Chapter 80 Neurological Problems of the Newborn
General Principles of Investigation and Management
Hypoxic-Ischemic Brain Injury in the Term Newborn
Hemorrhagic and Hypoxic-Ischemic Brain Injury in the Premature Newborn
Intraventricular Hemorrhage in the Term Newborn
Infections of the Central Nervous System
Mechanical Trauma to Extracranial, Central, and Peripheral Nervous System Structures
Neonatal Seizures
Seizures in newborns are rarely idiopathic and represent the most common feature of significant neurological disease in the neonate. Prompt recognition is essential because serious underlying diseases are often the cause of seizures. These diseases require treatment because they may interfere with supportive care such as ventilation and feeding. Experimental studies have shown a decrease in brain glucose concentration during prolonged seizures, an increase in brain lactate concentration, and excessive release of excitatory amino acids, which may interfere with deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) synthesis and subsequently with glial proliferation, differentiation, and myelination as well as increase in cerebral blood flow velocity (Jensen, 2009; Rennie and Boylan, 2007). Although the implications of these experiments for the human newborn are not entirely clear, their relevance is suggested by in vivo studies with magnetic resonance spectroscopy that demonstrate an association between abnormally low ratios of phosphocreatine to inorganic phosphate during seizures and long-term neurological sequelae.
Diagnosis
Seizure manifestations in newborns differ from those in older children in that newborns generally do not have well-organized, tonic-clonic seizures due to the immaturity of synaptic connections (Volpe, 2008). Table 80.1 summarizes the common types of neonatal seizures. The basis for classification should be a combination of clinical and electroencephalographic (EEG) abnormalities (Clancy, 2006). These seizure types are not specific for cause, but some are seen more often with certain underlying conditions. Tonic seizures, which may represent nonepileptic decerebrate posturing, occur in up to 50% of premature newborns with severe intraventricular hemorrhage (IVH). Focal clonic seizures in the term newborn are most commonly associated with focal cerebral infarction or traumatic injury, such as cerebral contusion.
| Neonatal Seizure Types | Clinical Manifestations | Age Distribution |
|---|---|---|
| Subtle | Eye deviation, blinking, fixed stare Repetitive mouth and tongue movements Apnea Pedaling, tonic posturing of limbs |
Premature and term |
| Tonic: focal or generalized | Tonic extension of limbs Tonic flexion of upper limbs, extension of legs |
Primarily premature |
| Clonic: multifocal or focal | Multifocal, clonic, synchronous, or asynchronous limb movements Nonordered progression Localized clonic limb movements Consciousness often preserved |
Primarily term |
| Myoclonic: focal, multifocal, or generalized | Single or several synchronous flexion jerks of upper more than lower limbs | Rare |
Determination of the Underlying Cause
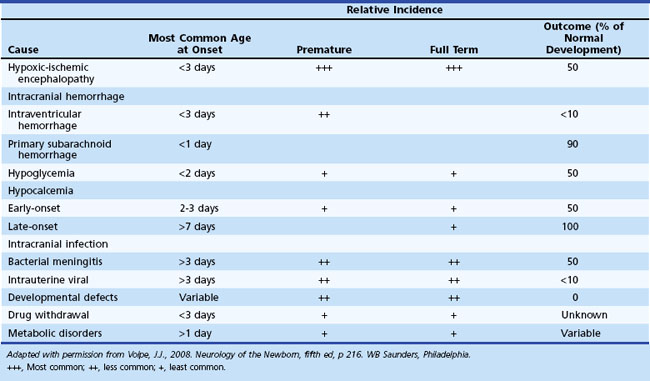
Diagnosis of the underlying cause allows specific treatment and a more precise prediction of outcome (Glass and Wu, 2009; Tekgul et al., 2006). Table 80.2 summarizes the major causes of neonatal seizures, their usual times of onset, and prognosis. Sometimes, several factors cause seizures (e.g., the combination of intracranial hemorrhage, metabolic derangement, and hypoxic-ischemic injury). Benign genetic epilepsies rarely have their onset in the neonatal period; the only example is benign familial neonatal epilepsy, an autosomal dominant trait for which two gene loci, KCNQ2 and KCNQ3, have been identified, which encode for voltage-gated potassium channels (Bellini et al., 2010).
