1. Dave, M, et al. Opportunistic infections due to inflammatory bowel disease therapy. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2014; 20(1):196–212.
2. Pariente, B, et al. Review article: why, when and how to de-escalate therapy in inflammatory bowel diseases. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2014; 40(4):338–353.
3. Curkovic, I, et al. Risks of inflammatory bowel disease treatment with glucocorticosteroids and aminosalicylates. Dig Dis. 2013; 31(3–4):368–373.
4. Florescu, DF, et al. Opportunistic viral infections in intestinal transplantation. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2013; 11(4):367–381.
5. Tonolini, M, et al. Acute HIV-related gastrointestinal disorders and complications in the antiretroviral era: spectrum of cross-sectional imaging findings. Abdom Imaging. 2013; 38(5):994–1004.
6. Werneck-Silva, AL, et al. Gastroduodenal opportunistic infections and dyspepsia in HIV-infected patients in the era of Highly Active Antiretroviral Therapy. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009; 24(1):135–139.
7. Hampton, DD, et al. Inflammatory bowel disease following solid organ transplantation. Clin Immunol. 2008; 128(3):287–293.
8. Ishida, T, et al. The management of gastrointestinal infections caused by cytomegalovirus. J Gastroenterol. 2003; 38(7):712–713.
9. Koh, DM, et al. Abdominal computed tomographic findings of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Mycobacterium avium intracellulare infection in HIV seropositive patients. Can Assoc Radiol J. 2003; 54(1):45–50.
10. Brantsaeter, AB, et al. CMV disease in AIDS patients: incidence of CMV disease and relation to survival in a population-based study from Oslo. Scand J Infect Dis. 2002; 34(1):50–55.
11. Hunter, PR, et al. Epidemiology and clinical features of Cryptosporidium infection in immunocompromised patients. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2002; 15(1):145–154.
12. Masur, H, et al. Guidelines for preventing opportunistic infections among HIV-infected persons—2002. Recommendations of the U.S. Public Health Service and the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Ann Intern Med. 2002; 137(5 Pt 2):435–478.
13. Oldfield, EC, 3rd. Evaluation of chronic diarrhea in patients with human immunodeficiency virus infection. Rev Gastroenterol Disord. 2002; 2(4):176–188.
14. Ukarapol, N, et al. Cytomegalovirus-associated manifestations involving the digestive tract in children with human immunodeficiency virus infection. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2002; 35(5):669–673.
15. von Reyn, CF, et al. Sources of disseminated Mycobacterium avium infection in AIDS. J Infect. 2002; 44(3):166–170.
16. Huh, JJ, et al. Mycobacterium avium complex peritonitis in an AIDS patient. Scand J Infect Dis. 2001; 33(12):936–938.
17. Pollok, RC. Viruses causing diarrhoea in AIDS. Novartis Found Symp. 2001; 238:276–283. [discussion 283-8].
18. Chamberlain, RS, et al. Ileal perforation caused by cytomegalovirus infection in a critically ill adult. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2000; 30(4):432–435.
19. Clemente, CM, et al. Gastric cryptosporidiosis as a clue for the diagnosis of the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Arq Gastroenterol. 2000; 37(3):180–182.
20. Wallace, MR, et al. Gastrointestinal manifestations of HIV infection. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2000; 2(4):283–293.
21. Drew, WL, et al. Cytomegalovirus: disease syndromes and treatment. Curr Clin Top Infect Dis. 1999; 19:16–29.
22. Lumadue, JA, et al. A clinicopathologic analysis of AIDS-related cryptosporidiosis. AIDS. 1998; 12(18):2459–2466.
23. Manabe, YC, et al. Cryptosporidiosis in patients with AIDS: correlates of disease and survival. Clin Infect Dis. 1998; 27(3):536–542.
