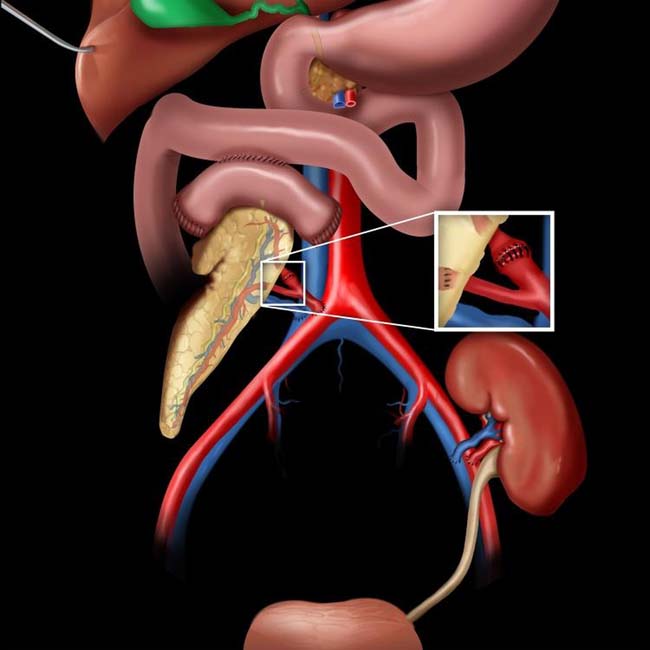
CT: Homogeneous soft tissue mass in right abdomen with adjacent suture line at duodenal stump
 MR: Normal pancreatic parenchyma is isointense to renal cortex on T1WI and isointense to muscle on T2WI
MR: Normal pancreatic parenchyma is isointense to renal cortex on T1WI and isointense to muscle on T2WI• Imaging of major complications
 and the pancreatic allografts
and the pancreatic allografts  show normal perfusion and parenchymal enhancement.
show normal perfusion and parenchymal enhancement.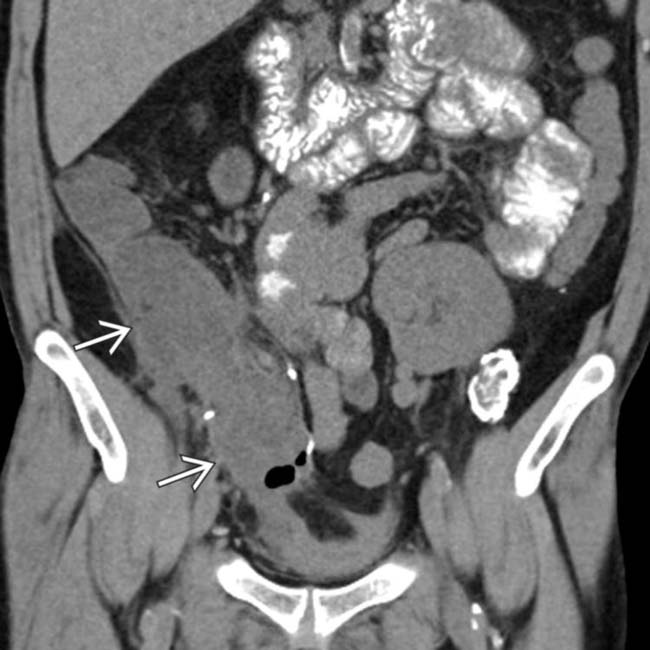
 to be enlarged and hypodense with adjacent fat stranding and induration. Based on the CT findings, this could represent either graft ischemia or pancreatitis.
