Echogenic curvilinear structure in GB fossa with dense acoustic shadowing
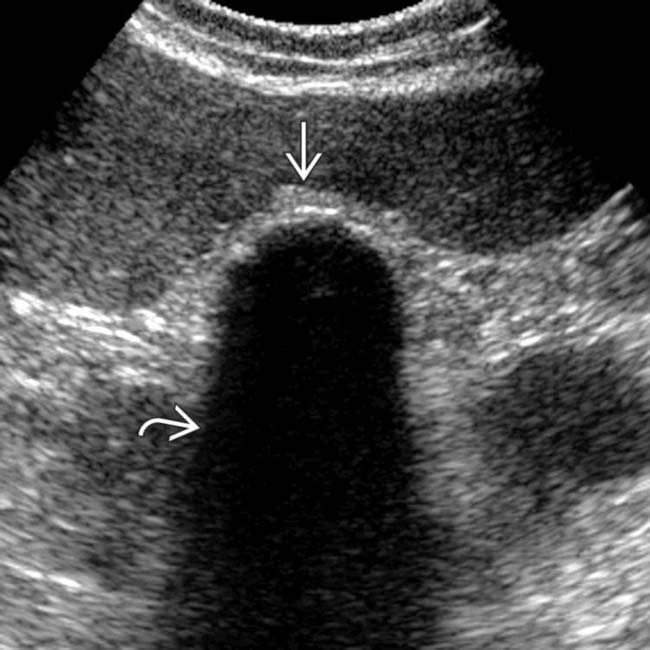
 in the gallbladder (GB) fossa with acoustic shadowing
in the gallbladder (GB) fossa with acoustic shadowing  , characteristic of a porcelain GB.
, characteristic of a porcelain GB.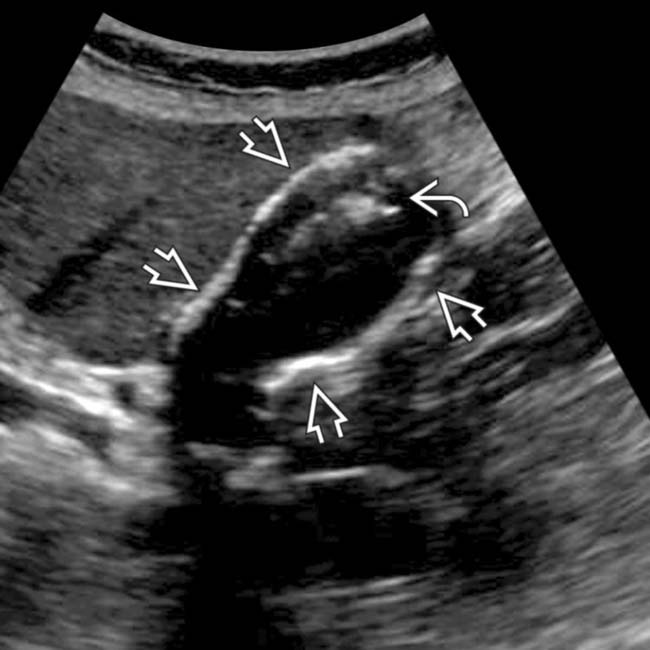
 and a mass
and a mass  within the fundus. The posterior GB wall is visible, unlike a GB filled with stones or emphysematous cholecystitis. Chronic cholecystitis, intramural calcification, and GB adenocarcinoma were identified at pathology.
within the fundus. The posterior GB wall is visible, unlike a GB filled with stones or emphysematous cholecystitis. Chronic cholecystitis, intramural calcification, and GB adenocarcinoma were identified at pathology.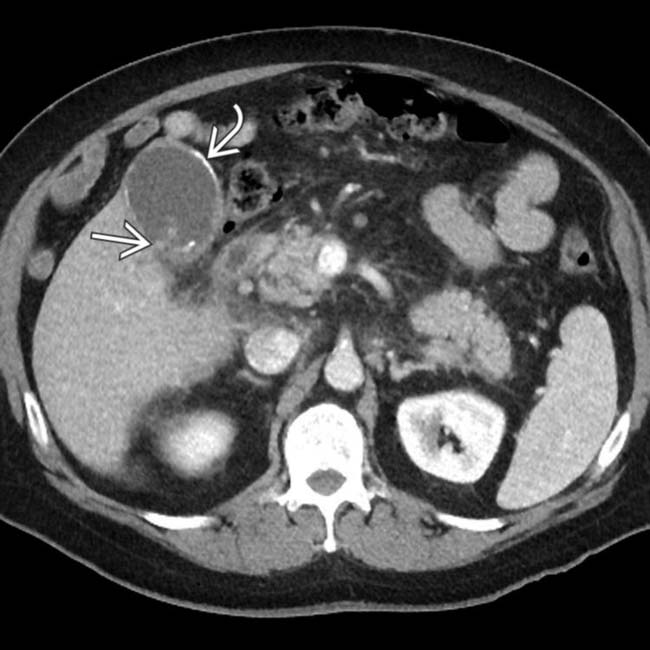
 . Note the subtle soft tissue density
. Note the subtle soft tissue density  within the GB and the blurred margin with the adjacent liver.