24. Rossi, P, et al. Gastric involvement in AIDS associated cryptosporidiosis. Gut. 1998; 43(4):476–477.
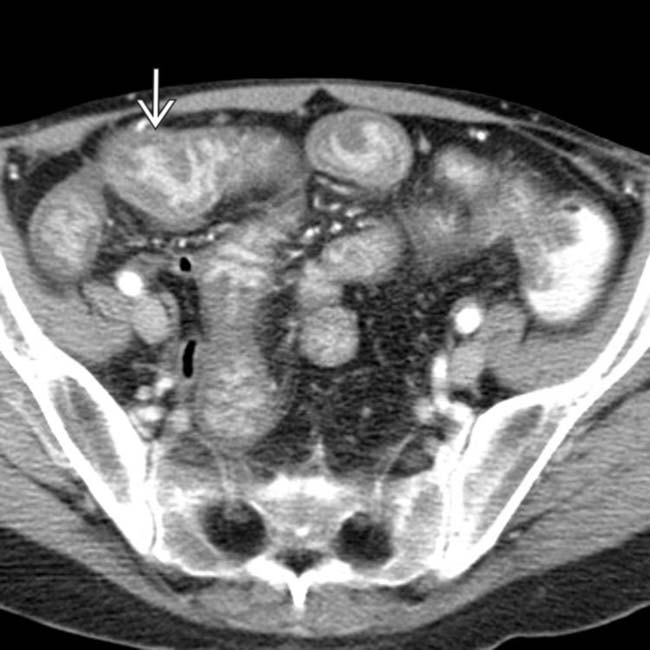
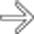 affecting most of the small bowel (SB).
affecting most of the small bowel (SB).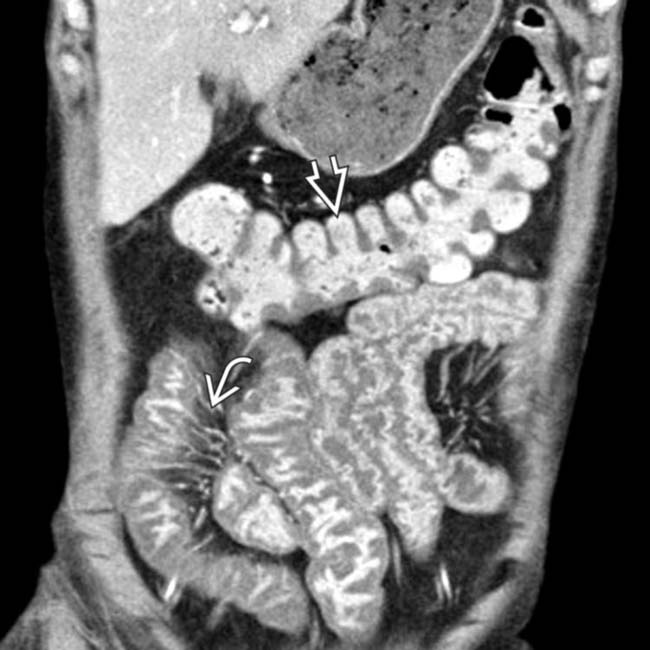
 . The colon
. The colon  is spared. Endoscopy and biopsy confirmed cytomegalovirus (CMV) enteritis.
is spared. Endoscopy and biopsy confirmed cytomegalovirus (CMV) enteritis.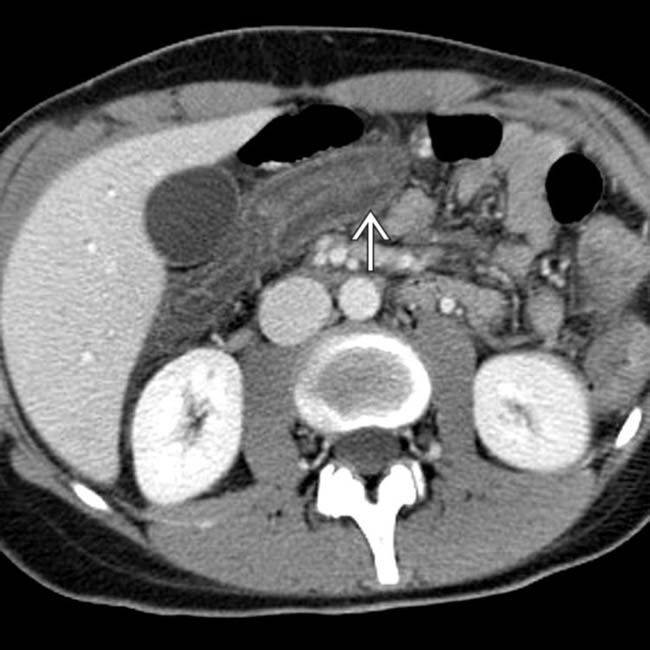
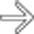 but no hyperenhancement of the mucosa.
but no hyperenhancement of the mucosa.