Electroencephalography
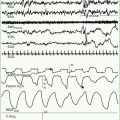
EEG, particularly continuous EEG monitoring when available, is a valuable aid in the diagnosis of neonatal seizures, especially in newborns paralyzed to assist ventilation and in those with suspected subtle seizures. Amplitude-integrated EEG is a more recent technique that may assist in detecting subtle and subclinical electrographic seizures (van Rooij et al., 2010). Concern exists that use of amplitude-integrated EEG criteria alone may lead to an overdiagnosis of neonatal seizures, so confirmation by standard EEG is advisable prior to treatment with anticonvulsants (Koh et al., 2010). EEG correlates of neonatal seizures are focal or multifocal spikes or sharp waves and focal monorhythmic discharges. Sharp transients are normal in premature newborns and should not be confused with seizure activity. Similarly, the trace alternant pattern of quiet sleep in normal term infants, in which normal low-amplitude reactivity is preserved between bursts, must be distinguished from the abnormal burst-suppression pattern, in which long periods of voltage suppression or absence of activity are recorded between bursts of high-voltage spikes and slow waves (Lamblin et al., 2010).
Management
Neonatal seizures require urgent treatment. Once adequate ventilation and perfusion are established, the blood glucose concentration is measured. If the glucose concentration is low, 10% dextrose should be administered in a dose of 2 mL/kg. In the absence of hypoglycemia, immediate treatment should be started with anticonvulsant medication, as outlined in Table 80.3. Studies for other underlying causes should proceed concurrently and specific treatment initiated whenever possible.
| I. Ensure adequate ventilation and perfusion. II. Begin therapy for specific metabolic disturbances (if present). |
||
| Acute Therapy | Maintenance Therapy | |
| Hypoglycemia: glucose (10% solution) | 2 mL/kg IV (0.2 g/kg) | Up to 8 mg/kg/min IV |
| Hypocalcemia: calcium gluconate (5% solution) | 4 mL/kg IV (monitor cardiac rhythm) | 500 mg/kg/24 h PO |
| Hypomagnesemia: magnesium sulfate (50% solution) | 0.2 mL/kg IM | 0.2 mL/kg/24 h IM |
| Pyridoxine deficiency: pyridoxine | 50-100 mg IV | 100 mg PO daily for 2 wk |
| III. Begin anticonvulsant therapy. | ||
| Acute Therapy | Maintenance Therapy (Begin 12 h After Loading Dose) |
|
| Phenobarbital | 20 mg/kg IV; if necessary, additional 5-25 mg/kg IV in 5 mg/kg aliquots | 4-6 mg/kg/24 h IV/IM/PO |
| Phenytoin* | 2 doses of 10 mg/kg IV, diluted in normal saline (monitor cardiac rate and rhythm) | 5-10 mg/kg/24 h IV |
| Lorazepam or midazolam continuous infusion | 0.05-0.10 mg/kg IV 1.5 µg/kg/min (ICU) |
|
IM, Intramuscularly; IV, intravenously; PO, orally.
* Fosphenytoin is an alternate form of phenytoin that may be used.
Phenobarbital alone controls seizures in most newborns after administering adequate dosages (up to a maximum of 40 mg/kg loading dose). Give phenytoin, 20 mg/kg, if seizures continue. Evaluation of fosphenytoin in the newborn, which is converted to phenytoin, is presently unknown, but initial data suggest that the rate of conversion is identical to that shown for older infants. Unfortunately, seizures are often incompletely controlled by phenobarbital and phenytoin (Jensen, 2009). When these drugs fail, other anticonvulsants (benzodiazepines: midazolam, lorazepam, levetiracetam, and topiramate) may be effective. These are not recommended as first-line drugs (Bassan et al., 2008; Jensen, 2009; Rennie and Boylan, 2007).
Pyridoxine deficiency, a rare cause of neonatal seizures, should be considered whenever no other cause is determined. Most infants have an unusual paroxysmal pattern on EEG, with generalized bursts of synchronous high-voltage activity of 1- to 4-Hz intermixed spikes and sharp waves. The diagnosis of pyridoxine deficiency is not excludable based on lack of response to a single large dose of intravenous (IV) pyridoxine with concurrent EEG recording; rather, large doses (50-100 mg daily) should be given orally for several days (Mills et al., 2010).
