Chapter 394 Pulmonary Abscess
Pathology and Pathogenesis
A number of conditions predispose children to the development of pulmonary abscesses, including aspiration, pneumonia, cystic fibrosis (Chapter 395), gastroesophageal reflux (Chapter 315.1), tracheoesophageal fistula (Chapter 311), immunodeficiencies, postoperative complications of tonsillectomy and adenoidectomy, seizures, and a variety of neurologic diseases. In children, aspiration of infected materials or a foreign body is the predominant source of the organisms causing abscesses. Initially, pneumonitis impairs drainage of fluid or the aspirated material. Inflammatory vascular obstruction occurs, leading to tissue necrosis, liquefaction, and abscess formation. Abscess can also occur as a result of pneumonia and hematogenous seeding from another site.
Diagnosis
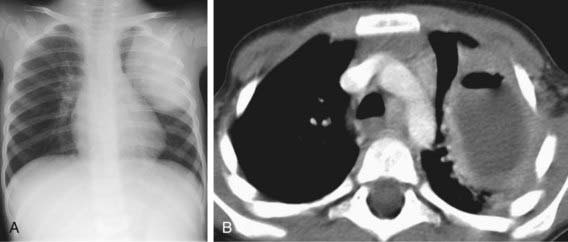
Diagnosis is most commonly made on the basis of chest radiography. Classically, the chest radiograph shows a parenchymal inflammation with a cavity containing an air-fluid level (Fig. 394-1). A chest CT scan can provide better anatomic definition of an abscess, including location and size (Fig. 394-2).
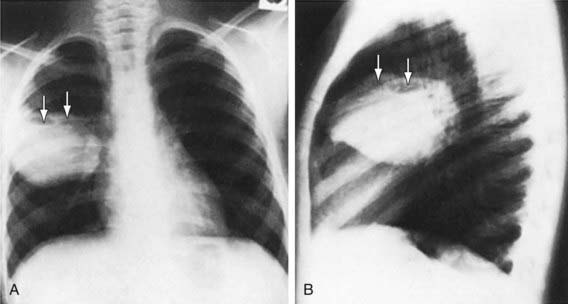
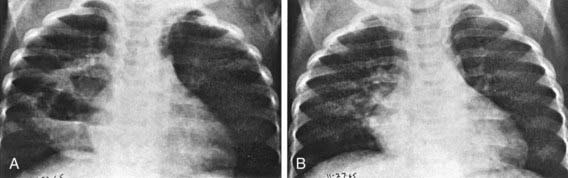
Figure 394-1 A and B, Multiloculated lung abscess (arrows).
(From Brook I: Lung abscess and pulmonary infections due to anaerobic bacteria. In Chernick V, Boat TF, Wilmott RW, et al, editors: Kendig’s disorders of the respiratory tract in children, ed 7, Philadelphia, 2006, Saunders, p 482.)
An abscess is usually a thick-walled lesion with a low-density center progressing to an air-fluid level. Abscesses should be distinguished from pneumatoceles, which often complicate severe bacterial pneumonias and are characterized by thin- and smooth-walled, localized air collections with or without air-fluid level (Fig. 394-3). Pneumatoceles often resolve spontaneously with the treatment of the specific cause of the pneumonia.
Bartlett JG. The role of anaerobic bacteria in lung abscess. Clin Infect Dis. 2005;40:923-925.
Chan PC, Huang LM, Wu PS, et al. Clinical management and outcome of childhood lung abscess: a 16-year experience. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2005;38:183-188.
Hewitson J. Lung abscess. In: Parikh DH, Crabbe DC, Auldist AW, et al, editors. Pediatric thoracic surgery. London: Springer-Verlag; 2009:145-159.
Hogan MJ, Coley BD. Interventional radiology treatment of empyema and lung abscesses. Paediatr Respir Rev. 2008;9:77-84.
Holston AM, Miller JR. Primary lung abscess caused by multidrug-nonsusceptible Streptococcus pneumoniae in a child. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2006;25:182-183.
Patradoon-Ho P, Fitzgerald DA. Lung abscess in children. Paediatr Respir Rev. 2007;8:77-84.
Peltola V, Svedstrom E, Waris M, et al. Pulmonary abscess of viral-bacterial etiology in a neonate. Eur J Pediatr. 2007;166:1301-1302.
Puligandla PS, Laberge JM. Respiratory infections: pneumonia, lung abscess, and empyema. Semin Pediatr Surg. 2008;17:42-52.
Yen C, Tang R, Chen S, et al. Pediatric lung abscess: a retrospective review of 23 cases. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2004;37:45-49.