 , proven to be due to CMV, which may induce ischemic injury to both the SB and colon in immunocompromised patients.
, proven to be due to CMV, which may induce ischemic injury to both the SB and colon in immunocompromised patients. Cytomegalovirus (CMV): Mucosal hyper- or hypoenhancement; submucosal edema
Cytomegalovirus (CMV): Mucosal hyper- or hypoenhancement; submucosal edema
 Mycobacterial
Mycobacterial
 Cytomegalovirus (CMV): Mucosal hyper- or hypoenhancement; submucosal edema
Cytomegalovirus (CMV): Mucosal hyper- or hypoenhancement; submucosal edema
 Mycobacterial
Mycobacterial
 .
.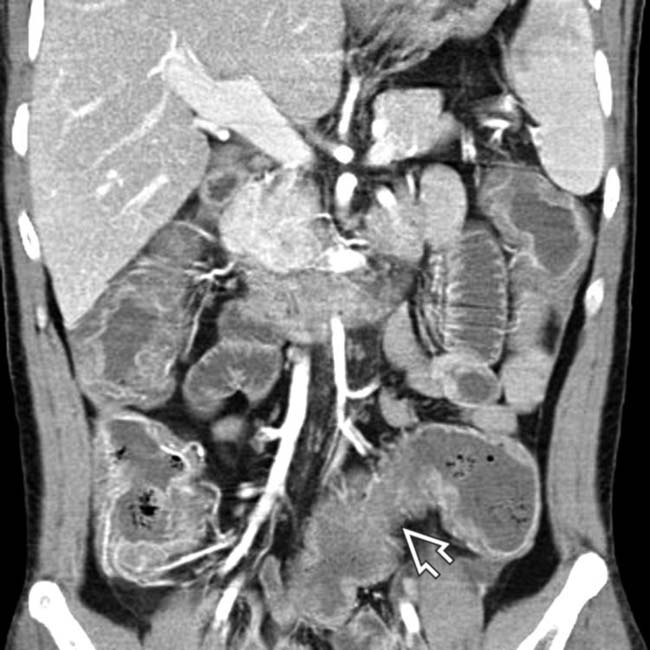
