Sensory and motor pathways
Spinal segments
The spinal cord is divided into 31 segments (Fig. 4.1A), each with a pair of dorsal (sensory) roots and a pair of ventral (motor) roots. The dorsal and ventral roots unite on each side to form a mixed spinal nerve (spinal nerve root) (Fig. 4.1B). Each nerve root divides into a small dorsal ramus, which supplies the paravertebral muscles and provides cutaneous sensation to the back, and a large ventral ramus which innervates the limbs and trunk. The dorsal root ganglia at each spinal level contain the cell bodies of sensory neurons that innervate an area of skin called a dermatome (Fig. 4.2). They also contain the cell bodies of sensory neurons innervating muscles, tendons, ligaments and joints.
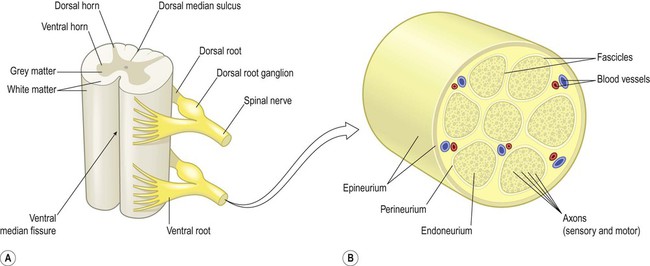
(A) Schematic illustrating two spinal cord segments; (B) A spinal nerve root shown in transverse section. The nerve root consists of sensory and motor axons arranged in bundles (fascicles) surrounded by connective tissue (endoneurium, perineurium, epineurium) and blood vessels. Modified from Fitzgerald: Clinical Neuroanatomy and Neuroscience 5e (2006) with permission.
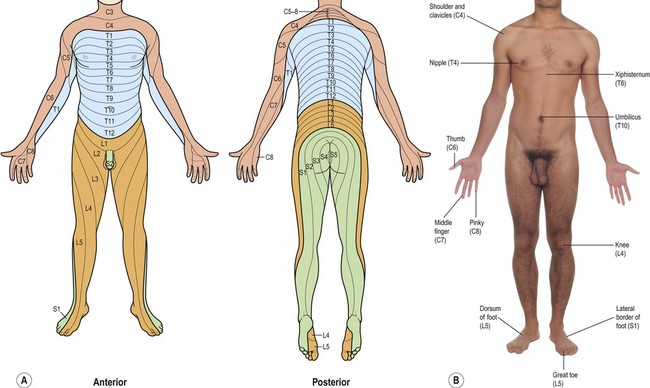
(A) Illustration of the complete dermatome map from anterior and posterior aspects, with the spinal root values indicated; (B) Photograph showing a number of key dermatome levels that it is clinically-useful to be familiar with.
Somatic sensory pathways
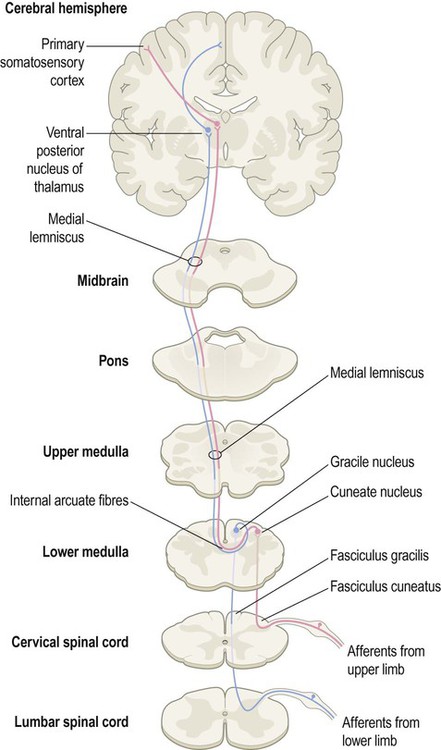
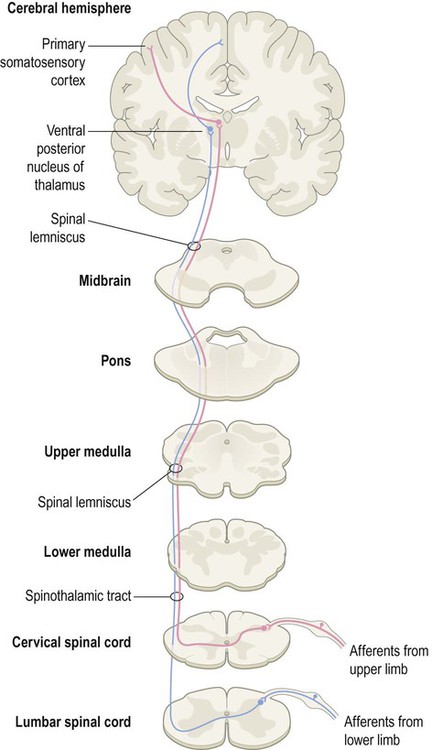
Two major spinal cord pathways carry sensory information to the cerebral cortex where it can be consciously perceived. The dorsal column pathway is concerned with precisely localized touch and joint position sense. The spinothalamic tract is primarily responsible for pain and temperature sensation. Each pathway is composed of a three-neuron chain with a similar arrangement (Fig. 4.3):
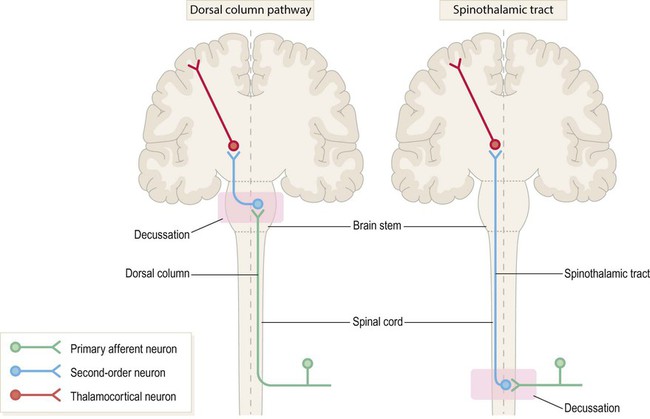
The first-, second- and third-order neurons are coloured green, blue and red respectively. Note that in both pathways the second-order neuron has its cell body in the central nervous system (CNS) and gives rise to an axon that crosses the midline and ascends to the thalamus. The main difference between the two pathways is the location of the second neuron (which in turn determines where each pathway crosses the midline).
