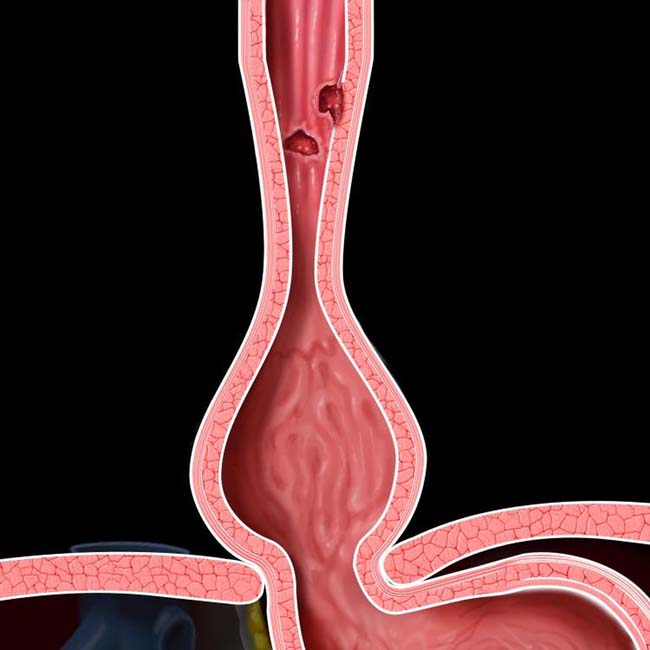
Probably result and not cause of reflux
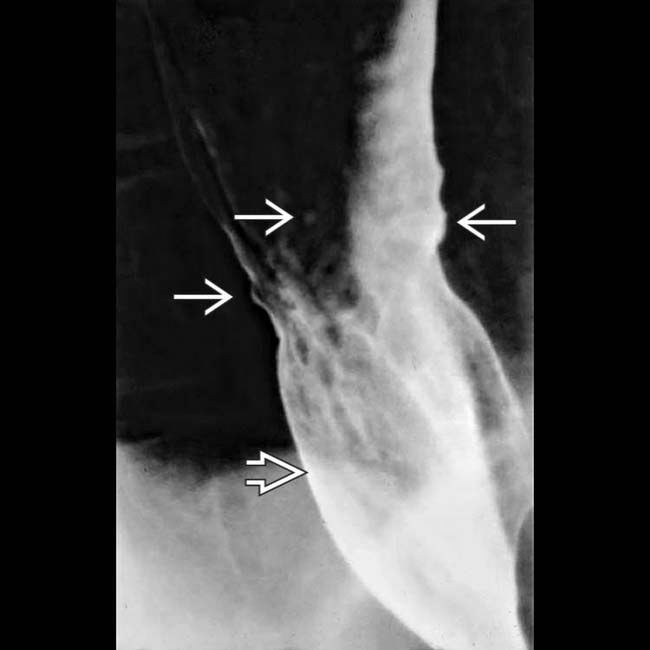
 , foreshortening of the esophagus, and a mild stricture at the gastroesophageal (GE) junction. There are several subtle esophageal ulcers
, foreshortening of the esophagus, and a mild stricture at the gastroesophageal (GE) junction. There are several subtle esophageal ulcers  at the level of the stricture.