within the GB and the blurred margin with the adjacent liver.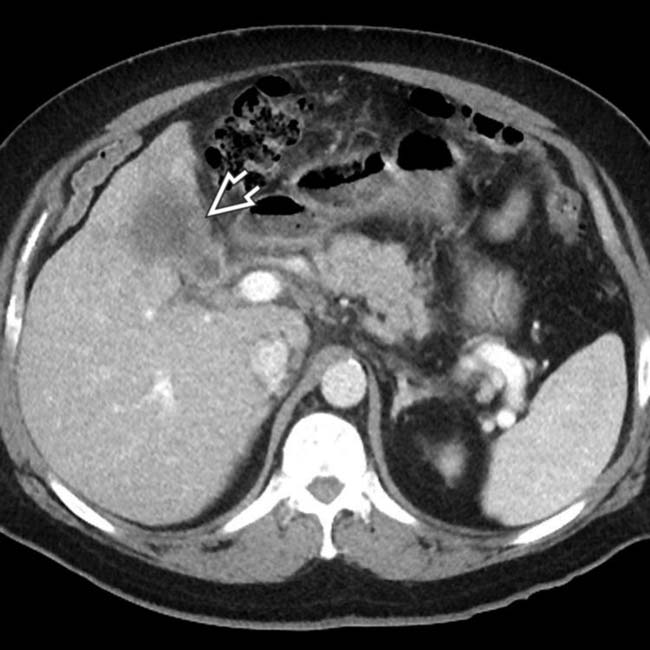
 in the GB invading the liver, a classic appearance for GB cancer. GB cancer is thought to be more likely with interrupted, partial GB wall calcification than with diffuse calcification.
in the GB invading the liver, a classic appearance for GB cancer. GB cancer is thought to be more likely with interrupted, partial GB wall calcification than with diffuse calcification.IMAGING
General Features
Ultrasonographic Findings
• Several different possible appearances
 Echogenic curvilinear structure in GB fossa with dense acoustic shadowing
Echogenic curvilinear structure in GB fossa with dense acoustic shadowing
 Echogenic curvilinear structure in GB fossa with dense acoustic shadowing
Echogenic curvilinear structure in GB fossa with dense acoustic shadowing
CLINICAL ISSUES
Presentation
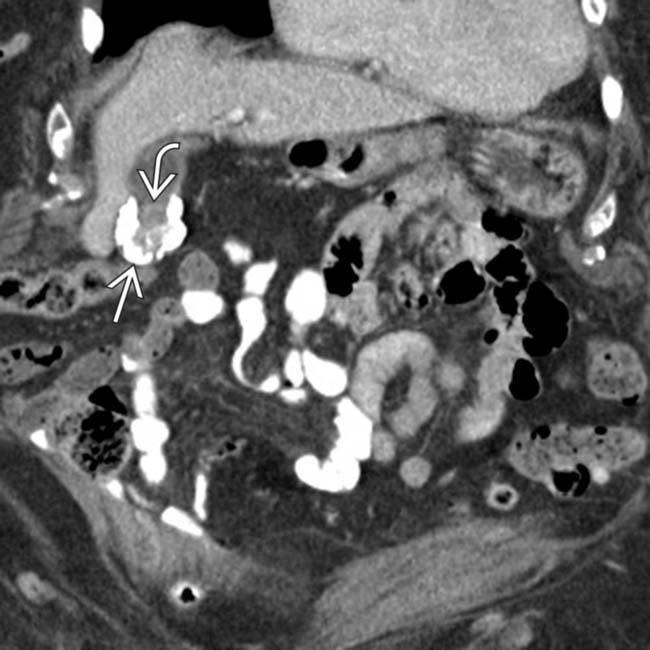
 of the wall of the GB fundus. Note the subtle soft tissue density
of the wall of the GB fundus. Note the subtle soft tissue density  in the GB fundus adjacent to the calfication. While the association is weaker than previously thought, such a finding should raise strong suspicion for coexistent malignancy.
