Parasites
I Introduction to Parasitology
1. Two groups of parasitic organisms cause human disease: the single-celled protozoa and the multicellular helminths (worms).
2. Like fungi, parasites are eukaryotes, but they lack the plant-like cell wall present in fungi.
1. Entry of organisms occurs primarily by ingestion or direct penetration of the skin (sometimes by bite of insect vector).
2. Replication of parasites takes place in specific cell types or organs.
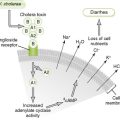
• A characteristic route of entry leads to infection.
• Site and route of entry and release are determined by the life cycle of the organism.
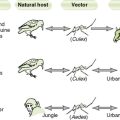
• Life cycle may differ in different hosts, for example, human versus snail or mosquito.
3. Cell and tissue damage result from four general mechanisms.
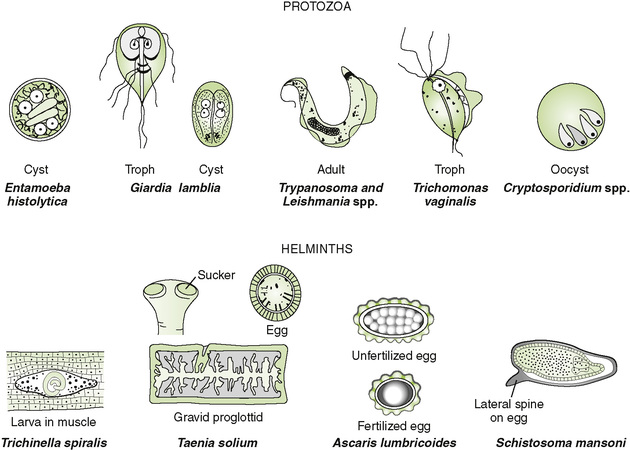
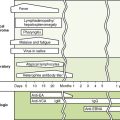
1. Definitive diagnosis of most parasitic diseases depends on microscopic identification of parasitic forms (e.g., larvae, eggs, and adults) in clinical specimens (Fig. 29-1).
2. Serologic testing is useful in diagnosis of Entamoeba and Strongyloides species infection.
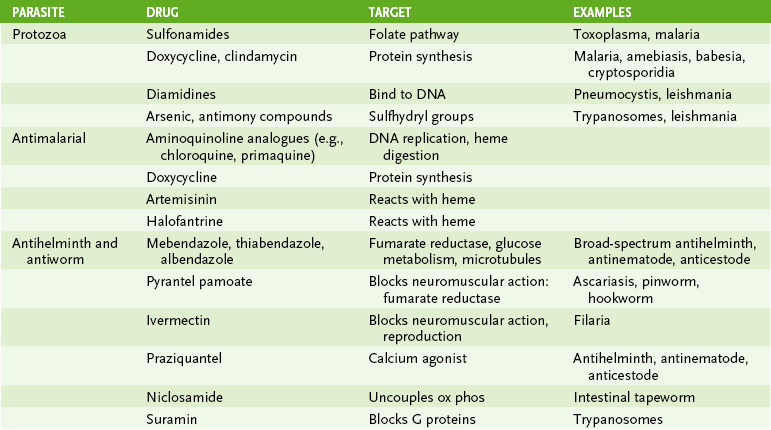
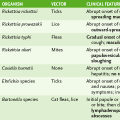
II Protozoan Parasites (Table 29-2)
TABLE 29-2
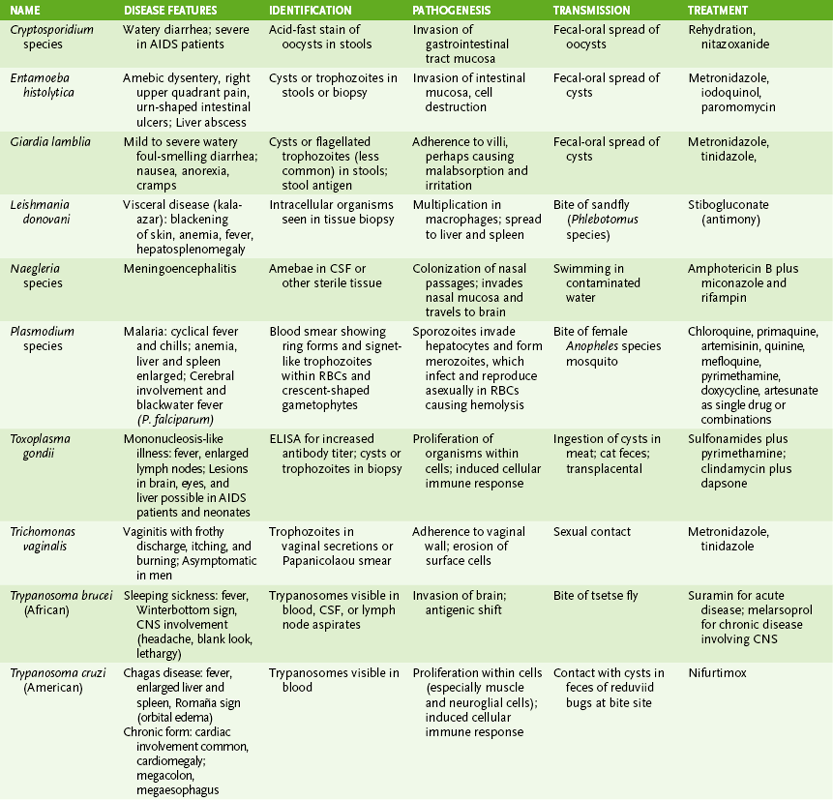
A Intestinal and urogenital protozoa
• Endemic to tropical and subtropical regions
• Transmitted by sandfly (Phlebotomus species)
• Infection of macrophages leading to cutaneous, mucocutaneous, or visceral disease
a. Characterized by episodic paroxysms of high fever and severe chills followed by sweats
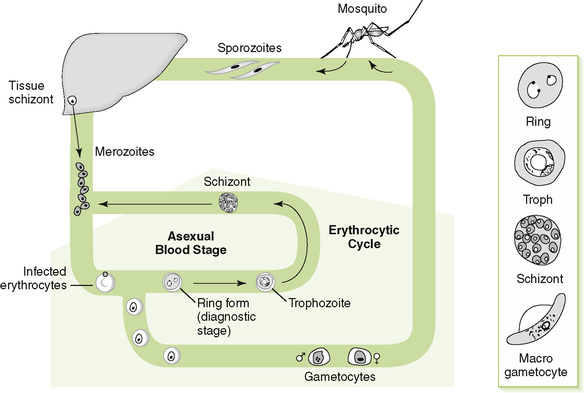
b. Life cycle of plasmodia within humans includes an exoerythrocytic phase within hepatocytes and a series of erythrocytic cycles within red blood cells (RBCs) (Fig. 29-2).