at the level of the stricture.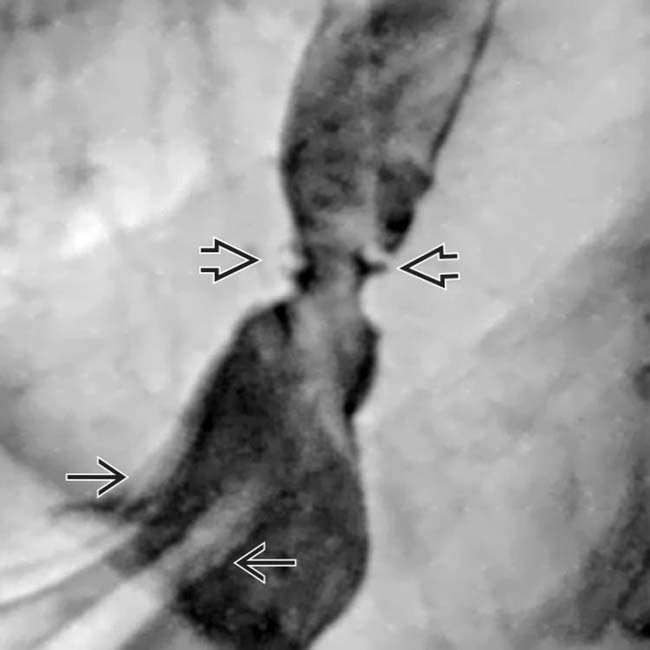
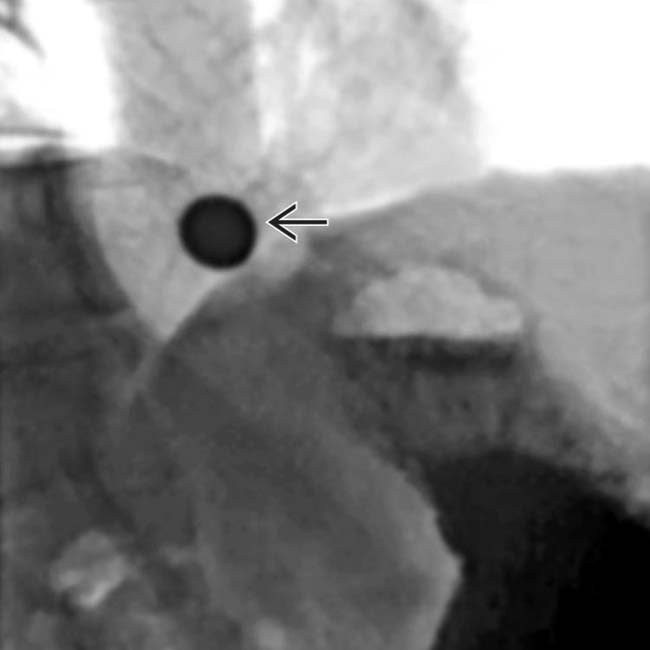
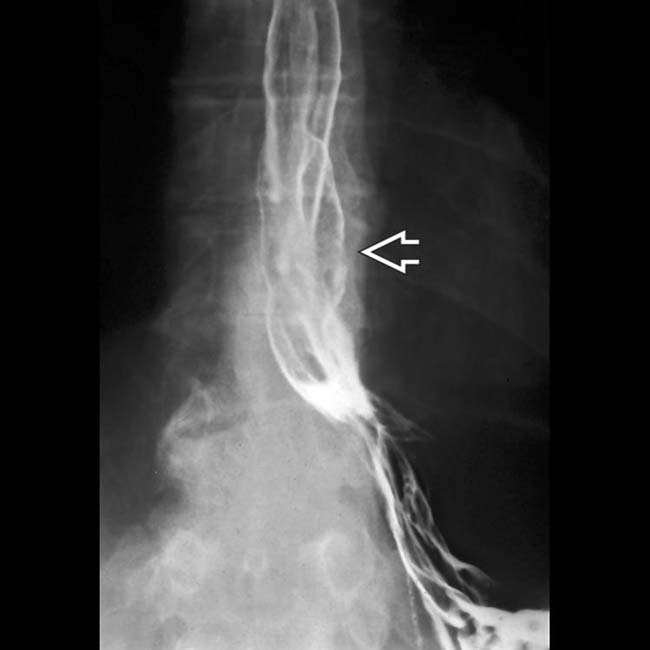
 extending above the diaphragm. The esophagus appears shortened, presumably due to spasm of the longitudinal muscles within its wall. A stricture is present at the GE junction, and persistent collections of barium indicate mucosal ulceration
extending above the diaphragm. The esophagus appears shortened, presumably due to spasm of the longitudinal muscles within its wall. A stricture is present at the GE junction, and persistent collections of barium indicate mucosal ulceration  .
.
 cannot pass through the peptic stricture.
cannot pass through the peptic stricture.IMAGING
General Features
Radiographic Findings
• Double-contrast esophagography
PATHOLOGY
General Features
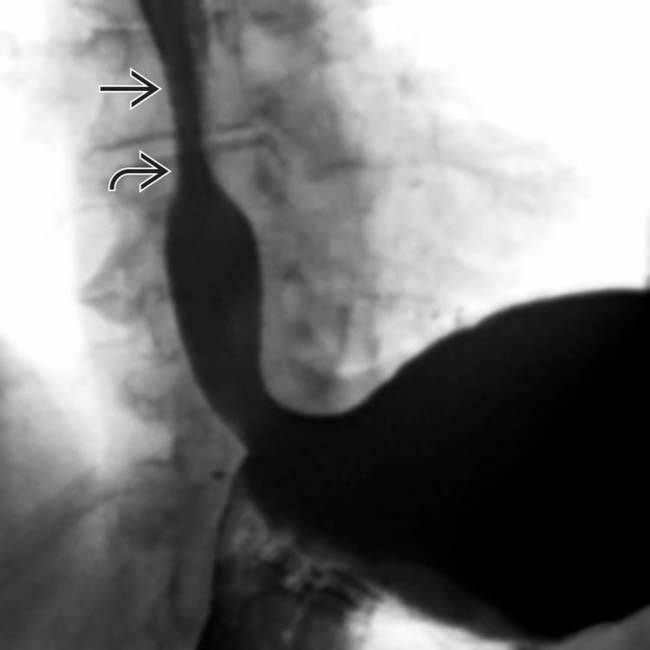
 and a stricture
and a stricture  at the GE junction. Tertiary contractions and diminished primary peristalsis were also noted during fluoroscopy.