to be enlarged and hypodense with adjacent fat stranding and induration. Based on the CT findings, this could represent either graft ischemia or pancreatitis.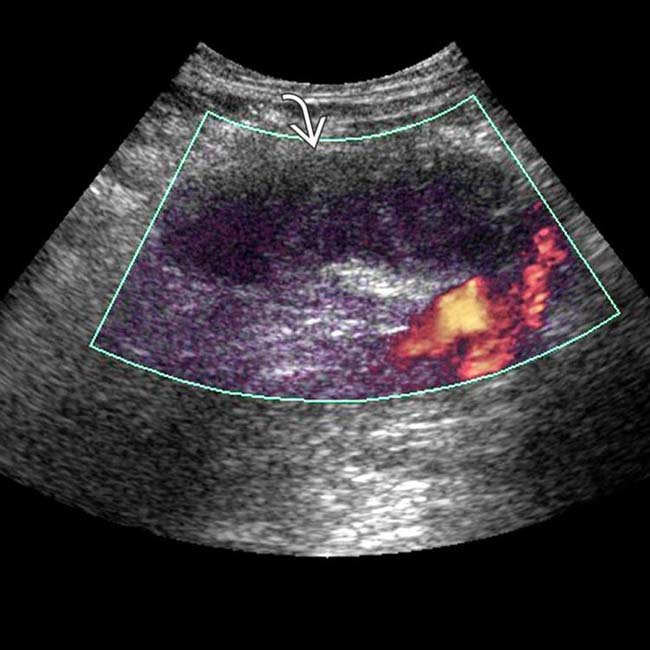
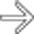
 to be enlarged and diffusely hypoechoic, without appreciable internal vascularity, compatible with infarction.
to be enlarged and diffusely hypoechoic, without appreciable internal vascularity, compatible with infarction.IMAGING
General Features
• Location
• Normal imaging appearance
 CT: IV contrast often not used due to renal toxicity and concurrent chronic renal failure
CT: IV contrast often not used due to renal toxicity and concurrent chronic renal failure
 CT: IV contrast often not used due to renal toxicity and concurrent chronic renal failure
CT: IV contrast often not used due to renal toxicity and concurrent chronic renal failure
– Homogeneous soft tissue mass closely associated with adjacent bowel (typically with adjacent suture line at duodenal stump)
• Imaging of major complications
 Allograft pancreatitis: Edema, enlargement, and heterogeneous enhancement of pancreas on CT and MR, typically with peripancreatic fluid
Allograft pancreatitis: Edema, enlargement, and heterogeneous enhancement of pancreas on CT and MR, typically with peripancreatic fluid
 Vascular complications: Venous thrombosis is more common than arterial
Vascular complications: Venous thrombosis is more common than arterial
 Postoperative hemorrhage: May be visualized on routine postoperative US, but full extent (and presence of active extravasation) best seen with CECT
Postoperative hemorrhage: May be visualized on routine postoperative US, but full extent (and presence of active extravasation) best seen with CECT
 Allograft pancreatitis: Edema, enlargement, and heterogeneous enhancement of pancreas on CT and MR, typically with peripancreatic fluid
Allograft pancreatitis: Edema, enlargement, and heterogeneous enhancement of pancreas on CT and MR, typically with peripancreatic fluid
 Vascular complications: Venous thrombosis is more common than arterial
Vascular complications: Venous thrombosis is more common than arterial
– Pseudoaneurysms and arteriovenous fistulae may be due to prior biopsy, pancreatitis, or surgical technique
 Postoperative hemorrhage: May be visualized on routine postoperative US, but full extent (and presence of active extravasation) best seen with CECT
Postoperative hemorrhage: May be visualized on routine postoperative US, but full extent (and presence of active extravasation) best seen with CECTUltrasonographic Findings
• Unable to distinguish among different causes of parenchymal abnormalities
PATHOLOGY
General Features
• Primary goal for pancreas transplantation is treatment of diabetes by restoring endogenous insulin secretion and preventing progression of diabetes complications
CLINICAL ISSUES
Presentation
Natural History & Prognosis
• Graft survival is better with combined pancreas-kidney transplant than with pancreas alone
• Graft pancreatitis is relatively common immediately after transplantation
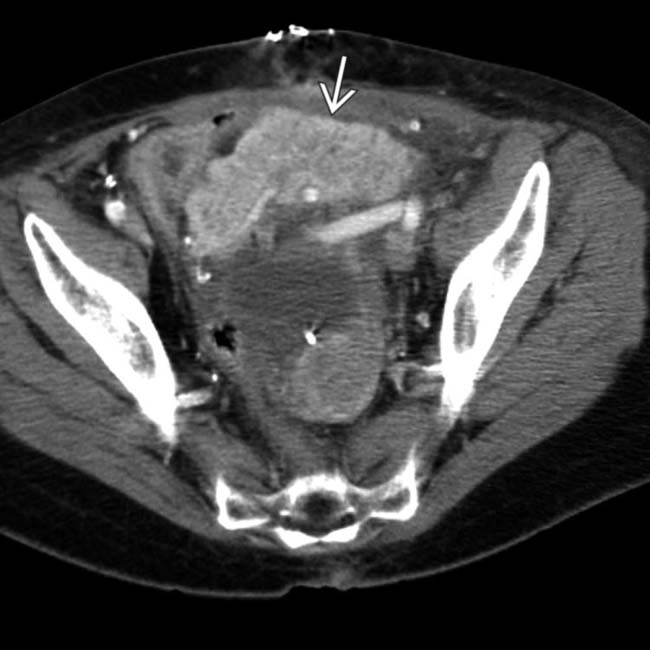
 with mild swelling of the gland and peripancreatic stranding, indicating mild pancreatitis, a finding seen frequently in the immediate post-transplant period.