Specific metabolic disorders require specific therapeutic considerations with rapid intervention to maximize the chance of a good outcome (Pearl, 2009). Glut-1 deficiency syndrome is another rare cause of seizures and major developmental delay associated with hypoglycorrhachia, which may have implications for treatment in that the ketogenic diet may be most effective for control of seizures (Moers et al., 2002).
Duration of Treatment and Outcome
The optimal duration of maintenance therapy for neonatal seizures is unknown. The duration of maintenance treatment for neonatal seizures depends on the risk for recurrence, underlying cause (see Table 80.3), results of the neurological examination, and EEG findings (Glass and Wirrell, 2009). Phenytoin should be discontinued when stopping IV therapy because adequate serum levels are difficult to maintain with oral phenytoin in the newborn. If seizures have stopped and the neurological examination and EEG are normal, phenobarbital should be discontinued before discharge from the hospital. If continuing phenobarbital after discharge, discontinuation should be considered as early as 1 month later based on the neurological status and EEG. Discontinuing zphenobarbital should be considered in an infant whose examination is not normal if EEG does not show epileptiform activity. The potential deleterious effects of phenobarbital on brain development are a concern. Infants should be treated with phenobarbital for the briefest possible time.
Hypoxic-Ischemic Brain Injury in the Term Newborn
Hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy results from reduced oxygen delivery to the brain and from the excessive accumulation of metabolites such as lactate, free radicals, and excitotoxic amino acids. It is a major cause of morbidity and mortality in both premature and term infants. Hypoxic-ischemic cerebral injury in the premature newborn is discussed later with IVH (see Hemorrhagic and Hypoxic-Ischemic Brain Injury in the Premature Newborn). In this section, we discuss only hypoxic-ischemic injury in the term newborn. Chapter 61 provides a rational approach to the diagnosis and management of neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Because most hypoxic-ischemic brain injury in term infants occurs antepartum and intrapartum, prevention depends principally on optimal obstetrical management. Advances in intrapartum monitoring such as fetal heart rate monitoring, assessment of fetal movements, and the use of the biophysical profile and scalp blood gases may result in earlier diagnosis and decrease in incidence of severe hypoxic-ischemic brain injury.
Diagnosis
Because asphyxia is mainly an intrauterine event, careful documentation of maternal risk factors and abnormalities of labor and delivery are important. An accurate history also may provide precise information about the type of insult as well as its severity, duration, and timing, which in turn determines in large part the specific pattern of brain injury. Acute, total, or near-total asphyxia may cause disproportionate injury to thalami, basal ganglia, and brainstem nuclei, whereas prolonged partial asphyxia causes injury principally to the cerebral cortex and subcortical white matter (Miller et al., 2005; Roland et al., 1998).
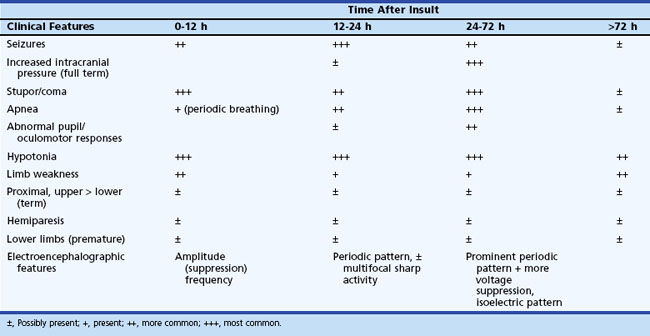
The initial clinical features of severe hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy include depressed level of consciousness, periodic breathing (due to bilateral hemisphere dysfunction), hypotonia, and seizures. When the hypoxic-ischemic insult is of the acute/near-total type, brainstem dysfunction may be a prominent feature. Between 24 and 72 hours of age, the level of consciousness, seizures, apnea, and other brainstem abnormalities become more prominent, which also correspond to the timing of maximum intracranial pressure. After 72 hours, infants who survive show continued (although diminishing) stupor, abnormal tone, and brainstem dysfunction, with disturbances of sucking and swallowing. Specific patterns of weakness related to the distribution of neuronal injury may become evident (Table 80.4). Table 80.5 summarizes the temporal profile of clinical features of severe hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy in the term newborn.