at the GE junction. Tertiary contractions and diminished primary peristalsis were also noted during fluoroscopy.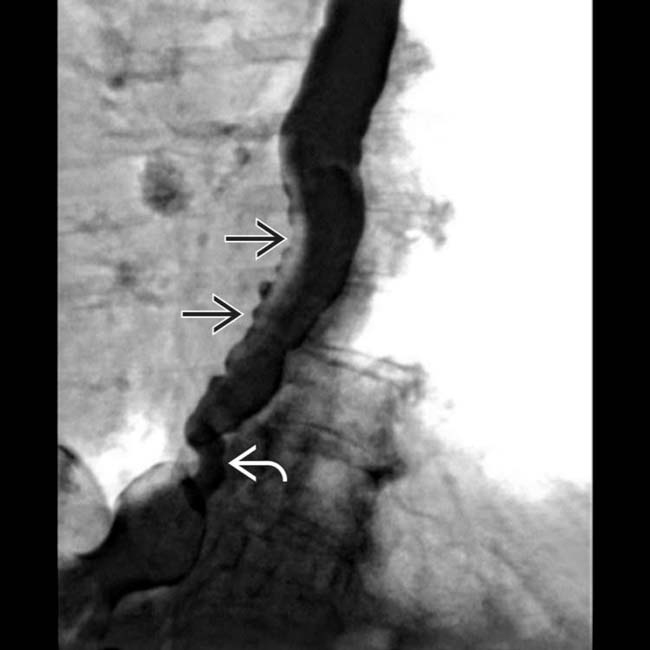
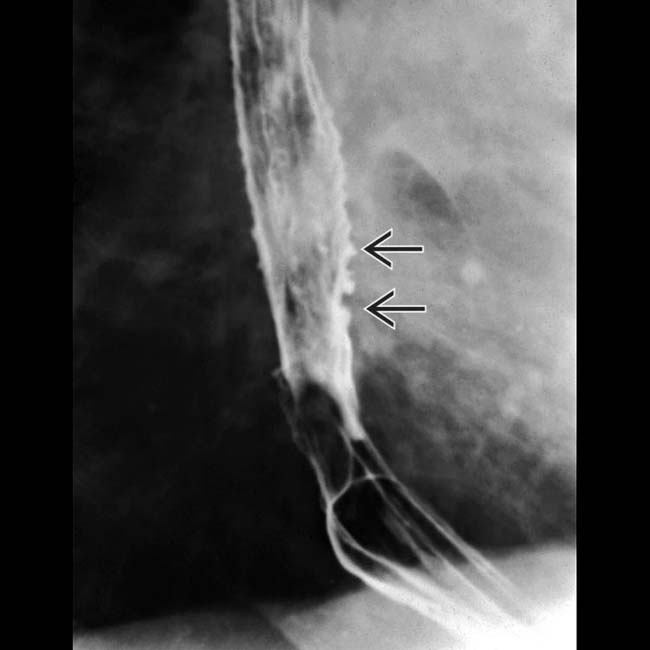
 at the GE junction is again noted on this prone film from the esophagram. Tertiary contractions
at the GE junction is again noted on this prone film from the esophagram. Tertiary contractions  are also seen.
