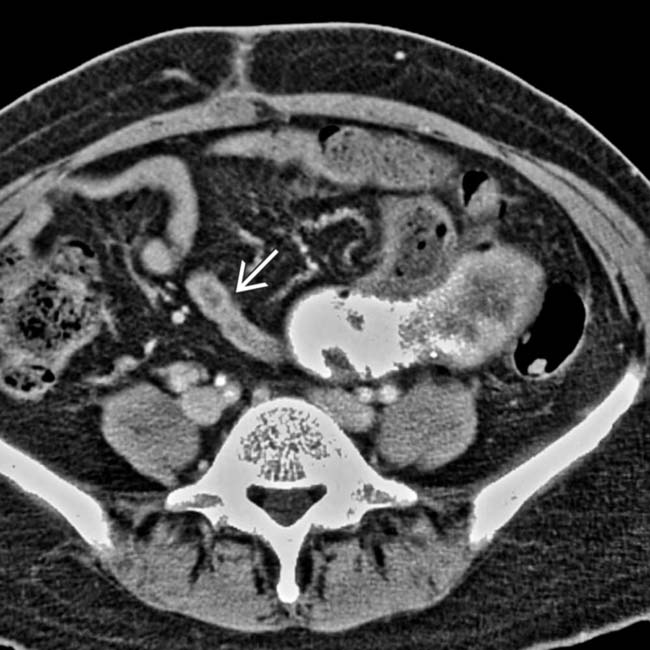
 with dilated bowel
with dilated bowel  entering through the defect and collapsed bowel
entering through the defect and collapsed bowel  exiting the hernia.
exiting the hernia.




























































 .
.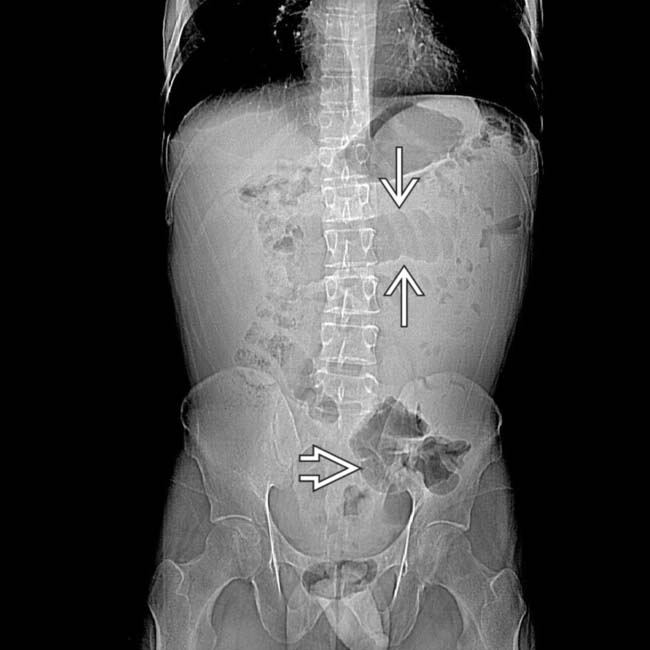
 disproportionate to colon
disproportionate to colon  .
.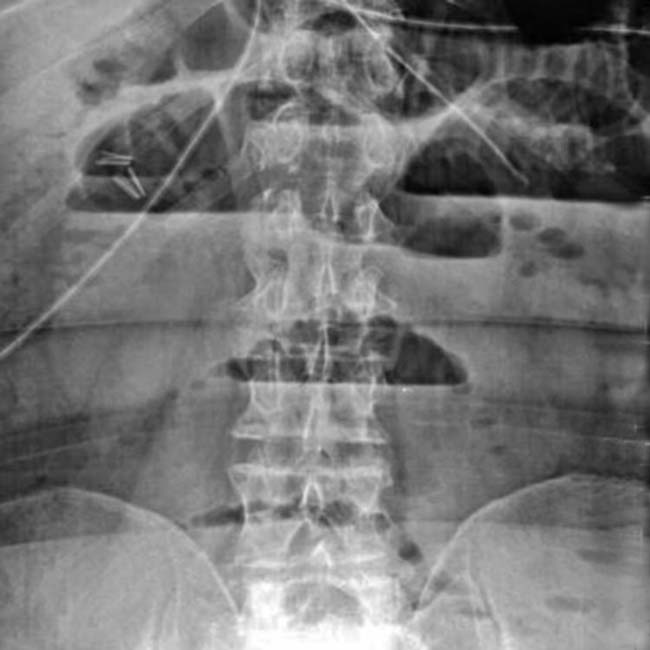
 .
.
 with mesenteric infiltration and blurred engorged blood vessels. Plain radiographs were “normal.”
with mesenteric infiltration and blurred engorged blood vessels. Plain radiographs were “normal.”


