Chapter 37 PURPURA
Medications Associated with Purpura
• Alkylating agents (decreased platelet formation)
• Antimetabolites (decreased platelet formation)
• Anticonvulsants (decreased platelet formation)
• Aspirin (platelet dysfunction)
• Chloral hydrate (vascular purpura)
• Chlorothiazide diuretics (decreased platelet formation)
• Cimetidine (immune thrombocytopenia)
• Clofibrate (platelet dysfunction)
• Corticosteroid therapy long term (defective vascular support tissue)
• Estrogens (decreased platelet formation)
• Furosemide (platelet dysfunction)
• Heparin (immune thrombocytopenia, platelet dysfunction)
• Nitrofurantoin (platelet dysfunction)
• Nonsteroidal anti inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs; platelet dysfunction)
• Penicillin (immune thrombocytopenia)
• Quinidine (immune thrombocytopenia)
• Sulfonamides (immune thrombocytopenia)
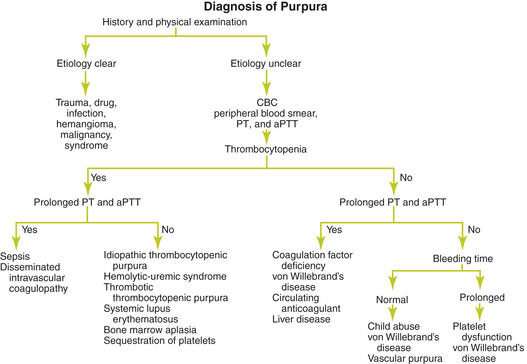
Causes of Purpura
Acquired coagulation factor deficiency
Hereditary deficiency of any coagulation factor. The most common are:
Key Historical Features
Key Physical Findings
 Vital signs, noting fever or hypertension
Vital signs, noting fever or hypertension
 Growth parameters and comparison with previous measurements
Growth parameters and comparison with previous measurements
 General evaluation of well-being
General evaluation of well-being
 Complete skin examination for purpura, pallor, rash, jaundice, café au lait spots, or telangiectasias
Complete skin examination for purpura, pallor, rash, jaundice, café au lait spots, or telangiectasias
 Evaluation for lymphadenopathy
Evaluation for lymphadenopathy
 Abdominal examination for tenderness or hepatosplenomegaly
Abdominal examination for tenderness or hepatosplenomegaly
 Genitourinary examination for scrotal edema
Genitourinary examination for scrotal edema
 Extremity examination for edema, palmar erythema, or evidence of hemarthrosis
Extremity examination for edema, palmar erythema, or evidence of hemarthrosis
Suggested Work-up
| Complete blood count (CBC) | To evaluate for thrombocytopenia or anemia |
| Peripheral blood smear | To evaluate for schistocytes suggesting hemolytic-uremic syndrome, thrombotic thrombocytopenia purpura, or disseminated intravascular coagulopathy. To evaluate for neutrophilia suggesting an infection. |
| Prothrombin time (PT) | To evaluate for a deficiency involving coagulation factors II, V, VII, X, or fibrinogen |
| Activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT) | To evaluate for a deficiency involving coagulation factors II, V, VIII, IX, X, XI, XII, or fibrinogen |
Additional Work-up
| Bleeding time | Rarely indicated in children. Measures the interval required for bleeding to stop after a standardized incision is made on the forearm. |
| Measurements of specific coagulation factors or von Willebrand factor | To confirm a specific factor deficiency or von Willebrand disease |
| Platelet aggregation tests using activators, clot retraction, prothrombin consumption test, and serotonin release | If a platelet function defect is suspected |
| Bone marrow biopsy | If a second bone marrow cell line is depressed or if the cause of thrombocytopenia is not clear after initial evaluation |
| Rheumatoid factor and antinuclear antibody | If the patient has arthritis or arthralgias |
| Urinalysis | To evaluate for hematuria if Henoch-Schönlein purpura, systemic lupus erythematosus, or hemolytic-uremic syndrome is suspected |
| Blood urea nitrogen (BUN), creatinine, and urinalysis | If renal disease is suspected |
| Liver function tests | If liver disease is suspected |
| Abdominal ultrasonography or computed tomography (CT) scanning | If organomegaly is present |
| Cranial ultrasound | To evaluate for intracranial bleeding if the neonatal platelet count is less than 50 × 103 per μL |
1. Bolton-Maggs H.B. Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Arch Dis Child. 2000;83:220–222.
2. Cines D.B., Blanchette V.S. Immune thrombocytopenic purpura. N Engl J Med. 2002;346:995–1008.
3. Cohen A.R., et al. Rash—purpura. In: Fleisher G.A., Ludwig S., editors. Textbook of Pediatric Emergency Medicine. 3rd ed. Baltimore: Williams & Wilkins; 1993:430–438.
4. Leung A.K.C., Chan K.W. Evaluating the child with purpura. Am Fam Physician. 2001;64:419–428.
5. Roberts I., Murray N.A. Neonatal thrombocytopenia: causes and management. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2003;88:359–364.
6. Tizard J. Henoch-Schönlein purpura. Arch Dis Child. 1999;80:380–383.