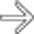
with mild swelling of the gland and peripancreatic stranding, indicating mild pancreatitis, a finding seen frequently in the immediate post-transplant period.
 , consistent with post-transplant pancreatitis. Note the normally enhancing transplanted kidney in the left lower quadrant
, consistent with post-transplant pancreatitis. Note the normally enhancing transplanted kidney in the left lower quadrant  .
.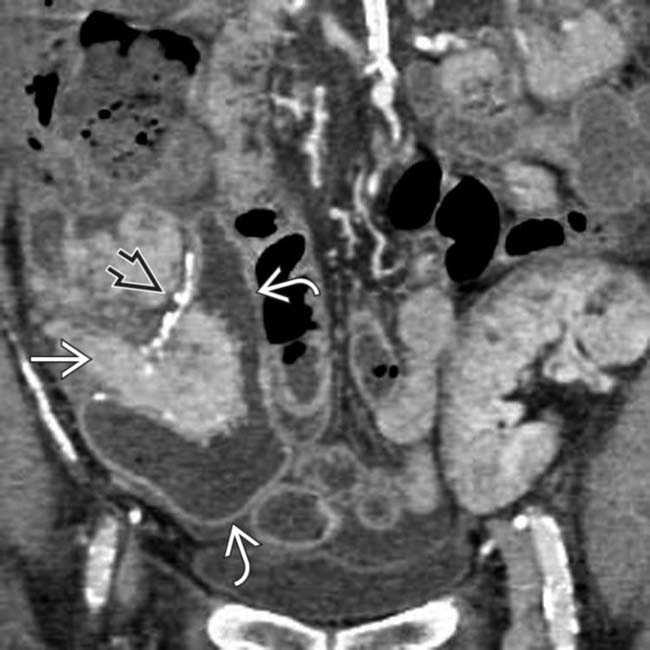
 surrounding the pancreas transplant
surrounding the pancreas transplant  . Note the communication between the fluid collection and the duodenum consistent with suture line dehiscence
. Note the communication between the fluid collection and the duodenum consistent with suture line dehiscence  . Emergent surgical drainage and repair was performed.