are also seen.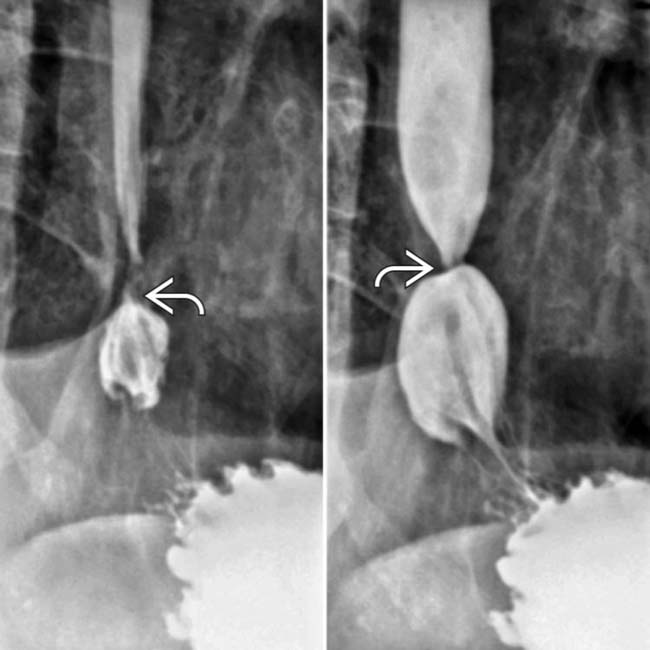
 at the GE junction. Endoscopic biopsy of the strictured lesion was performed to rule out Barrett metaplasia.
at the GE junction. Endoscopic biopsy of the strictured lesion was performed to rule out Barrett metaplasia.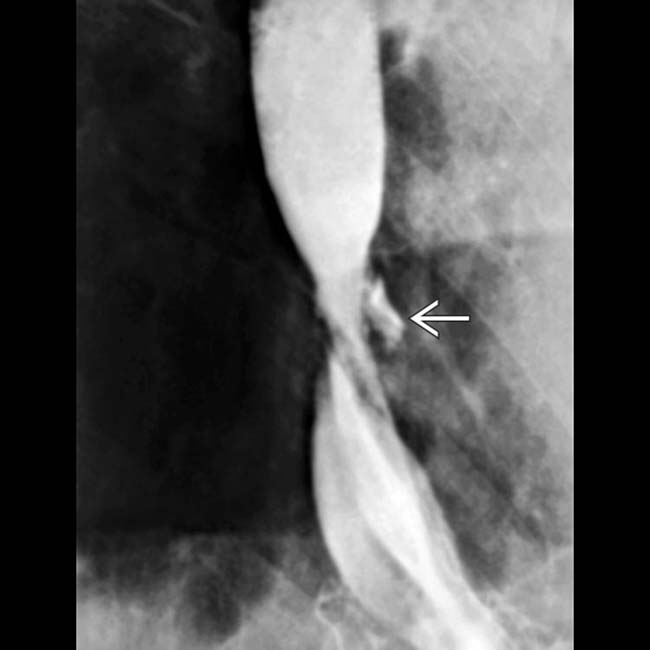
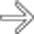 from the biopsy site. Leaks such as this can also result from balloon dilation of strictures.
from the biopsy site. Leaks such as this can also result from balloon dilation of strictures.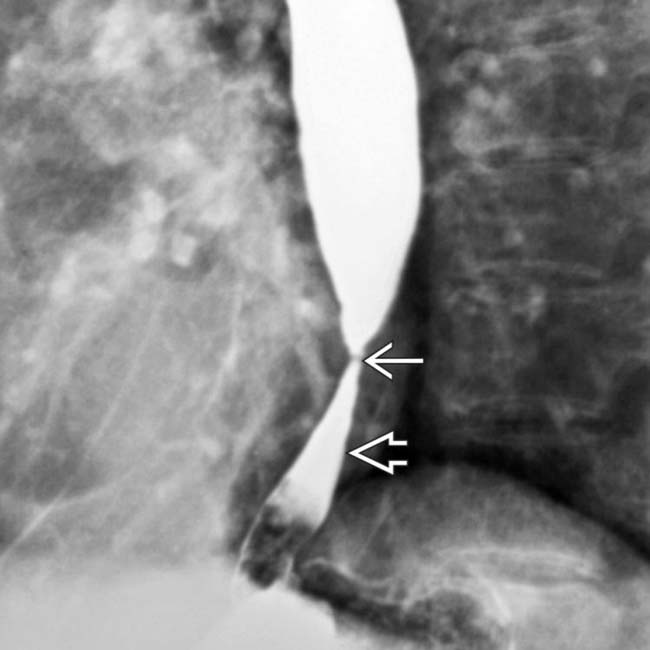
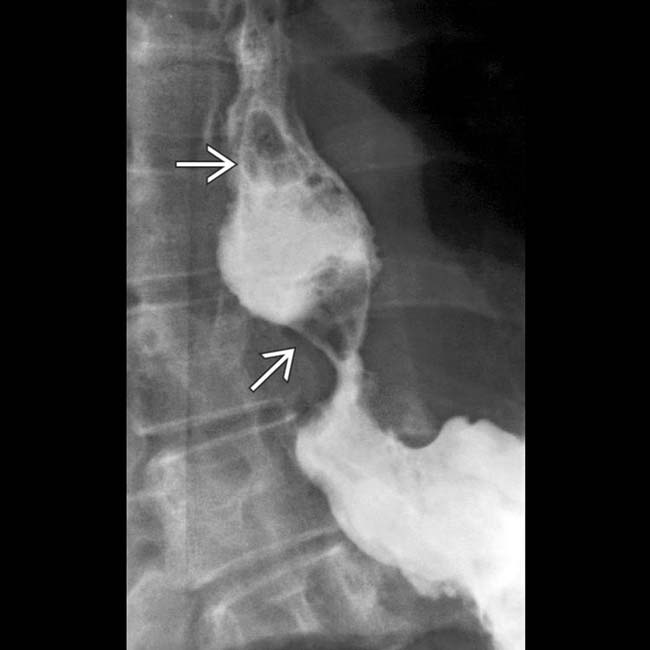
 just above the GE junction with upstream dilation of the esophagus. The herniated stomach
just above the GE junction with upstream dilation of the esophagus. The herniated stomach  is pulled taut as a result of the foreshortening of the esophagus, a common and important sign of reflux esophagitis.
