Chapter 129 Principles and Clinical Indications
The donor immune system exerts its T cell–mediated GVL effect through alloreactions directed against not shared recipient histocompatibility antigens displayed on recipient leukemia cells. Because some of these histocompatibility antigens are also displayed on tissues, however, T cell–mediated alloreactions may ensue. Specifically, donor alloreactive cytotoxic CD8+ effector T cells may attack recipient tissues—in particular, the skin, gastrointestinal tract, and liver—causing acute graft versus host disease (GVHD), a condition of varying severity, that, in some cases, can be life-threatening (Chapter 131).
Hsct from an Hla-Identical Sibling Donor
Allogeneic HSCT from an HLA-compatible sibling is the treatment of choice for children with hematological malignancies and congenital diseases (Table 129-1). Best results are achieved in patients with congenital or acquired nonmalignant disorders because the risk of disease recurrence is low and the cumulative transplant-related mortality is lower than in children transplanted for hematological malignancies.
Table 129-1 INDICATIONS FOR ALLOGENEIC HEMATOPOIETIC STEM CELL TRANSPLANTATION FOR PEDIATRIC DISEASES
Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL)
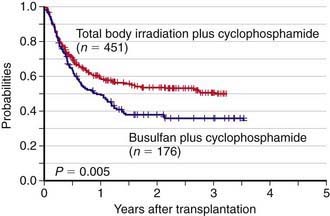
Allogeneic HSCT is used for pediatric patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), either in the 1st complete remission when a child is considered to be at high risk of leukemia recurrence (such as, for example, those with Ph+ ALL or with high levels of minimal residual disease), or in 2nd or further complete remission after previous marrow relapse. ALL is the most common indication for HSCT in childhood (Chapter 489). Several patient-, donor-, disease-, and transplant-related variables may influence the outcome of patients with ALL given an allogeneic HSCT. The long-term probabilities of event-free survival for patients with ALL transplanted in the 1st or 2nd complete remission is 60-70% and 50%, respectively. Inferior results are obtained in patients transplanted in more advanced disease phases. The use of radiotherapy, total body irradiation (TBI), during the preparative regimen offers an advantage in terms of better event-free survival compared to a regimen consisting of cytotoxic drugs alone (Fig. 129-1). Less intensive GVHD prophylaxis is also associated with a better outcome. Bone marrow is still the preferred source of stem cells to be employed for transplantation.
Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML)
Allogeneic HSCT from an HLA-identical sibling is largely employed as postremissional treatment of pediatric patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) (Chapter 489). Many studies have shown that children with AML in 1st complete remission given allogeneic HSCT as consolidation therapy have a better probability of event-free survival as compared to those treated with either chemotherapy alone or with autologous transplantation. Results obtained in patients given HSCT from an HLA-identical sibling after either a TBI-containing or a chemotherapy-based preparative regimen are similar, the probability of event-free survival being on the order of 60-70%. Children with acute promyelocytic leukemia in molecular remission at the end of treatment with chemotherapy and all-trans retinoic acid or with AML and either translocation t(8;21) or inversion of chromosome 16 (inv.16) are no longer considered eligible for allogeneic HSCT in 1st complete remission in view of their excellent prognosis with alternative treatments. Around 40% of pediatric patients with AML in the 2nd complete remission can be rescued by an allograft from an HLA-identical sibling.
Acquired Aplastic Anemia
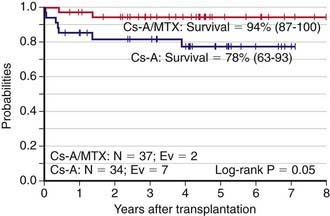
HSCT from an HLA-identical sibling is the treatment of choice for children with the severe form of acquired aplastic anemia, defined as two of the following: platelet count <20,000/mm3, absolute neutrophil count <500/mm3, or reticulocyte count <1% when anemia is present, together with hypoplastic bone marrow (<20% total cellularity) (Chapter 463). The probability of survival with sustained donor engraftment for these patients is >80%, with younger patients having even better outcomes. Every child diagnosed with severe acquired aplastic anemia should undergo HLA-typing as early as possible in order to identify a suitable HLA-compatible family donor. Graft rejection represents the most important cause of treatment failure. Blood transfusion should be avoided whenever possible because sensitization to blood products increases the likelihood of graft rejection. GVHD prophylaxis combining cyclosporine and short-term methotrexate is associated with a better outcome as compared to cyclosporine alone (Fig. 129-2). Some studies have suggested that the addition of antithymocyte globulin to the classical conditioning regimen consisting of cyclophosphamide (200 mg/kg) can reduce the risk of graft rejection, particularly in patients with previous heavy sensitization to blood products. The use of G-CSF mobilized peripheral blood progenitors has provided inferior results with respect to the infusion of bone marrow cells.
Constitutional Aplastic Anemia
Fanconi anemia and dyskeratosis congenita are genetic disorders associated with a high risk of developing pancytopenia (Chapter 462). Fanconi anemia is an autosomal recessive disease characterized by spontaneous chromosomal fragility, which is increased after exposure of peripheral blood lymphocytes to DNA cross-linking agents, including clastogenic compounds, such as diepoxybutane, mitomycin C, and melphalan. Besides being at risk of pancytopenia, patients with Fanconi anemia show a high propensity to develop clonal disorders of hematopoiesis, such as myelodysplastic syndromes and acute myeloid leukemia. HSCT can rescue aplastic anemia and prevent the occurrence of clonal hematopoietic disorders. In view of their defects in DNA repair mechanisms, which are responsible for the chromosomal fragility, Fanconi anemia patients have an exquisite sensitivity to alkylating agents. Thus, they must be prepared for the allograft with reduced doses of cyclophosphamide. Many patients were once successfully transplanted after receiving low-dose cyclophosphamide and thoraco-abdominal irradiation. However, the use of this regimen is associated with an increased incidence of post-transplant head and neck cancers. Either reduced doses of cyclophosphamide alone or low-dose cyclophosphamide with fludarabine are currently employed for preparing Fanconi anemia patients to the allograft. Using these regimens, the success rate of HSCT from an HLA-identical sibling is on the order of 70-80%.