in the GB fundus adjacent to the calfication. While the association is weaker than previously thought, such a finding should raise strong suspicion for coexistent malignancy.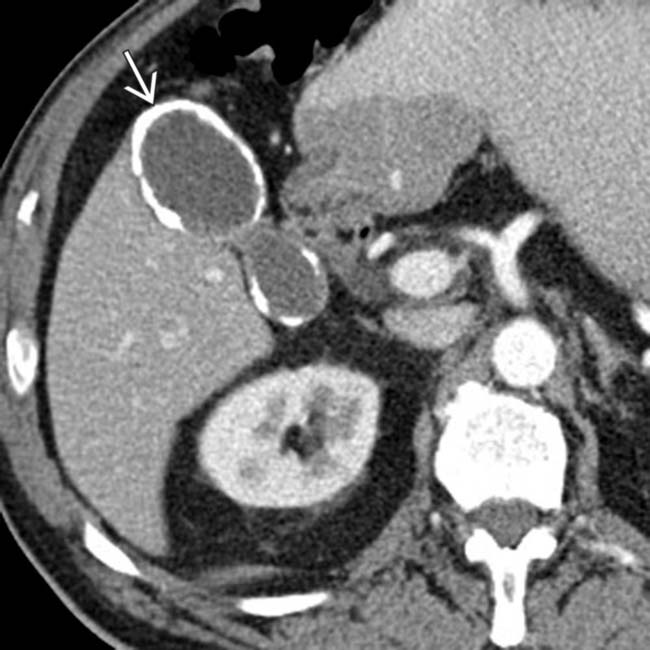
 of the GB wall. No malignancy was identified at cholecystectomy.
of the GB wall. No malignancy was identified at cholecystectomy.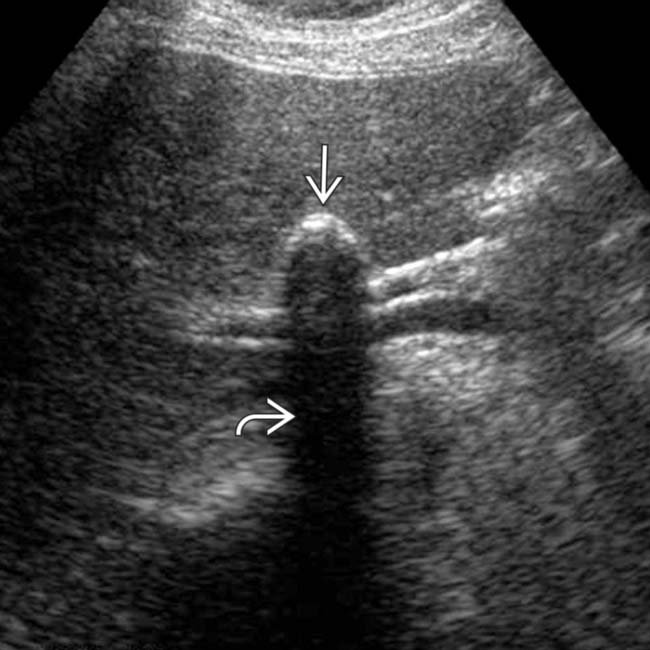
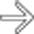
 of the anterior GB wall, in keeping with a porcelain GB. Note the lack of a “wall-echo-shadow” complex (unlike stones) and the clean posterior acoustic shadowing
of the anterior GB wall, in keeping with a porcelain GB. Note the lack of a “wall-echo-shadow” complex (unlike stones) and the clean posterior acoustic shadowing  (unlike the dirty shadowing of emphysematous cholecystitis).