 The first-order neurons have their cell bodies in the dorsal root ganglia, each with one process that contributes to a peripheral nerve and another that enters the spinal cord.
The first-order neurons have their cell bodies in the dorsal root ganglia, each with one process that contributes to a peripheral nerve and another that enters the spinal cord.
 The second-order neurons have their cell bodies in the grey matter of the brain stem or spinal cord and give rise to axons that cross the midline, before ascending to the thalamus.
The second-order neurons have their cell bodies in the grey matter of the brain stem or spinal cord and give rise to axons that cross the midline, before ascending to the thalamus.
 The third-order neurons are located in the ventral posterior (VP) nucleus of the thalamus and project to the primary somatosensory cortex, via the posterior limb of the internal capsule (see Ch. 3).
The third-order neurons are located in the ventral posterior (VP) nucleus of the thalamus and project to the primary somatosensory cortex, via the posterior limb of the internal capsule (see Ch. 3).
Dorsal column pathway
The dorsal column pathway is mainly responsible for precisely localized touch and proprioception (awareness of one’s own body; Latin: proprius, one’s own) including joint position sense. It contains large myelinated axons (A-alpha fibres) which transmit impulses at speeds of up to 120 metres per second. Integrity of the dorsal columns is best assessed clinically using a tuning fork (Clinical Box 4.1).
Spinothalamic tract
The spinothalamic tract mediates pain and temperature sensations. Impulses are transmitted by small-diameter unmyelinated c-fibres and thinly-myelinated A-delta fibres which conduct impulses at relatively slow speeds of 0.5–15 metres per second. This pathway can be tested clinically using a sterile pin (Clinical Box 4.2).
The spinoreticulothalamic pathway
Some spinothalamic axons contribute to a spinoreticular pathway which synapses in the reticular formation of the brain stem. From here, reticulothalamic fibres ascend to the intralaminar nuclei of the thalamus before projecting on to the limbic lobe and insula, which have visceral and emotional roles including pain perception (Clinical Box 4.3).