Thalassemia
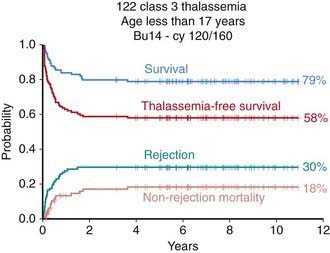
Conventional treatment (blood transfusion and iron chelation therapy) has dramatically improved both the survival and quality of life of patients with thalassemia, changing a previously fatal disease with early death to a chronic, slowly progressive disease compatible with prolonged survival (Chapter 456.9). HSCT remains the only curative treatment for patients with thalassemia. In these patients the risk of dying from transplant-related complications is primarily dependent on patient age, iron overload, and concomitant hepatic viral infections. Adults, especially when affected by chronic active hepatitis, have a poorer outcome than children. Among children, 3 classes of risk have been identified on the basis of 3 parameters, namely regularity of previous iron chelation, liver enlargement, and presence of portal fibrosis. In pediatric patients without liver disease who have received regular iron chelation (class 1 patients), the probability of survival with transfusion independence is >90%, whereas for patients with low compliance with iron chelation and signs of severe liver damage (class 3 patients), the probability of survival is 60% (Fig. 129-3). As in other nonmalignant disorders the best pharmacologic combinations (such as that including cyclosporine A and methotrexate) should be employed to prevent GVHD.
Sickle Cell Disease
Disease severity varies greatly among patients with sickle cell disease (SCD), with 5-20% of the overall population suffering significant morbidity from vaso-occlusive crises and pulmonary, renal, or neurologic damage (Chapter 456.1). Despite the fact that hydroxyurea, an agent favoring the synthesis of HbF, has been demonstrated to reduce the frequency and severity of vaso-occlusive crises and to improve the quality of life for patients with sickle cell disease, allogeneic HSCT is the only curative treatment for this disease. Although HSCT can cure homozygous HbS disease, selecting appropriate candidates for transplantation is difficult. Patients with SCD may survive for decades, but some patients have a poor quality of life, with repeated hospitalizations for painful vaso-occlusive crises and central nervous system infarcts. The main indications for performing HSCT in patients with sickle cell disease are history of strokes, magnetic resonance imaging of central nervous system lesions associated with impaired neuropsychologic function, failure to respond to hydroxyurea as shown by recurrent acute chest syndrome, and/or recurrent vaso-occlusive crises and/or severe anemia and/or osteonecrosis. The results of HSCT are best, with a probability of cure of 80-90%, when performed in children with an HLA-identical sibling. The use of antithymocyte globulin during the preparative regimen has been shown to improve patient outcomes, preventing graft failure.
Immunodeficiency Disorders
HSCT is the treatment of choice for children affected by severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) and other inherited immunodeficiencies (see Table 129-1). With an HLA-identical sibling, the probability of survival approaches 100%, with less favorable results for patients transplanted from an unrelated volunteer or an HLA-partially matched relative. Some children with SCID may be transplanted without receiving any preparative regimen, in particular those without residual NK activity or maternal T-cell engraftment. Sustained donor engraftment is more difficult to achieve in children with Omenn syndrome, hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis, or leukocyte adhesion deficiency. Life-threatening opportunistic fungal and viral infections occurring before the allograft adversely affect the patient’s outcome after HSCT. Patients with the most severe immunodeficiencies must be transplanted as early as possible.
Antoine C, Muller S, Cant A, et al. for the European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation, European Society for Immunodeficiency: Long-term survival and transplantation of haemopoietic stem cells for immunodeficiencies: report of the European experience 1968–1999. Lancet. 2003;361:553-560.
Copelan EA. Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. N Engl J Med. 2006;354:1813-1826.
Cwynarski K, Roberts IA, Iacobelli S, et al. Stem cell transplantation for chronic myeloid leukemia in children. Blood. 2003;102:1224-1231.
Davies S, Ramsay NK, Klein JP, et al. Comparison of preparative regimens in transplants for children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 2000;18:340-347.
Godley LA, van Besien K. The next frontier for stem cell transplantation. JAMA. 2010;303(14):1421-1422.
Gooley TA, Chien JW, Pergam SA, et al. Reduced mortality after allogeneic hematopoietic-cell transplantation. N Eng J Med. 2010;363(22):2091-2100.
Locatelli F, Bruno B, Zecca M, et al. Cyclosporin A and short-term methotrexate versus cyclosporin A as graft versus host disease prophylaxis in patients with severe aplastic anemia given allogeneic bone marrow transplantation from an HLA-identical sibling: results of a GITMO/EMBT randomized trial. Blood. 2000;96:1690-1697.
Locatelli F, Rocha V, Reed W, et al. Related umbilical cord blood transplantation in patients with thalassemia and sickle cell disease. for the Eurocord Transplant Group CBT. Blood. 2003;101:2137-2143.
Locatelli F, Nöllke P, Zecca M, et al. Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) in children with juvenile myelomonocytic leukemia (JMML): results of the EWOG-MDS/EBMT trial. Blood. 2005;105:410-419.
Vicente R, Adjali O, Jacquet C, et al. Intrathymic transplantation of bone marrow–derived progenitors provides long-term thymopoiesis. Blood. 2010;115(10):1913-1920.