(unlike the dirty shadowing of emphysematous cholecystitis).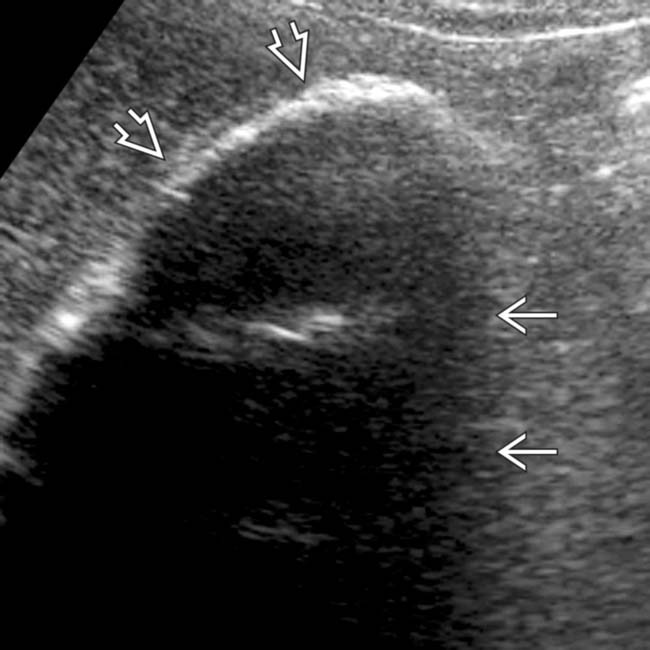
 within the GB wall. Marked shadowing
within the GB wall. Marked shadowing  makes it impossible to assess the GB lumen. (Courtesy K.T. Wong, MBChB.)
makes it impossible to assess the GB lumen. (Courtesy K.T. Wong, MBChB.)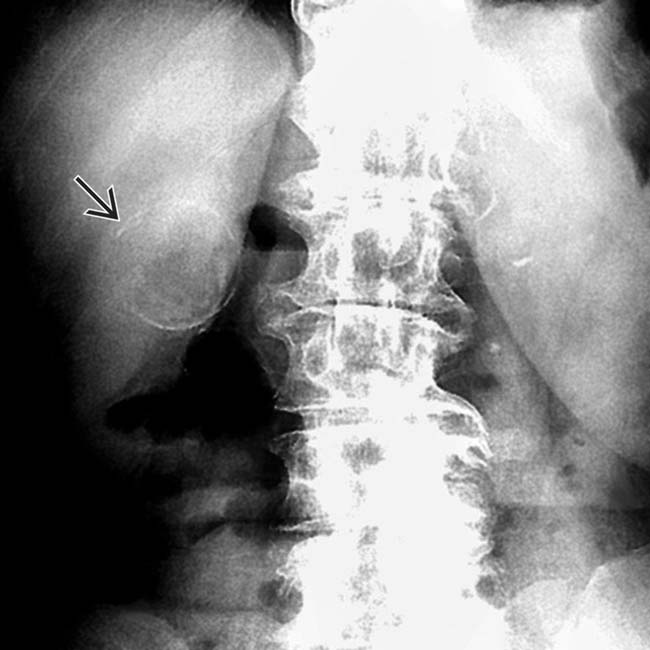
 in the right upper quadrant, which is the typical appearance for a calcified GB wall.
in the right upper quadrant, which is the typical appearance for a calcified GB wall.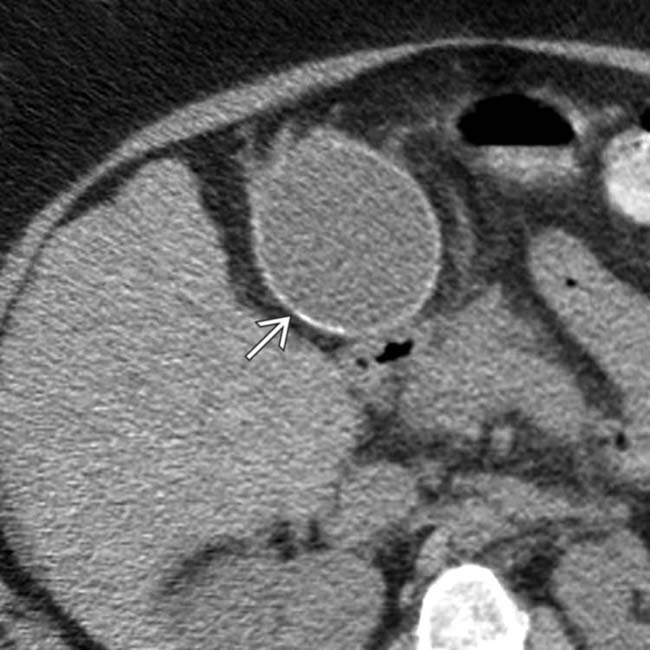
 . The liver is nodular as a result of cirrhosis. Patients with cirrhosis have an increased prevalence of gallstones but uncommonly develop porcelain GB.