Pain arising from the internal organs
Visceral and viscerosomatic pain
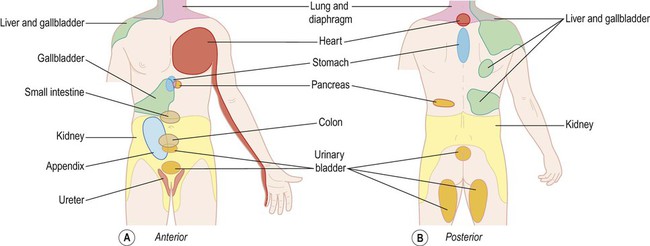
Visceral pain is diffuse, poorly localized and centred on the midline. It is often associated with autonomic features such as sweating, nausea, vomiting and pallor. In contrast, viscerosomatic pain is sharp and well-localized. It occurs when inflammatory exudate from a diseased organ makes contact with a somatic (body-wall) structure such as the parietal peritoneum. Abdominal pathology (e.g. appendicitis) may therefore present with diffuse visceral pain, before progressing to sharp viscerosomatic pain (Fig. 4.6).
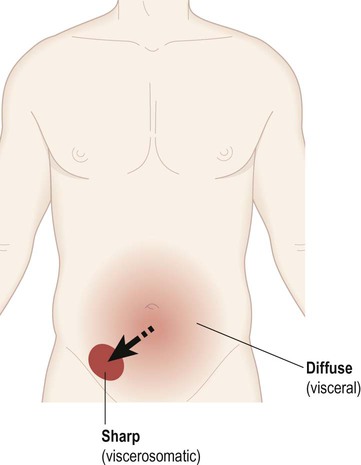
In the early stages of appendicitis the patient typically describes a dull, nauseating, poorly localized (visceral) pain centred on the umbilicus. As the inflammation spreads to involve the abdominal wall, a sharp (viscerosomatic) pain arises in the lower right quadrant of the abdomen, corresponding to the position of the appendix.
Referred pain
This is pain that is perceived at a distance from the affected organ (e.g. in the left arm during a myocardial infarction or in the right shoulder with inflammation of the gallbladder) (Fig. 4.7). It is thought to be due to convergence of visceral and somatic afferent fibres on second-order spinothalamic tract neurons so that pain of visceral origin is perceived (‘misinterpreted’) as somatic pain at that segmental level.
Sensory gating and antinociception
In the spinal cord, transmission of noxious signals from first-order to second-order neurons (of the spinothalamic tract) is gated in a part of the dorsal horn known as the substantia gelatinosa. This contains excitatory and inhibitory interneurons that influence transmission of pain-related impulses to the brain. The connections are arranged in such a way that activity in large-diameter cutaneous afferents blocks transmission in nociceptive fibres, accounting for the beneficial effect of rubbing a sore knee (Fig. 4.8).
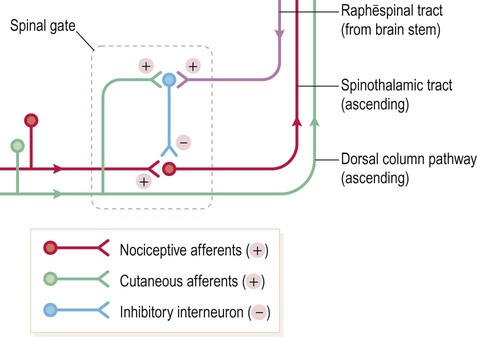
This is a schematic to illustrate the concept that the transmission of pain-related impulses from the spinal cord to the brain can be inhibited, either by activity in large-diameter cutaneous afferents or by descending projections from the brain stem. (NB The actual synaptic connections within the substantia gelatinosa are not certain.)
Supraspinal influences
The periaqueductal grey matter (PAG) of the midbrain is involved in the supraspinal modulation of pain. Studies in non-human primates have shown that electrical stimulation of the PAG exerts a powerful antinociceptive (analgesic) action, blocking pain signals from the spinal cord. This is mediated by connections with the reticular formation and the serotonergic raphē nuclei of the brain stem (see Ch. 1). These raphēspinal fibres synapse in the substantia gelatinosa where they inhibit synaptic transmission between first-order and second-order afferents of the spinothalamic tract (see Fig. 4.8). This partially explains why tricyclic antidepressants (e.g. amitriptyline) have analgesic properties, since they enhance serotonergic neurotransmission.
Trigeminothalamic pathways
In the head and neck, general somatic sensation is mediated by two analogous trigeminothalamic pathways. These transmit sensations from the territory of the trigeminal (V) nerve (Fig. 4.9) which is tested clinically by eliciting the corneal reflex (Fig. 4.10).