. Emergent surgical drainage and repair was performed.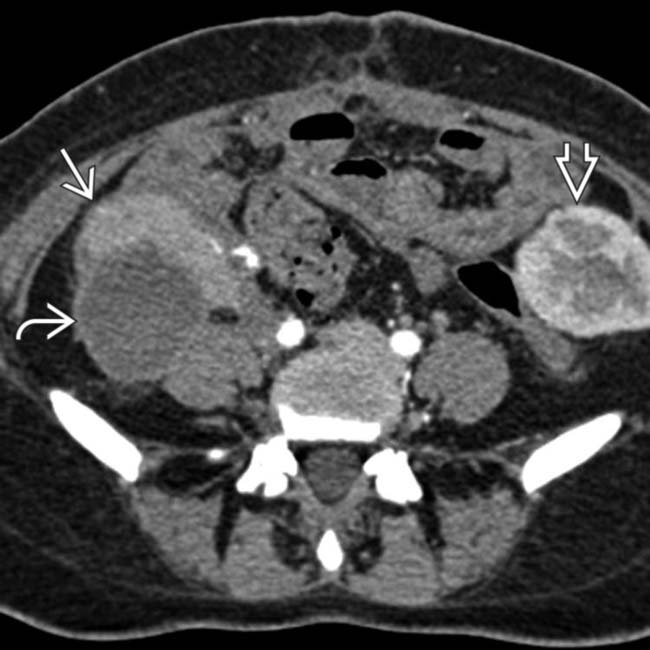
 adjacent to the transplant pancreas
adjacent to the transplant pancreas  in a patient with a history of pancreatitis, compatible with a pseudocyst. A transplant kidney is noted in the left lower quadrant
in a patient with a history of pancreatitis, compatible with a pseudocyst. A transplant kidney is noted in the left lower quadrant  .
.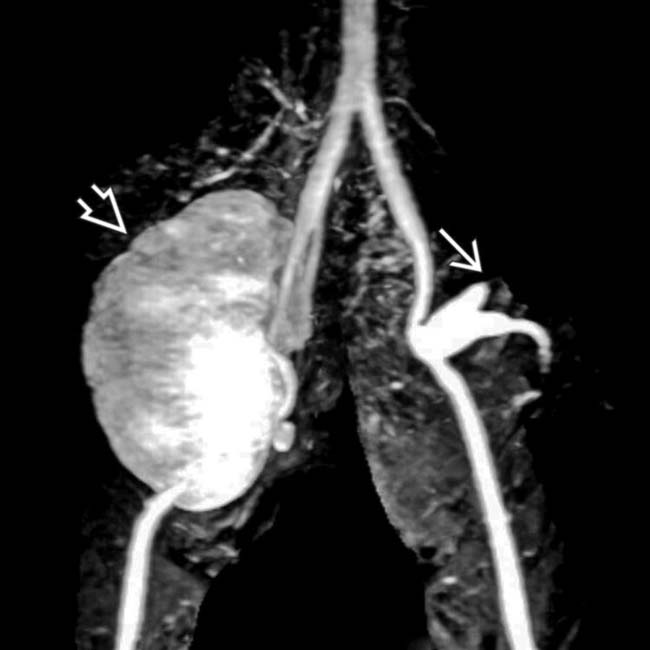
 , while the branching arterial supply to the pancreatic allograft
, while the branching arterial supply to the pancreatic allograft 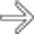 is totally occluded. The infarcted pancreatic allograft was then resected.
is totally occluded. The infarcted pancreatic allograft was then resected.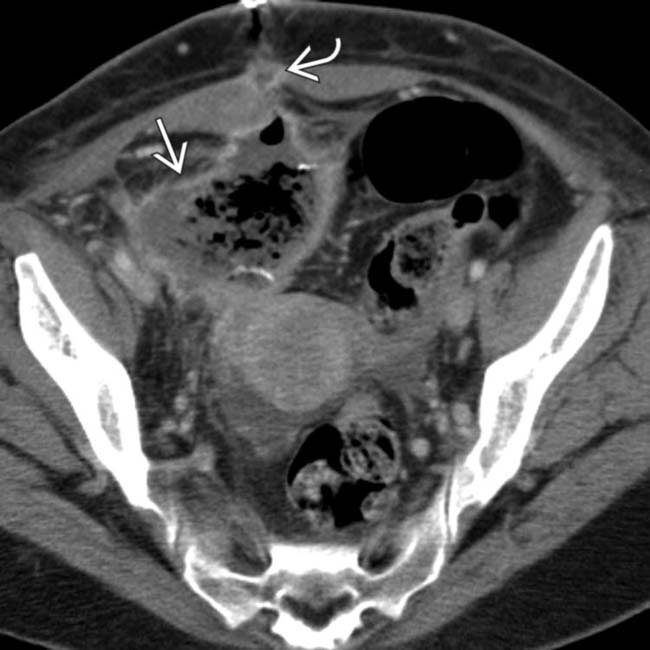
 replacing the pancreatic allograft in the right iliac fossa, with a fistulous tract
replacing the pancreatic allograft in the right iliac fossa, with a fistulous tract  to the skin. At resection, infected necrosis of the pancreatic allograft related to pancreatitis was noted.