. The liver is nodular as a result of cirrhosis. Patients with cirrhosis have an increased prevalence of gallstones but uncommonly develop porcelain GB.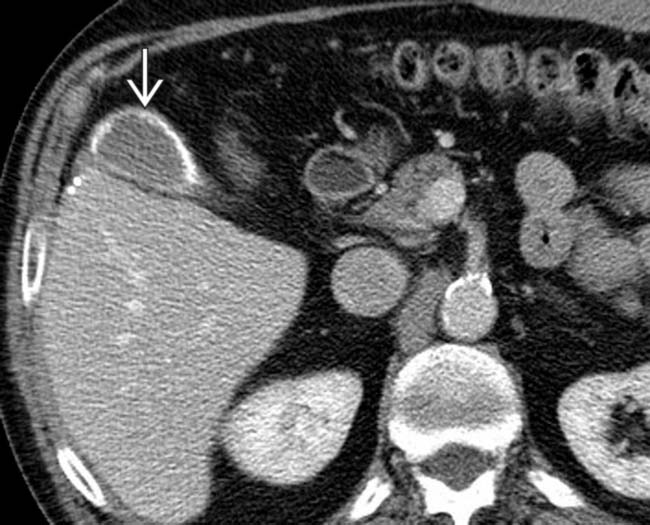
 of the GB wall is seen without associated mass or enhancement.
of the GB wall is seen without associated mass or enhancement.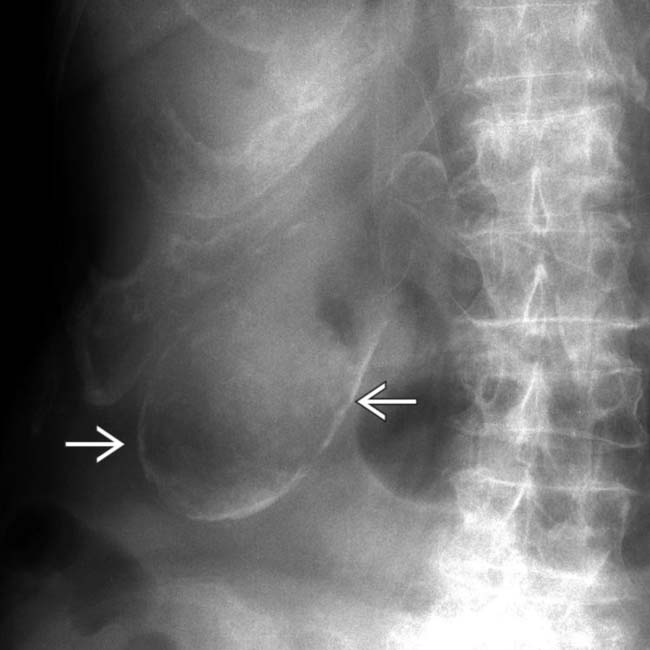
 in the right upper quadrant conforming to the shape of the GB.
in the right upper quadrant conforming to the shape of the GB.



























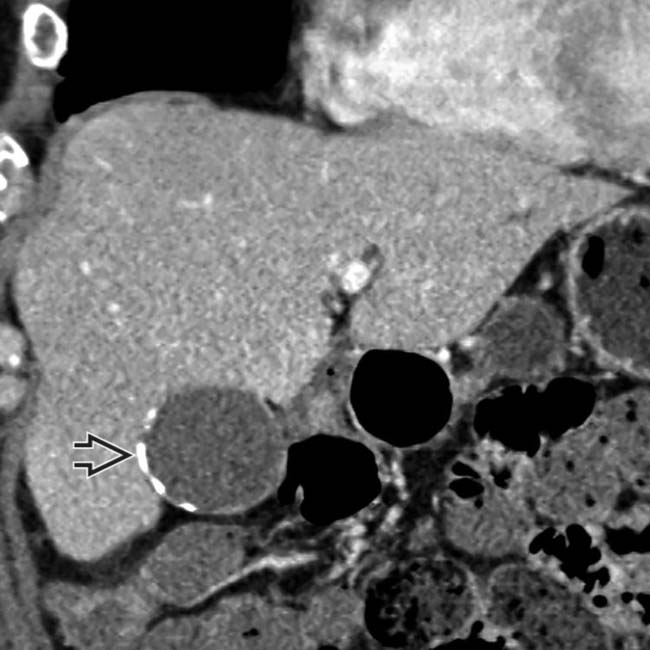
 in the lateral aspect of the GB wall.