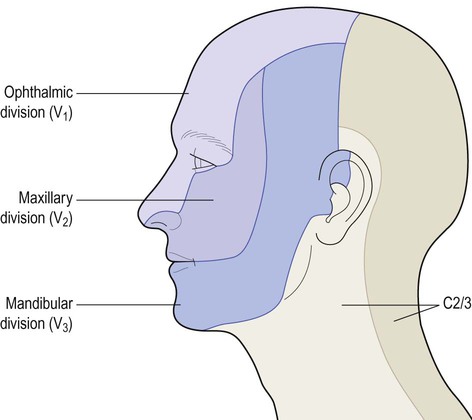
The trigeminal nerve also innervates the oral and nasal cavities, paranasal air sinuses, teeth, intracranial dura and cerebral arteries.
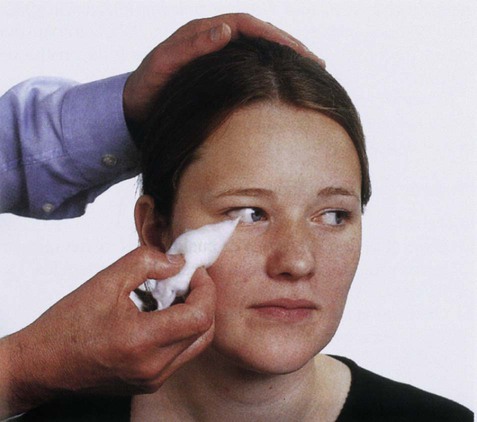
The cornea, which is innervated by the ophthalmic division of the trigeminal nerve, is gently touched using a wisp of cotton wool. Reflexive blinking of both eyes demonstrates that the trigeminal (sensory) and facial (motor) limbs of the reflex are intact. From Munro et al.: Macleod’s Clinical Examination 10e with permission.
General tactile sensation
The cell bodies of trigeminal sensory neurons are located in the trigeminal sensory ganglion, which is analogous to a dorsal root ganglion. The second-order neurons in the trigeminothalamic pathway are located in the chief sensory nucleus of the trigeminal nerve, in the pons. This gives rise to fibres that cross the midline and ascend to the thalamus in the trigeminal lemniscus. These axons also terminate in the ventral posterior nucleus of the thalamus, medial to those from the trunk and limbs. Third-order thalamocortical neurons then project to the ‘face area’ of the primary sensory cortex (see Ch. 3).
Somatic motor pathways
The control of voluntary movement is complex and incompletely understood, with contributions from several brain regions (see Ch. 3). The prefrontal cortex, which lies anterior to the motor and premotor areas of the frontal lobe, is involved in planning and organization of goal-directed behaviour. The premotor cortex is concerned with the preparation and execution of complex movement sequences, whereas the primary motor cortex has a more direct influence over individual muscle groups.
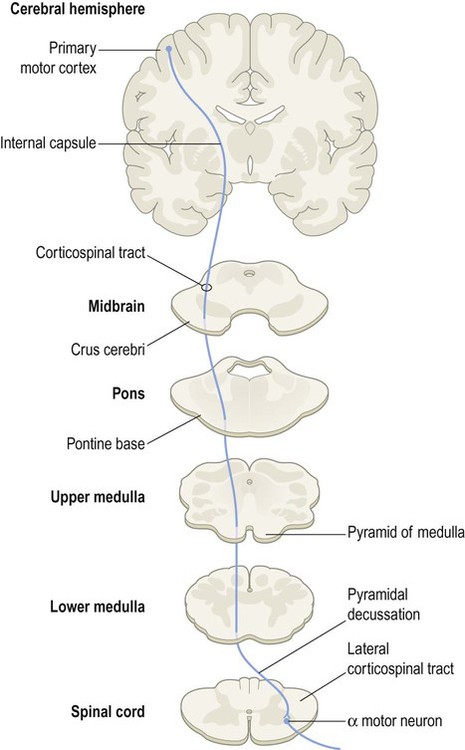
Corticospinal tract
The corticospinal tract is the principal somatic motor pathway and the longest continuous white matter tract in the CNS. It is particularly important for finely-fractionated voluntary movements of the distal limb musculature (e.g. control of the hands). The corticospinal tract is composed of more than a million myelinated axons on each side, two thirds of which arise from the primary motor and premotor areas of the frontal lobe (Fig. 4.11).