to the skin. At resection, infected necrosis of the pancreatic allograft related to pancreatitis was noted.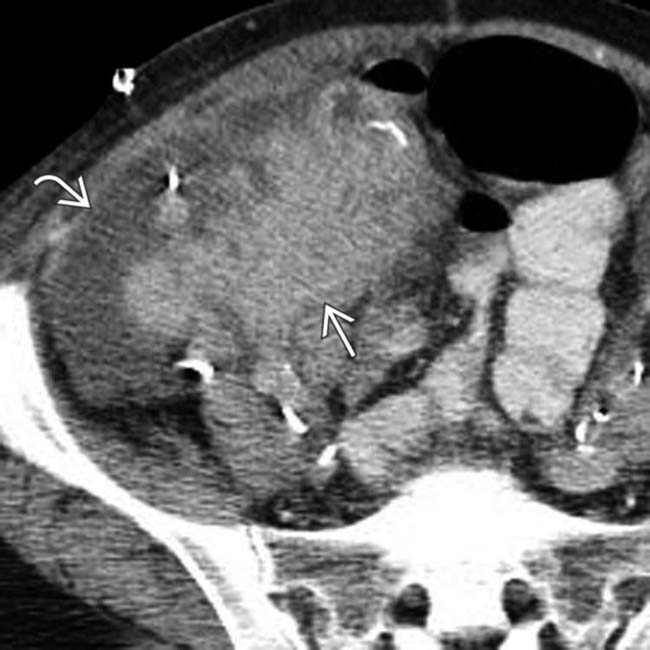
 and heterogeneous enhancement of the transplant pancreas
and heterogeneous enhancement of the transplant pancreas  . These findings are consistent with the clinical diagnosis of acute post-transplant pancreatitis. Unfortunately the pancreatitis was accompanied by graft rejection and this ultimately resulted in graft failure.
. These findings are consistent with the clinical diagnosis of acute post-transplant pancreatitis. Unfortunately the pancreatitis was accompanied by graft rejection and this ultimately resulted in graft failure.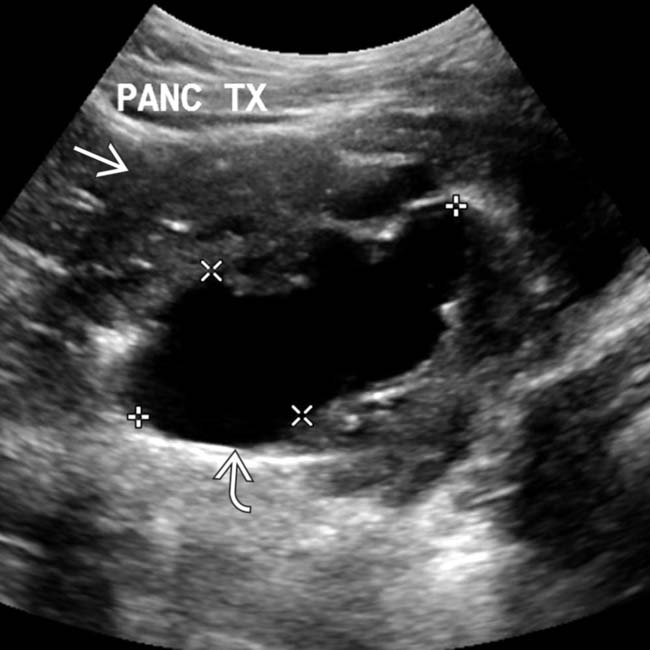
 adjacent to the transplant pancreas
adjacent to the transplant pancreas 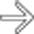 , representing a pseudocyst related to a prior bout of pancreatitis.