Table 80.4 Neuropathological Patterns of Neonatal Hypoxic-Ischemic Brain Injury and Clinical Correlation
| Pattern of Injury | Neuropathological Injury | Clinical Features in Neonatal Period |
|---|---|---|
| Cortical/subcortical watershed | Cortex, subcortical white matter Brainstem nuclei, thalamus, basal ganglia |
Term: coma, seizures, hypotonia Term > premature: oculomotor abnormalities, abnormal sucking, swallowing |
| Thalamic/basal ganglia | Cerebral cortex, subcortical white matter in parasagittal regions | Term: proximal limb weakness, upper > lower |
| White matter injury of prematurity | Periventricular and diffuse white matter | Premature: unknown (probably lower limb weakness) |
| Focal/multifocal | Unilateral or bilateral cerebral cortex and subcortical white matter | Premature and term: variable hemiparesis/quadriparesis, stereotyped, nonhabituating reflex responses |
Electroencephalography and Cortical Evoked Responses
The usefulness of the visual, auditory, and somatosensory evoked responses in the diagnosis and prognosis of hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy is more limited (see Chapter 32A), although there may be a role for visual evoked responses in the diagnosis of periventricular leukomalacia (PVL) and for auditory evoked responses in the diagnosis of brainstem injury.
Metabolic Biomarkers
Hypoglycemia, hypocalcemia, hyponatremia (inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion), and lactic acidosis may contribute to the neurological syndrome of hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Uncorrected metabolic derangements may worsen the cerebral injury (Hanrahan et al., 1998).
Neuroimaging
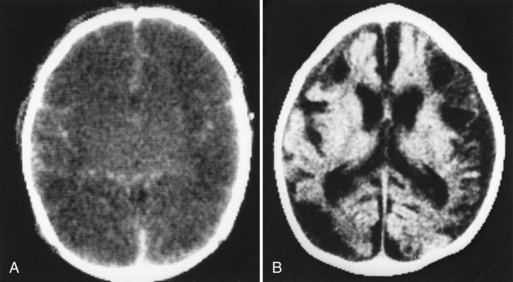
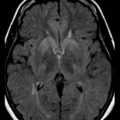
Neuroimaging has major value for locating and quantifying cerebral injury. MRI in the term newborn and US and MRI in the premature newborn are especially valuable. Although MRI has superseded CT in many instances, CT still has a role in the assessment of acute hypoxic-ischemic brain injury, especially in term newborns unable to tolerate the prolonged scanning time required with MRI (Chau et al., 2009). CT performed between 3 and 5 days of age may show decreased attenuation. More precise anatomical delineation of mild brain injury or selective involvement of thalamus and basal ganglia or cerebellum may be assessed more accurately by MRI (Rutherford et al., 2010) (Fig. 80.1). More advanced MRI techniques may prove especially useful (e.g., diffusion tensor imaging, functional MRI, diffusion tractography) (Counsell et al., 2010; Miller and Ferreiro, 2009).
Several techniques may also provide additional insight into the functional disturbances of newborn hypoxic-ischemic cerebral injury. For example, positron emission tomography, single-photon emission computed tomography, and near-infrared spectroscopy show disturbances of cerebral perfusion, and magnetic resonance spectroscopy shows decreased brain levels of high-energy phosphates in asphyxiated infants (Barkovich et al., 2006).
Hypothermia
Therapeutic active or passive cerebral hypothermia of 33°C to 35°C initiated early during the “latent phase” of hypoxic-ischemic brain injury (within 8 hours after insult) shows great promise for providing lasting neuroprotection as well as prolonging the latent phases of injury and delaying the onset of secondary energy failure, thereby hopefully lengthening the window of time when additional beneficial interventions may be initiated (Roland, 2008). Despite unanswered questions about the efficacy and safety of specific cooling protocols, therapeutic cooling, which decreased mortality and improved neurodevelopmental outcome in survivors (Jacobs et al., 2007), is emerging as one of the most promising options for neuroprotection in asphyxiated term newborns with moderate to severe hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy.