 . CMV colitis infects an immunocompromised host with a virus that causes vasculitis.
. CMV colitis infects an immunocompromised host with a virus that causes vasculitis.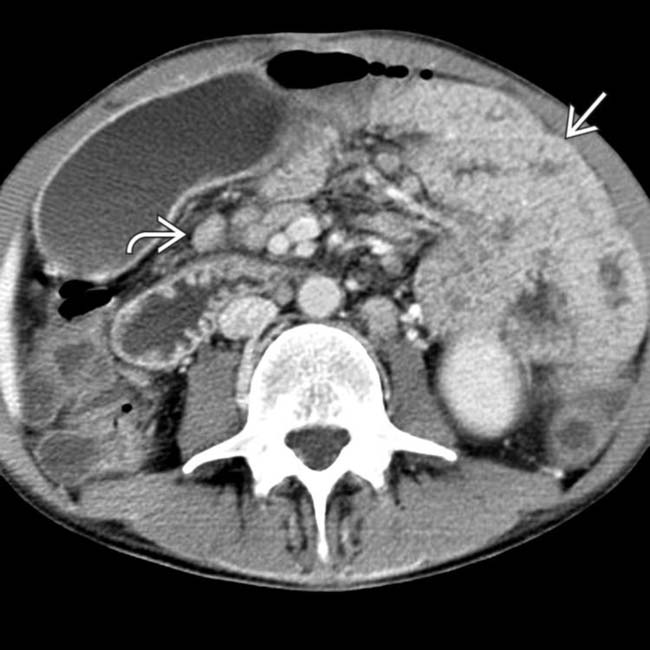
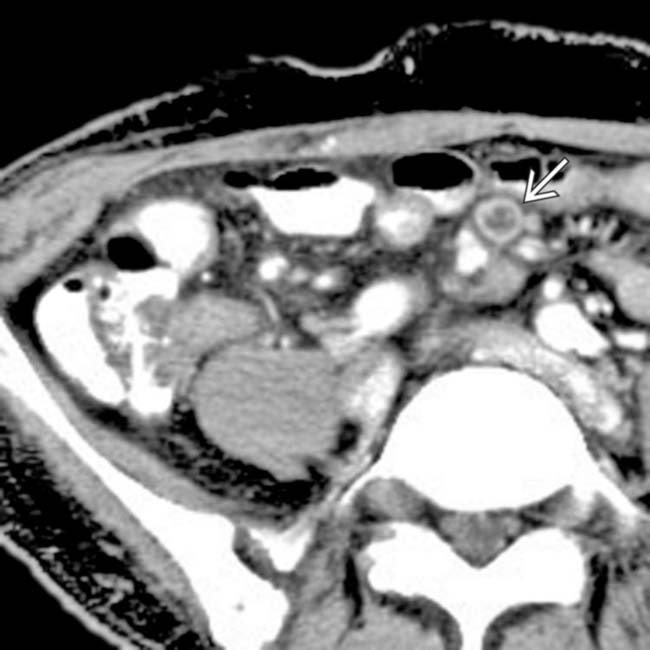
 and mesenteric adenopathy
and mesenteric adenopathy  .
.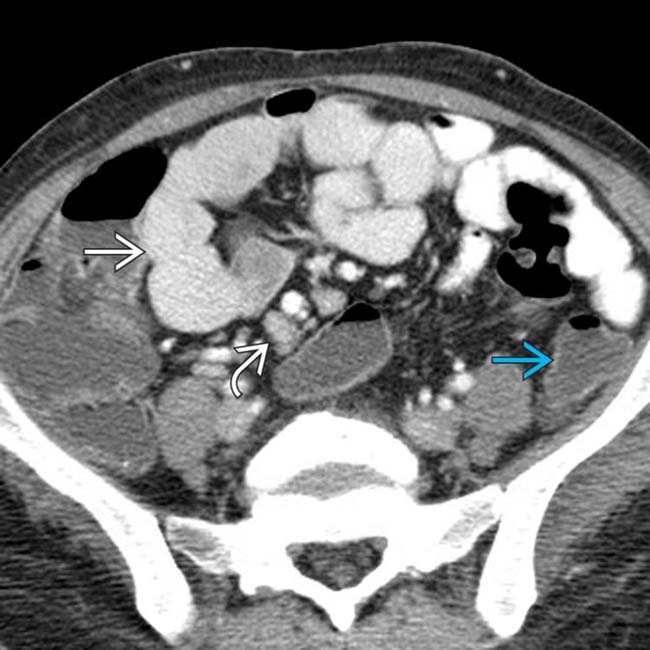
 and large bowel
and large bowel  , along with mesenteric lymphadenopathy
, along with mesenteric lymphadenopathy 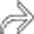 . Cryptosporidium was the causative organism and typically causes diarrhea.
. Cryptosporidium was the causative organism and typically causes diarrhea.
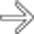 .
.