, representing a pseudocyst related to a prior bout of pancreatitis.
 , in keeping with global infarction.
, in keeping with global infarction.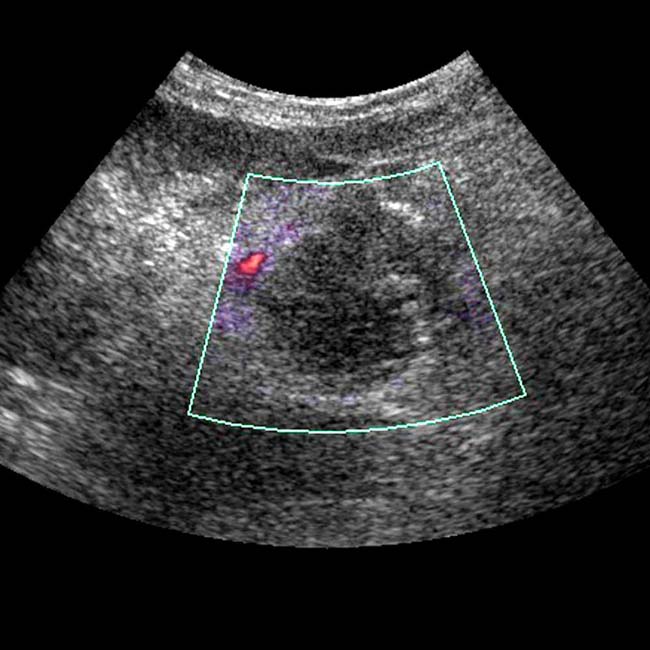
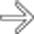 as an enlarged, hypoechoic structure with virtually no evidence of blood flow within it.
as an enlarged, hypoechoic structure with virtually no evidence of blood flow within it.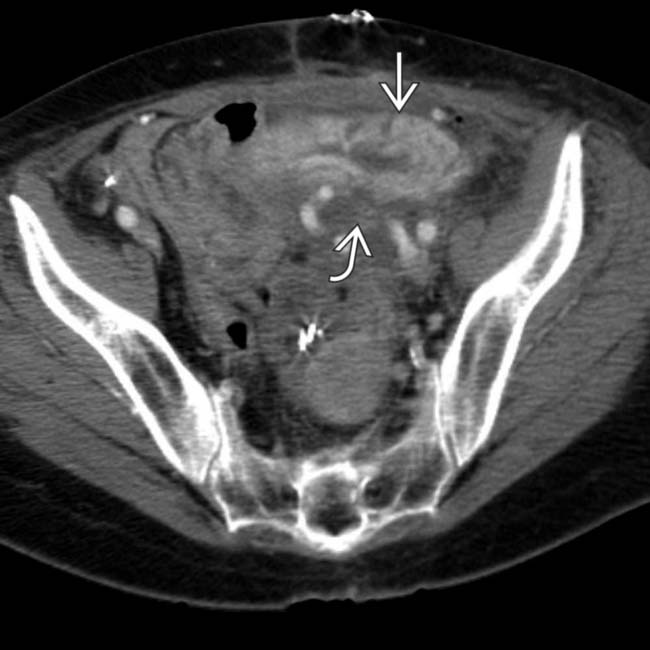
 in the immediate postoperative period. There is mild diffuse swelling of the allograft and soft tissue infiltration of the adjacent fat planes
in the immediate postoperative period. There is mild diffuse swelling of the allograft and soft tissue infiltration of the adjacent fat planes  . These findings are seen frequently in the immediate post-transplant period and represent the normal post-transplant CECT appearance of the allograft.