c. Malarial paroxysms are due to simultaneous hemolysis of large numbers of infected RBCs and release of motile merozoites.
d. Asexual ring forms and signet-like trophozoites within RBCs and crescent-shaped gametocytes in blood are diagnostic.
• Plasmodium malariae infects only old erythrocytes.
a. Infects all erythrocytes and causes the most serious disease
b. Has shortest incubation period (7 to 10 days)
c. Only species that involves the central nervous system
d. Only species with only ring forms and gametocytes in the peripheral blood
e. Typical paroxysms, if present, initially occur daily, then every 36 to 48 hours.
• Acquired from cat litter, ingestion of undercooked meat, or in utero
• Mononucleosis-like syndrome in healthy individuals
• Potentially fatal encephalitis in immunocompromised patients
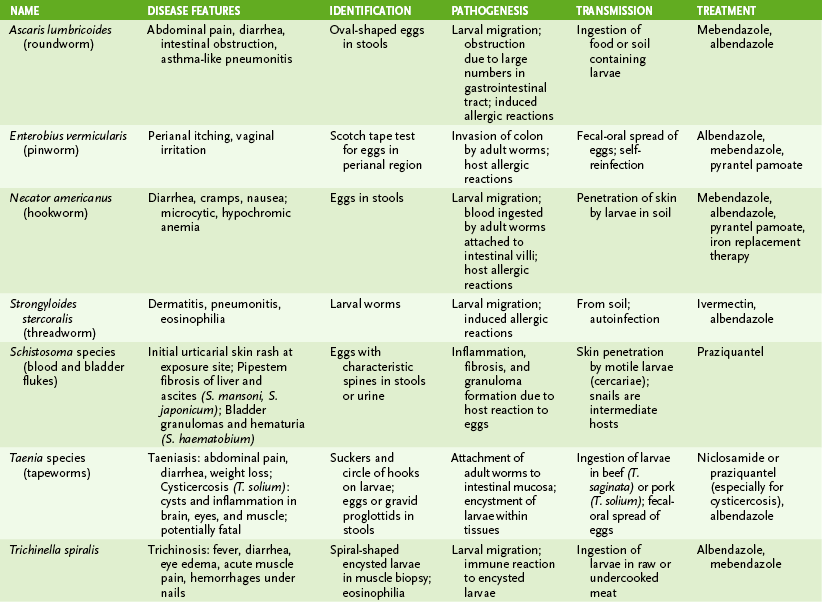
III Helminthic Parasites (Table 29-3)
1. Ascaris lumbricoides (roundworm)
• Accumulation of large worms that may cause small intestinal obstruction
• Pneumonitis with eosinophilia associated with larval migration
2. Enterobius vermicularis (pinworm)
• Perianal pruritus and itching
• Self-reinfection by scratching anal area and transmitting eggs to mouth
• Other conditions: acute appendicitis, urethritis in girls
3. Necator and Ancylostoma species (hookworm)
4. Strongyloides stercoralis (threadworm)
• Dermatitis, pneumonitis with eosinophilia
• Disseminated hyperinfection in immunocompromised
1. Schistosoma species (blood and bladder flukes)
2. Taenia species (beef and pork tapeworms)
C Disease manifestations caused by infection with representative helminthic parasites
1. Creeping eruption or serpent-like lesions caused by migrating larva in the skin (cutaneous larva migrans)
2. Subcutaneous swelling or nodules due to infections of subcutaneous tissue (not commonly seen in the United States)
• Loa loa (worm native to West Africa)
• Dracunculus medinensis (worm native to India, Africa, Arabian peninsula)
3. Pulmonary infiltrates with eosinophilia caused by passage of migrating larva through the lungs
• Necator americanus, Ancylostoma duodenale (hookworm)
4. Central nervous system involvement
• Toxoplasma gondii (especially in patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome [AIDS])
• P. falciparum (cerebral malaria)
• T. brucei (African sleeping sickness)
5. Lesions in the liver and the lungs
• Clonorchis sinensis, Fasciola hepatica (liver flukes)
• Schistosoma species (blood fluke)
• Paragonimus westermani (lung fluke)