is pulled taut as a result of the foreshortening of the esophagus, a common and important sign of reflux esophagitis.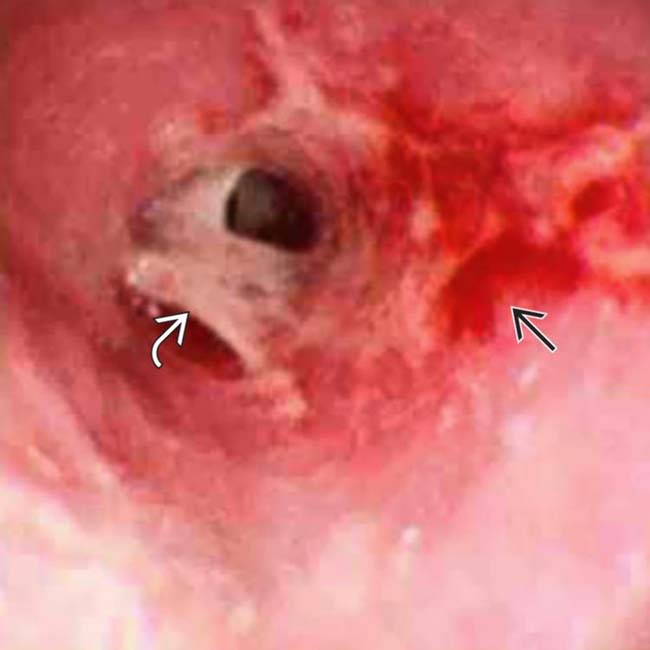
 , mucosal ulceration
, mucosal ulceration  , nodularity, and stricture.
, nodularity, and stricture.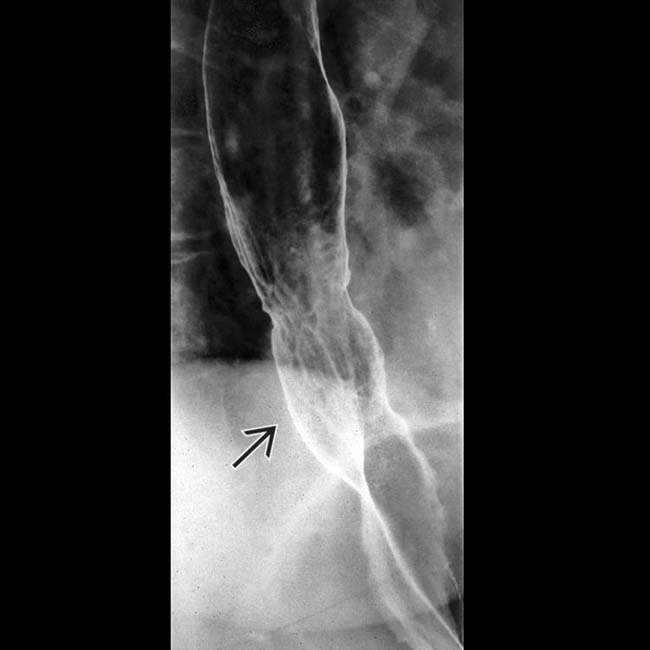
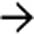 with shallow round and linear esophageal ulcers.
with shallow round and linear esophageal ulcers.























































 .
.
 .
.
 .
.