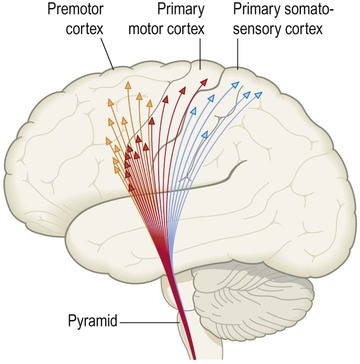
This consists of the corticospinal tract (supplying the trunk and limbs) and the corticobulbar tract (for the cranial nerve motor nuclei). Modified from Fitzgerald: Clinical Neuroanatomy and Neuroscience 5e (2006) with permission.
Corticobulbar tract
Termination of corticobulbar fibres
Fibres from the corticobulbar projection part company with the corticospinal tract as they descend in the brain stem and gradually ‘peel off’ to reach their target nuclei. The corticobulbar tract projects directly to four motor cranial nerve nuclei in the pons and medulla, controlling muscles that: (i) are attached to the lower jaw, including those involved in chewing; (ii) are involved in facial expression; (iii) mediate speech, swallowing and the efferent limb of the ‘gag’ reflex (see Clinical Box 4.4); and (iv) control the tongue.
Voluntary eye movements are initiated by the frontal eye fields (see Ch. 3). These project to vertical and lateral gaze centres in the midbrain and pons, via the anterior limb of the internal capsule. The brain stem gaze centres then influence the cranial nerve nuclei innervating the extraocular muscles.
Lower motor neurons
Motor units and graded contraction
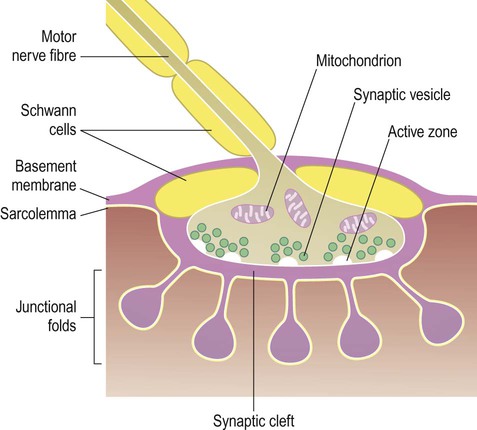
The neuromuscular junction
The point of contact between lower motor neurons and skeletal muscle is the neuromuscular junction (NMJ) which is similar in structure to a synapse (Fig. 4.13). The transmitter is acetylcholine (ACh) which acts on nicotinic ACh receptors. The NMJ is ‘fail-safe’, meaning that 100% of nerve impulses generated in a lower motor neuron will trigger a muscle twitch. Neuromuscular transmission is impaired in the autoimmune disorder myasthenia gravis (Clinical Box 4.5).
Reflexes and muscle tone
Muscle tone
The stretch reflex
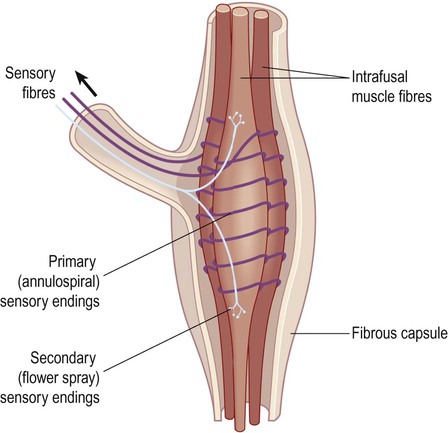
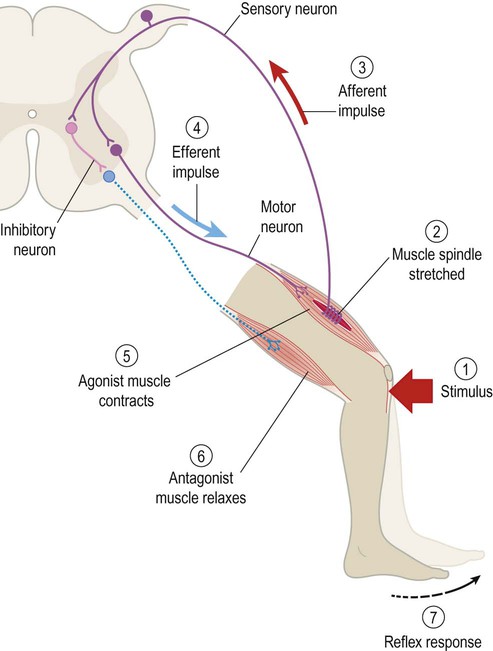
The afferent limb of the stretch reflex originates from proprioceptive organs called muscle spindles (Fig. 4.14). These are roughly the same size and shape as a grain of rice and are scattered throughout the skeletal musculature. They contain striated muscle within a spindle-shaped (fusiform) connective tissue capsule. Muscle fibres inside the spindle are referred to as intrafusal, whereas those making up the bulk of the muscle are extrafusal. Muscle spindles are in parallel with extrafusal fibres, so that any tension applied to the long axis of the muscle will stretch both types of fibre.