. These findings are seen frequently in the immediate post-transplant period and represent the normal post-transplant CECT appearance of the allograft.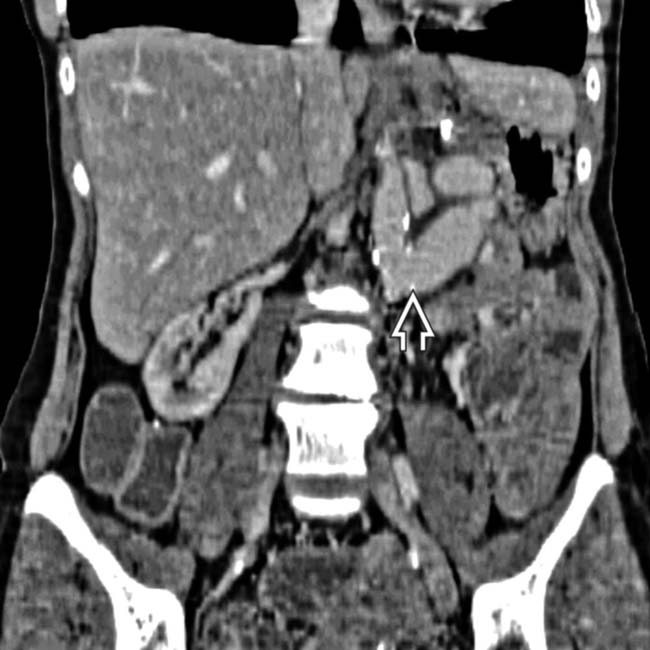
 with this vessel feeding the small bowel, liver, and pancreatic allografts. All of the allografts functioned well and the patient made an uneventful recovery.
with this vessel feeding the small bowel, liver, and pancreatic allografts. All of the allografts functioned well and the patient made an uneventful recovery.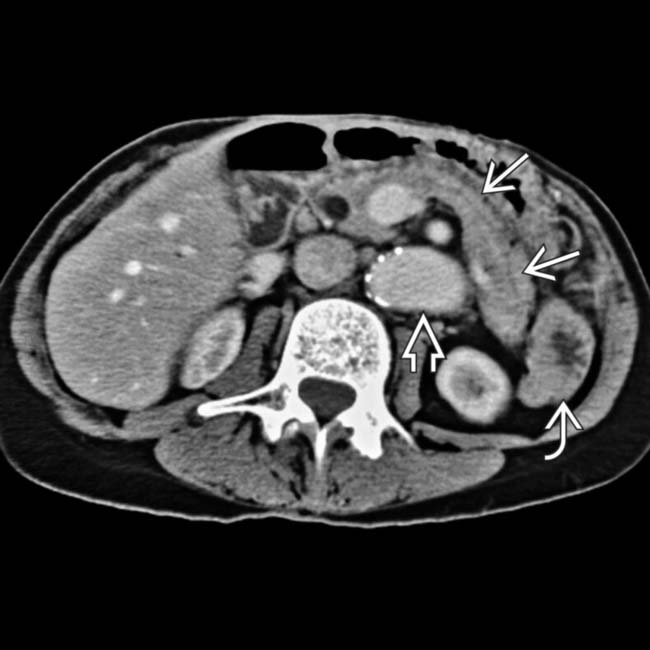
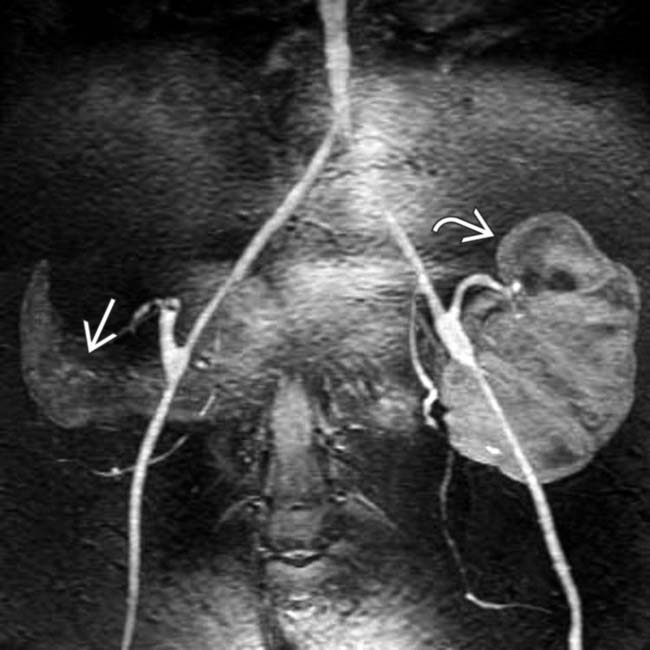
 and the transplanted pancreas
and the transplanted pancreas  , small bowel
, small bowel  , and liver, all of which enhance and function normally.