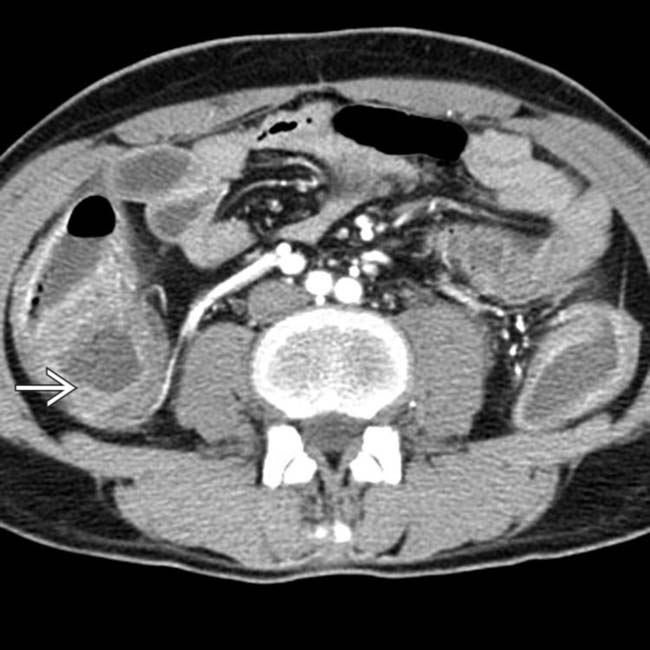
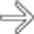
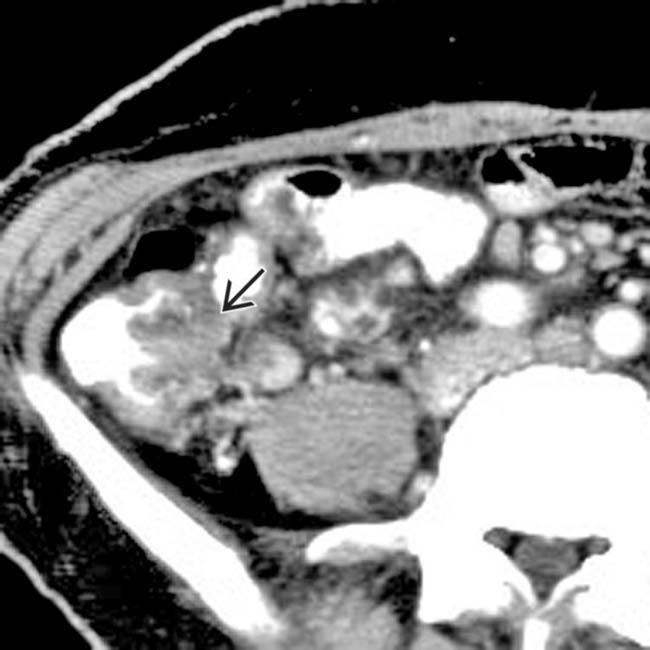
 and mesenteric edema. Note the atrophic native kidneys
and mesenteric edema. Note the atrophic native kidneys  . In spite of prompt diagnosis and treatment, the colitis progressed to perforation and emergency colectomy.
. In spite of prompt diagnosis and treatment, the colitis progressed to perforation and emergency colectomy.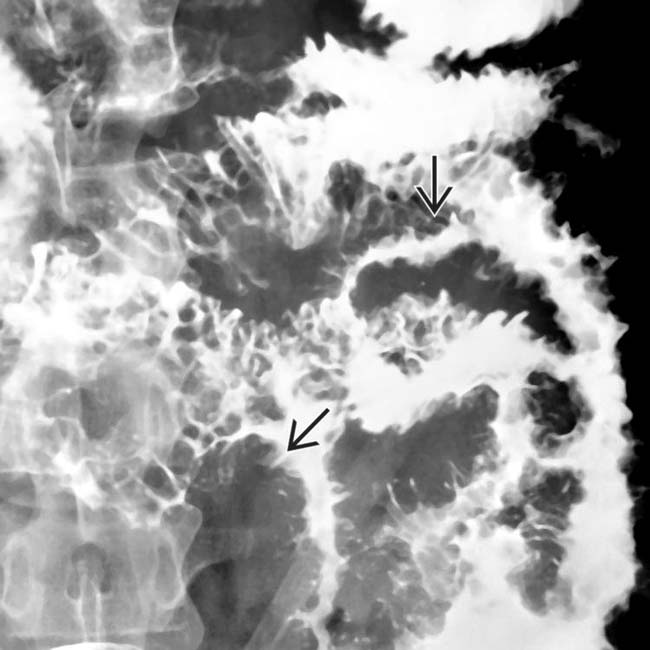
 in this patient with advanced cryptosporidiosis of the small bowel.