Afferent fibres enter the dorsal roots of the spinal nerves, then synapse directly on anterior horn cells innervating the homonymous (same) muscle group (Fig. 4.15). In addition, collateral fibres make synaptic connections with motor neurons supplying antagonistic muscle groups via inhibitory interneurons. The stretch reflex is fundamentally important in clinical neurology because it is responsible for muscle tone and tendon reflexes (Clinical Box 4.6).
Long-latency stretch reflex
Electrical recordings from muscle show that the stretch reflex has two components. There is an early, short-latency component that occurs within 25–40 milliseconds, consistent with a monosynaptic reflex. A long-latency component can also be recorded at around 50–75 milliseconds, which probably involves the cerebral cortex. Over-activity in the ‘long-loop component’ of the stretch reflex may be responsible for the characteristic rigidity (increased muscle tone) in Parkinson’s disease (Ch. 13).
Hypertonia and spasticity
Sensitivity of the stretch reflex is regulated by the brain to ensure normal muscle tone. Descending reticulospinal projections (from the reticular formation of the brain stem) inhibit spinal motor neurons and ‘damp down’ the stretch reflex to optimize muscle tone. This influence is usually lost following an upper motor neuron lesion (by an uncertain mechanism) which results in hyperactivity of the stretch reflex (Clinical Box 4.7).
Spasticity
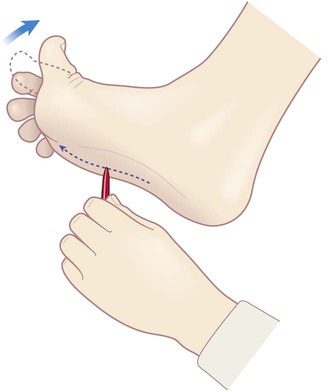
A marked increase in muscle tone is called spasticity (Fig. 4.16), characterized by firm resistance to passive manipulation of the limbs. It is velocity-dependent, so that rapid flexion or extension of the affected joints is met by an abrupt ‘spastic catch’ (similar to the resistance felt when pulling sharply on a car seatbelt). Spasticity can be overcome by force so that the joint suddenly ‘gives way’ (the clasp-knife phenomenon). This is a safety mechanism that prevents tendon rupture due to excessive load. Spasticity is usually accompanied by an abnormal plantar response (Clinical Box 4.8). A combination of upper motor neuron features, together with lower motor neuron signs, is seen classically in motor neuron disease (Clinical Box 4.9).
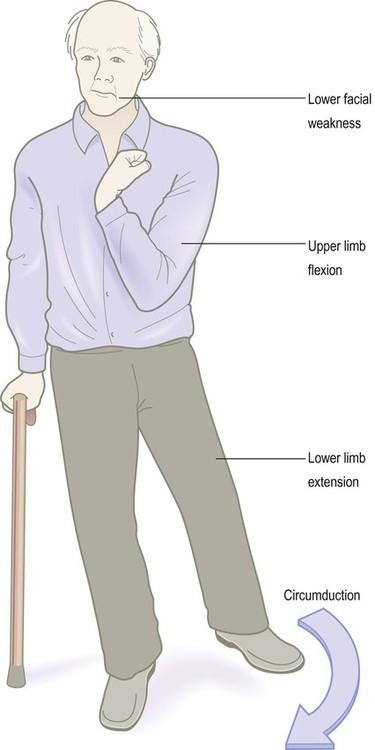
The patient illustrated has suffered a large right hemisphere stroke leading to weakness and spasticity affecting the left side of his body. In the upper limbs, flexion dominates since the upper limb flexors are stronger than the extensors, reflecting their functional importance (e.g. for reaching and grasping). The lower limb is extended and rigid, reflecting the greater power of the extensor (antigravity) muscles.