, and liver, all of which enhance and function normally.
































































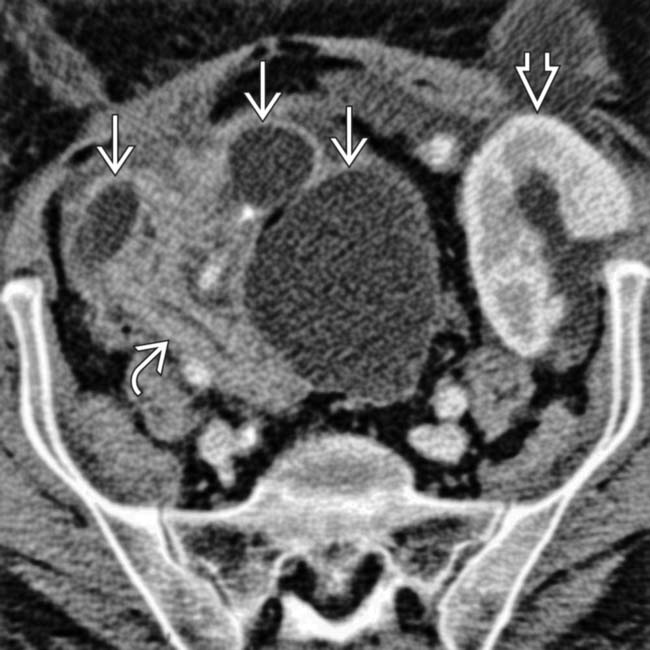
 and renal allograft
and renal allograft  in the iliac fossae. Both show normal parenchymal enhancement and no sign of infarction or rejection. There are several small and large pseudocysts
in the iliac fossae. Both show normal parenchymal enhancement and no sign of infarction or rejection. There are several small and large pseudocysts  near the pancreatic allograft. These were aspirated and drained with US guidance.
near the pancreatic allograft. These were aspirated and drained with US guidance.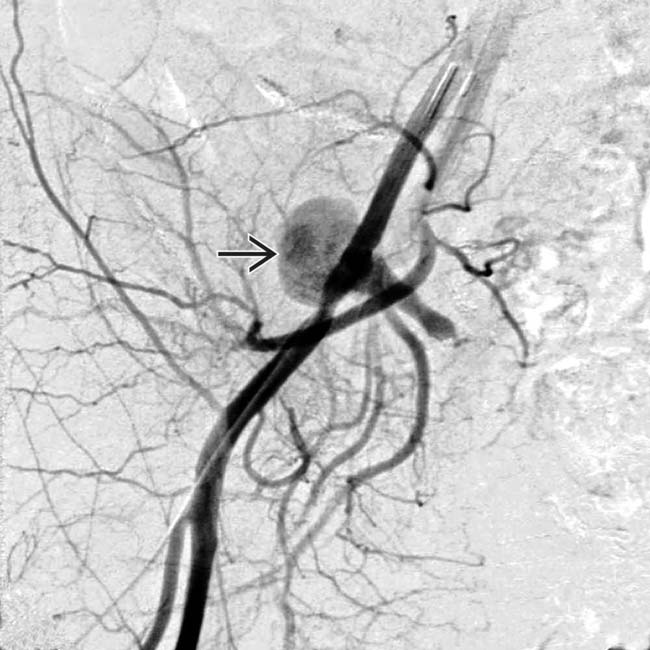
 at the site of the arterial anastomosis (iliac artery of donor to recipient internal iliac artery). This was treated with coil embolization.
at the site of the arterial anastomosis (iliac artery of donor to recipient internal iliac artery). This was treated with coil embolization.


