One-lung ventilation and methods of improving oxygenation
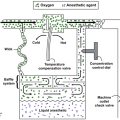
One-lung ventilation (OLV) is achieved through a double-lumen tracheal tube, through a single-lumen tracheal tube advanced into either the right or left mainstem bronchus, or by advancing a bronchial blocker though a single-lumen tracheal tube into one of the mainstem bronchi. Multiple indications for OLV are noted in Table 158-1.
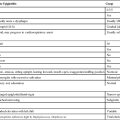
Table 158-1
Indications for One-Lung Ventilation
| Absolute | Relative |
| Video-assisted thoracoscopy Protective isolation (infection, hemorrhage) Differential ventilation (bronchopleural fistula) Pulmonary alveolar lavage |
Surgery on thoracic aorta or esophagus Pneumonectomy or lobar resection* |
*If one-lung ventilation is used, the surgical incision can be smaller because the deflation of the nondependent lung enables the surgeon to have better surgical access without a large thoracotomy incision.