Prognosis
Severe hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy is associated with significant injury. Following a prolonged partial insult, there is often widespread injury involving the cortex and subcortical white matter, and subsequent clinical features are microcephaly, mental retardation, seizures, and spastic quadriparesis (see Chapter 61). When injury is less severe, it affects primarily the parasagittal watershed regions, which may cause shoulder weakness. Acute near-total hypoxic-ischemic insult of brief duration results in injury to the brainstem, thalami, and basal ganglia, often associated with brainstem dysfunction and feeding difficulties and later onset of choreoathetosis (dystonic or mixed cerebral palsy). Unilateral focal lesions result principally in hemiplegia with cognitive difficulties and possibly epilepsy
Selected aspects of the neurological syndrome and neurodiagnostic studies are helpful in determining outcome in hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (Box 80.1). Because most instances of hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy begin before birth, assessment of fetal well-being in utero is useful. Apgar scores at 1 and 5 minutes are notoriously unreliable because of interobserver variability, the effects of drugs given to the mother before delivery, and the stress of delivery, which may be reversible. In contrast, low extended Apgar scores after 10 minutes may suggest that a major prior insult has occurred.
Hemorrhagic and Hypoxic-Ischemic Brain Injury in the Premature Newborn
Periventricular-intraventricular hemorrhage (PIVH) occurs in approximately 20% of premature newborns with birth weight less than 1500 g but may be as high as 45% in smaller, sicker newborns of birth weight 500 to 750 g. PIVH occurs on the first day in 50% of affected premature newborns and before the fourth day in 90%. PIVH originates from rupture of small vessels in the subependymal germinal matrix. Approximately 80% of germinal matrix hemorrhages extend into the ventricular system. Hemorrhagic lesions in the cerebral parenchyma often accompany severe hemorrhages in the ventricular system. Parenchymal hemorrhages are usually unilateral and result from hemorrhagic venous infarction in the periventricular region (Bassan et al., 2006; Volpe, 2008).
Diagnosis
The high incidence of PIVH in premature infants has led to the routine use of US scanning at 3 to 4 days in all newborns of less than 32 weeks’ gestation. CT and MRI are also informative, but US is generally considered to be the technique of choice because it can be performed noninvasively in the intensive care nursery, and no ionizing radiation is involved. CT and MRI remain the techniques of choice for demonstration of epidural, subdural, and subarachnoid hemorrhage, as well as most intracerebral and posterior fossa hemorrhages (Dyet et al., 2006).
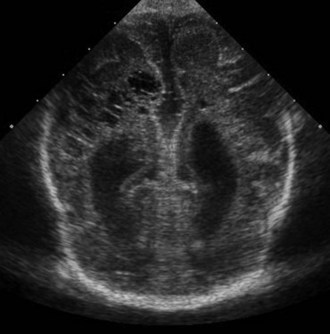
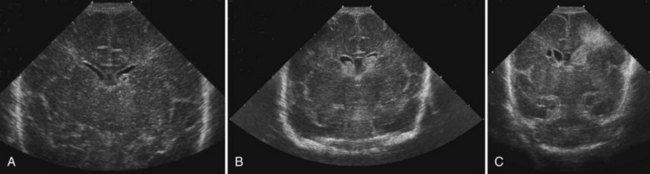
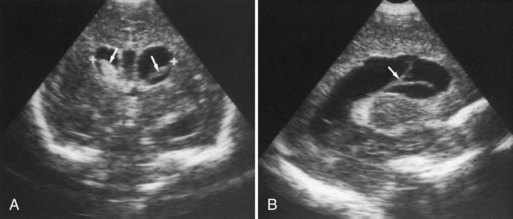
CT has limited value in assessing acute hypoxic-ischemic cerebral injury in premature newborns because the immature brain has high water content, and low tissue attenuation is a normal feature. Routine US scans reveal PVL in premature newborns by increased echogenicity in the periventricular regions during the first days of life and subsequent cyst formation in the same areas after the first several weeks (Fig. 80.2). Although PIVH may be diagnosed with CT, cranial ultrasonography is the technique of choice for diagnosis of intraventricular hemorrhage and PIVH (Fig. 80.3). The ability of US to distinguish between hemorrhagic and ischemic injury (see Fig. 80.3), and to reliably identify mild or diffuse injury in the white matter is limited. MRI performed at term shows increased signal in cerebral white matter on T2-weighted images. Diffusion-weighted MRI may demonstrate diffuse white matter injury even earlier than conventional MRI (Inder et al., 1999). After the neonatal period, PVL is demonstrable by CT or MRI.
Pathogenesis and Management
Table 80.6 summarizes the current concepts of pathogenesis and management of PIVH. Fluctuations of cerebral blood flow are a major factor in the pathogenesis of PIVH.