in the lateral aspect of the GB wall.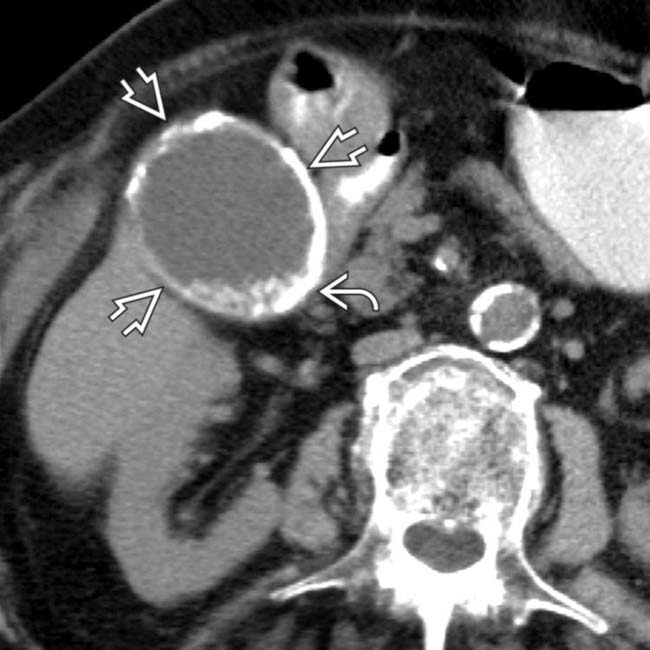
 and dependent calcified stones
and dependent calcified stones  . The association between porcelain GB and carcinoma is weaker than suggested in early surgical series, but cholecystectomy may still be indicated depending on patient demographics and the type of wall calcification.
. The association between porcelain GB and carcinoma is weaker than suggested in early surgical series, but cholecystectomy may still be indicated depending on patient demographics and the type of wall calcification.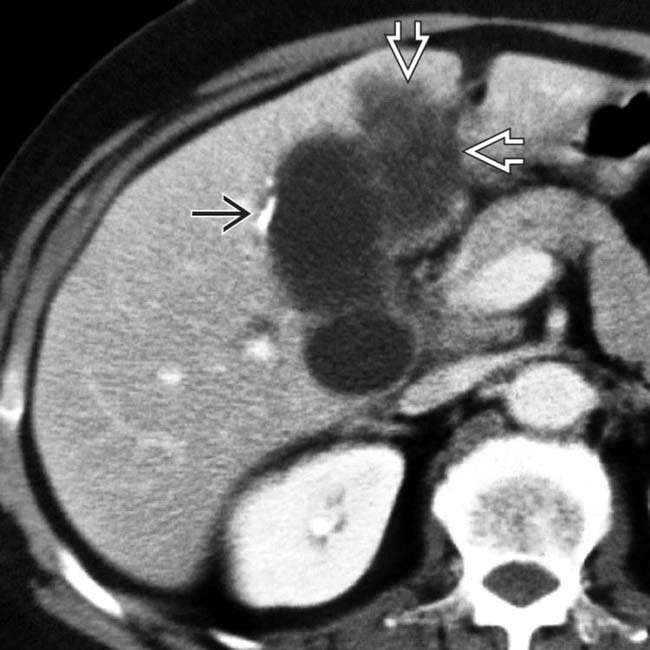
 and a heterogeneous low-attenuation mass
and a heterogeneous low-attenuation mass  invading the adjacent liver representing GB carcinoma. The relationship between porcelain GB and GB cancer is controversial, but probably not as strong as previously thought.
invading the adjacent liver representing GB carcinoma. The relationship between porcelain GB and GB cancer is controversial, but probably not as strong as previously thought.


