Chapter 18 Sedation and monitoring
Sedation
Sedation is the use of a drug or drugs to produce a state of depression of the central nervous system that enables interventional procedures or treatment to be carried out. Over recent years the complexity and number of interventional procedures in radiology departments has increased; often these patients are frail or medically unfit for surgery. Sedation is only part of a ‘package’ of care comprising pre-assessment, properly informed consent, adequate facilities, good techniques and risk avoidance.1
Sedative drugs may be combined with drugs used for pain relief (analgesia). Some drugs, such as benzodiazepines, have purely sedative effects but others, such as opioids, have combined sedative and analgesic effects. Although sedative and analgesic agents are generally safe, catastrophic complications related to their use can occur, often as a result of incorrect drug administration or inadequate patient monitoring.2 The incidence of adverse outcomes is reduced by improved understanding of the pharmacology of drugs used, appropriate monitoring of sedated patients and by recognizing those at increased risk of adverse event.
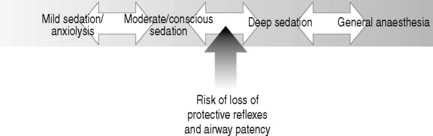
There is a continuum between the main types of sedation (see Fig. 18.1) defined as:
The joint Royal College of Radiologists/Royal College of Anaesthetists Working Party on Sedation and Anaesthesia in Radiology3 recommended establishment of local guidelines for sedation in radiology. These should include:
DRUGS
As part of a sedation protocol the following may be used:
LOCAL ANAESTHESIA
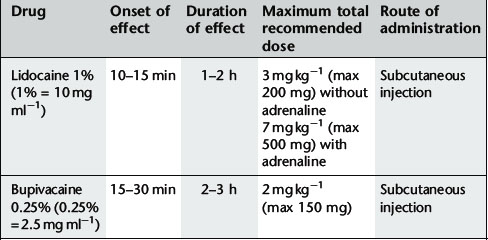
For recommended doses see Table 18.1.
Commonly used local anaesthetics for subcutaneous infiltration are:
INTRAVENOUS ANALGESIA
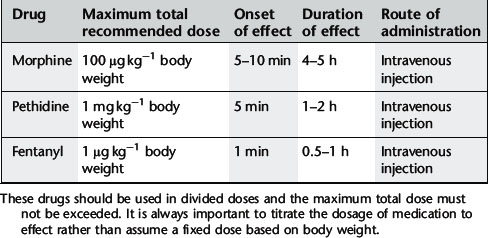
These drugs are used for pain control but also have a dose-dependant sedative effect. Most commonly used are the opioid drugs morphine, pethidine and fentanyl. These drugs must be given in small, divided doses and dose titrated to the patient’s need. It is extremely important to titrate the dosage to effect rather than assume a fixed dose based on body weight. The maximum recommended dose must not be exceeded because of the risk of adverse events, particularly respiratory depression. For recommended dosage see Table 18.2.
Effects of opioids can be reversed by the competitive antagonist naloxone (dose 0.4–2 mg). Naloxone should be administered intravenously in a solution containing 0.4 mg in 10 ml and given in 1 ml increments. It has peak effect at 1–2 min with duration of 20–60 min. As a result of the relatively short duration of action, repeated doses of naloxone may be necessary.
SEDATIVE DRUGS
Sedation of children
Each child should be individually assessed. In most circumstances parents should stay with the child, and with patience and encouragement the need for sedation may be avoided in some cases. Short procedures such as CT can often be achieved in neonates by keeping them awake and then feeding the child and swaddling just prior to the procedure. Often, children over the age of 4–5 years will not need sedation and will cooperate. Local anaesthetic cream, e.g. Ametop, can be applied to a suitable vein prior to insertion of a venous cannula if venous access is required. Oral sedation does not work well in children over the age of 4 and older children who are unable to co-operate will usually require general anaesthetic.
For many years chloral hydrate has been the mainstay for sedation of young children for a variety of procedures. Triclofos is an active metabolite of chloral hydrate which causes less gastric irritation and vomiting. Alimemazine (Vallergan) is a sedating antihistamine, with anticholinergic effects. The recommendations in Table 18.3 are made as being suitable for the majority of patients, in respect of both safety and efficacy. It is recognized that, for certain patients, deviation from these guidelines will be appropriate on clinical or weight grounds (Table 18.3).
Table 18.3 Sedation recommendations made as being suitable for the majority of child patients. These doses are used to acheive deep sedation: a nurse should be present throughout.
| Age/weight | Sedation | Dose |
|---|---|---|
| <1 month old | Feed only or Triclofos | 30 mg kg−1 |
| >1 month old but <5 kg | Triclofos | 50–70 mg kg−1 |
| 5–10 kg | Triclofos | 100 mg kg−1 |
| >10 kg–4 years | Triclofos + Alimemazine | 100 mg kg−1 (maximum 2 g) 1 mg kg−1 (maximum 30 mg) |
| Over 4 years | Consider oral sedation as above or general anaesthetic |
Children should have nothing to eat or drink prior to sedation as follows:
Complications
Major complications are rare, but include:
1 Royal College of Radiologists. Safe Sedation, Analgesia and Anaesthesia within the Radiology Department. London: The Royal College of Radiologists, 2003.
2 Martin M.L., Lennox P.H. Sedation and analgesia in the interventional radiology department. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol.. 2003;14(9 Pt 1):1119-1128.
3 Royal College of Radiologists/Royal College of Anaesthetists joint publication. Sedation and Anaesthesia in Radiology. London: The Royal College of Radiologists, 1992.
Monitoring
Equipment
SEDATION AND MONITORING FOR MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING
Sedation should be given in a quiet area close to the scanner and there should be an appropriate recovery area available.
All equipment used for monitoring and all anaesthetic equipment must be MR compatible, e.g. MR compatible pulse oximeters with fibre-optic cabling. Potential problems include effects from the gradient field and radiofrequency fields. Heat induction in conducting loops formed by ECG leads can cause superficial burns and induced current in monitoring equipment may produce unreliable readings or malfunction of syringe drivers resulting in incorrect drug-dose delivery (see Chapter 1). Responsibility for safe use of MRI monitoring equipment should be allocated to a small number of experienced and appropriately trained staff.