in this patient with advanced cryptosporidiosis of the small bowel.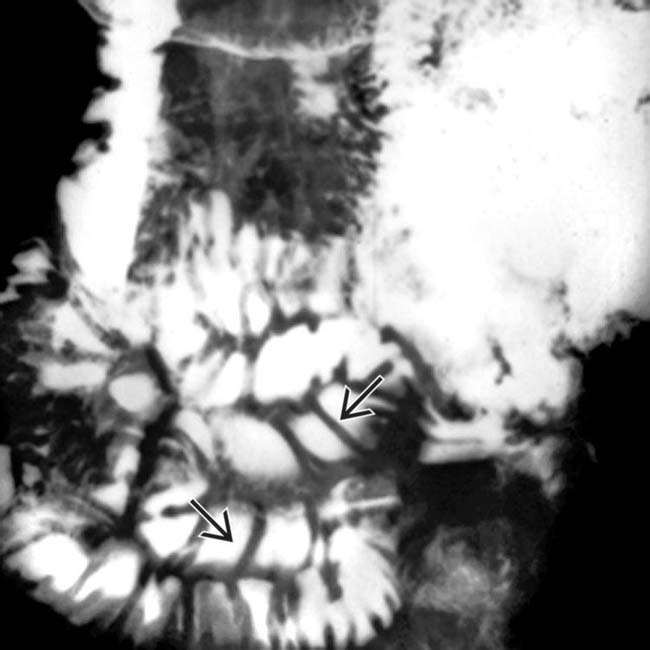
 in this patient with early cryptosporidiosis of the small bowel.
in this patient with early cryptosporidiosis of the small bowel.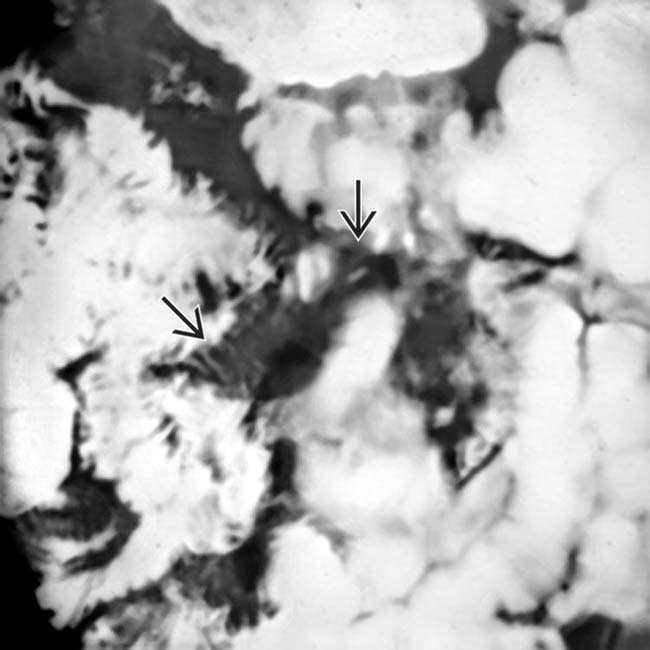
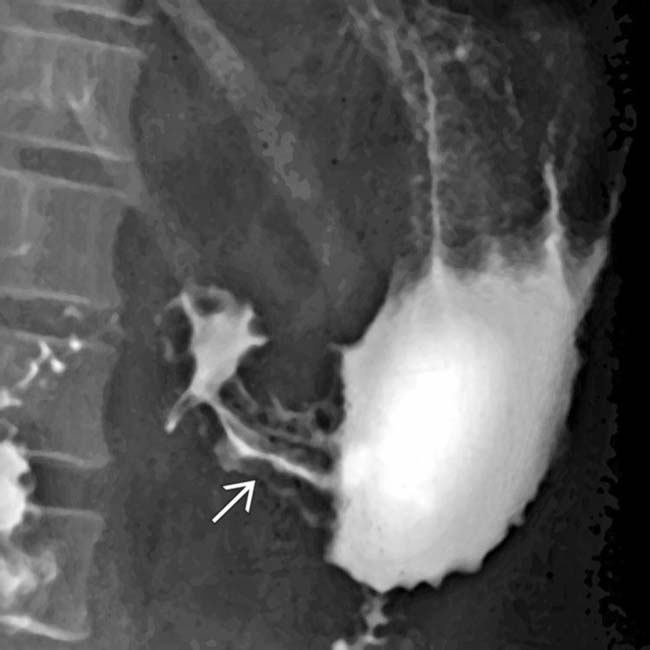
 .
