CHAPTER 5 Preoperative and postoperative care
Preoperative preparation
Assessment
Principles of preoperative preparation
Postoperative care
Conditions affecting surgical risk
Medical problems in surgical patients
Cardiovascular
Respiratory disease
Renal disease
Hepatic disease
Obstructive jaundice
There is usually a clear history. Surgery will usually have been necessary to deal with the problem.
Haematological disease
Endocrine disease
Diabetes
This poses numerous risks and affects many systems. Complications include:
Thyroid disease
Hyperthyroidism
Patients should be euthyroid prior to elective surgery (→ Ch. 11). Hyperthyroidism is associated with arrhythmias and hypertension. A thyroid crisis is associated with oversecretion and may be triggered by infection. This presents as hyperthermia, arrhythmias, cardiorespiratory failure and coma.
American society of anesthesiologists’ classification of physical status (ASA grading)
The ASA grading system for quantifying anaesthetic risk is as follows:
Postoperative complications
All operations carry a risk of complications (a Classification is shown in Table 5.1). Complications may be divided as:
| Haemorrhage | Early postoperative Secondary haemorrhage |
| Wound | Infection Bleeding Haematoma Seroma Suture sinus Breakdown: |
MI
Pulmonary oedema
Arrhythmias
DVT
Aspiration
Pneumonia
PE
Pulmonary oedema
Pneumothorax
ARDS
Stroke
UTI
Acute renal failure
Mechanical obstruction
Acute gastric dilatation
Constipation
Wound problems
Infection
Incidence varies according to type of surgery and potential for contamination (→ Ch. 6). Factors leading to increased risk of wound infection include: haematoma, poor nutritional state, diabetes mellitus, reduced immunity, nasal carriage of Staphylococcus aureus.
Anastomotic breakdown
This is a major cause of postoperative morbidity and mortality after bowel surgery.
Causes
Anastomotic breakdown may result in generalized peritonitis, paracolic abscess, abscesses between loops of bowel or fistula formation. However, presentation can be surprisingly subtle with mild pyrexia, persistent tachycardia and general failure to progress as the only signs of anastomotic leak (→ Chs 6 and 14).
Lung problems
Pneumonia
Predisposing factors include smoking, atelectasis, COPD, aspiration, debilitated patients.
Pulmonary oedema
Pulmonary embolus (PE)
Diagnosis
Treatment
Pneumothorax
Adult respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS; shock lung)
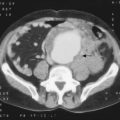
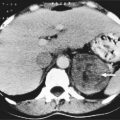
This is acute respiratory failure with tachypnoea, hypoxia, decreased lung compliance and diffuse pulmonary infiltrates on CXR. The exact aetiology is unknown but there is interference with the pulmonary epithelial/endothelial cell interface with increased interstitial oedema, vascular congestion and ultimately fibrosis (Table 5.2).
| Infection | Septicaemia |
| Inhalation | Smoke, vomit, water, high O2 concentrations, chlorine, ammonia |
| Embolism | Fat, amniotic fluid, air |
| Cerebral | Head injury, cerebral haemorrhage |
| Drugs | Opiates, barbiturates |
| Others | Pancreatitis, DIC, blood transfusion, cardiopulmonary bypass, major trauma with shock |
Treatment
Urinary tract problems
Urinary tract infection (UTI)
This is common, especially in females. Catheterization may predispose.
Acute renal failure (ARF)
Oliguria is passage of <30 mL of urine per hour. Anuria is failure to pass any urine.
Treatment of anuria/oliguria
Gastrointestinal problems
Paralytic ileus
Symptoms and signs
Abdominal distension, vomiting, constipation. Tense tympanitic abdomen. Absent bowel sounds (Table 5.3).
TABLE 5.3 Factors distinguishing paralytic ileus and mechanical obstruction
| Ileus | Obstruction | |
|---|---|---|
| Time | Usually settles in 3–4 days | May persist longer |
| Bowel sounds | Absent | High-pitched and tinkling |
| Pain | Painless | Colicky abdominal pain |
| AXR | General gaseous dilatation of small and large bowel | Localized small bowel distension with absent gas in colon and rectum |
Postoperative pain relief
Methods of postoperative pain control
Parenteral analgesia
Intercostal nerve blocks
These are useful for upper abdominal surgery or in thoracic injuries, e.g. fractured ribs
Blood transfusion
Blood products and alternatives to transfusion
Blood products used in clinical practice include:
Alternatives to the use of stored blood include:
Clinical aspects of blood transfusion
Complications of blood transfusion
Acute
Fluid and electrolyte balance
Crystalloid and colloid
Intravenous fluids can be divided into crystalloids and colloids.
Hartmann’s solution
With this in mind, a suitable regime of postoperative fluids may include:
Management of Na+ and K+ imbalance
Hypernatraemia (i.e. high Na+)
This is uncommon in the surgical patient. It may occur during dehydration and in the postoperative period if too much saline is given at a time when aldosterone secretion is high and sodium is being conserved. Rarely it may be caused by Conn’s syndrome (→ Ch. 11). If the cause is dehydration (i.e. clinically dry with low CVP and oliguria), the patient will need water replacement, whereas in the postoperative period with normovolaemia, sodium restriction is required.

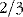 or 28 L is intracellular fluid (ICF)
or 28 L is intracellular fluid (ICF)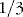 or 14 L is extracellular fluid (ECF) –
or 14 L is extracellular fluid (ECF) – 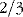 of this or 10 L is interstitial and
of this or 10 L is interstitial and 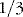 or 4 L is plasma
or 4 L is plasma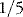 the amount of sodium of normal saline, i.e. 30 mmol/L and 4% dextrose.
the amount of sodium of normal saline, i.e. 30 mmol/L and 4% dextrose.