.
 from antral CMV gastritis.
from antral CMV gastritis.













































































 .
.
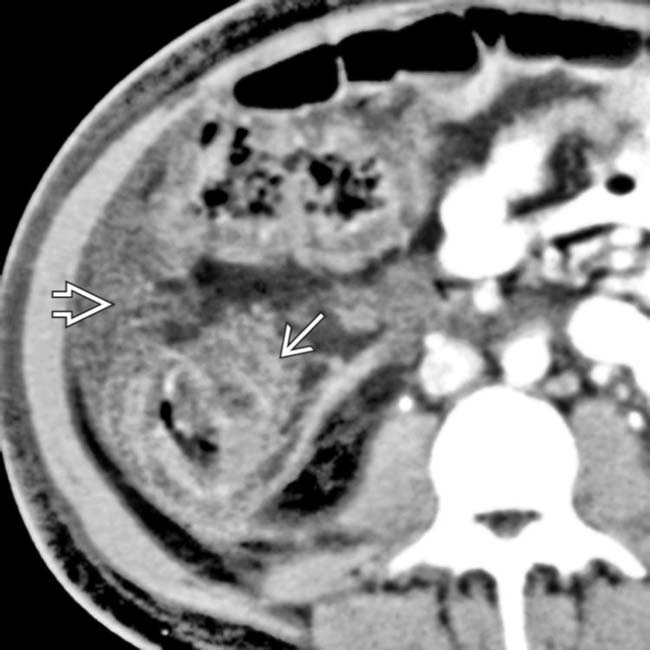
 .
.
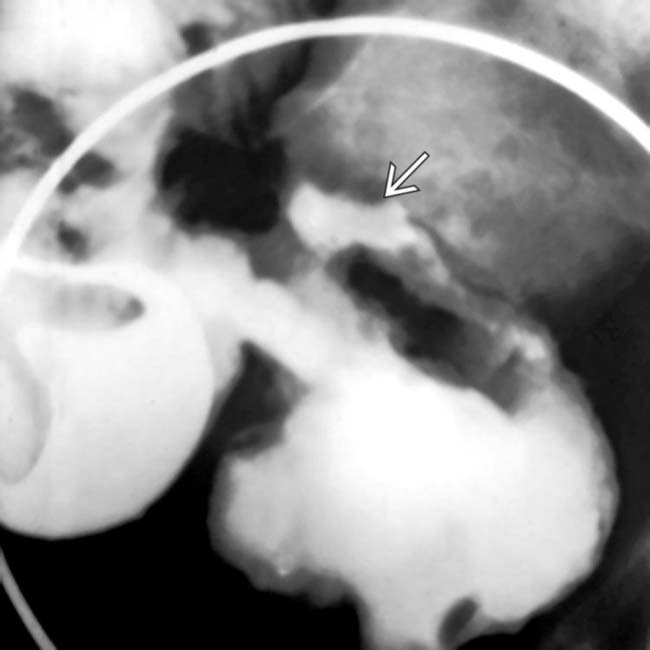
 with pericolonic soft tissue stranding
with pericolonic soft tissue stranding  .
.
 from CMV colitis.
from CMV colitis.