Table 80.6 Pathogenesis and Management of Periventricular-Intraventricular Hemorrhage
| Pathogenesis | Management |
|---|---|
| INTRAVASCULAR FACTORS | |
| Fluctuating cerebral blood flow | Paralysis of ventilated preterm infants with pancuronium bromide |
| Increases in cerebral blood flow |
Avoidance of systemic hypertension associated with routine handling and rapid volume expansion, exchange transfusions, colloid infusions, seizures, pneumothorax Decreases in cerebral blood flow Increases in cerebral venous pressure and flow Avoidance of systemic hypotension Avoidance of prolonged labor and difficult vaginal delivery Avoidance of pneumothorax, positive pressure ventilation; minimal handling |
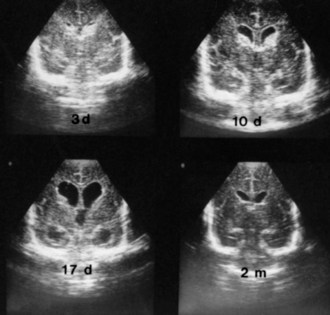
Serial US scans and measurements of head circumference are needed in every newborn with PIVH for early diagnosis of the development of posthemorrhagic hydrocephalus (Fig. 80.4), which may be caused by arachnoiditis in the posterior fossa or aqueductal obstruction. Significant ventriculomegaly may precede measurable increases in head circumference. Factors that influence the management of posthemorrhagic hydrocephalus are the rate of progression, ventricular size, and intracranial pressure. In approximately 50% of premature newborns with posthemorrhagic hydrocephalus, ventriculomegaly arrests or resolves spontaneously without intervention, usually within 4 weeks (see Fig. 80.4). In the other 50%, dilatation progresses beyond 4 weeks and requires intervention. However, rapid ventricular enlargement with clinical evidence of increased intracranial pressure requires intervention at any time. The definitive treatment is placement of a ventriculoperitoneal shunt, but often, temporary CSF drainage by external ventriculostomy or placement of a ventricular catheter with subcutaneous reservoir or subgaleal shunt is helpful. Placement of a ventriculoperitoneal shunt in infants with rapidly progressive hydrocephalus is required, despite the morbidity associated with shunt placement in small, premature infants.
Prognosis
The prognosis after PIVH relates to the severity of hemorrhage and to the concomitant hypoxic-ischemic cerebral injury (Bassan et al., 2006; Dyet et al., 2006; Hamrick et al., 2004). Germinal matrix hemorrhage alone is rarely a cause of significant neurological morbidity. The prognosis after finding blood in the ventricles is relatively good unless ventricular dilation occurs. Newborns with severe ventricular dilatation and intraparenchymal hemorrhage may die in the neonatal period, and most survivors develop posthemorrhagic hydrocephalus. Prognosis does not always correlate with the severity of PIVH and posthemorrhagic hydrocephalus; hypoxic-ischemic parenchymal injury, principally PVL, is a major determinant of outcome. However, PVL may be more difficult to document radiologically (Hamrick et al., 2004; Ment et al., 1999).
Intraventricular Hemorrhage in the Term Newborn
Although IVH is primarily a lesion of the premature newborn, it occurs in approximately 3.5% of healthy term newborns. The pathogenesis of major IVH in term newborns is similar to that in premature infants in that hypoxia and trauma are relevant factors in approximately 50% of infants. However, traumatic delivery may be relatively more significant, presumably causing increased cerebral venous pressure and altered cerebrovascular autoregulation. Furthermore, the sites of origin of IVH are more variable in the term newborn and include residual germinal matrix, choroid plexus, vascular malformations, tumor, or sinovenous thrombosis, often with hemorrhagic venous infarction of the thalamus (Roland et al., 1998; Wu et al., 2003). IVH from the latter usually presents somewhat later, at several days or weeks of age.
Infections of the Central Nervous System
Neonatal Meningitis
Management
In an attempt to prevent neonatal meningitis, the American College of Obstetrics and Gynecology and the American Academy of Pediatrics recommend IV administration of ampicillin during labor for mothers with rectal or genital cultures positive for group B Streptococcus or other major risk factors for neonatal sepsis (Schrag et al., 2000). The initial empirical treatment of a neonate with bacterial meningitis of unknown cause is a combination of ampicillin, an aminoglycoside such as gentamicin, and possibly cefotaxime administered IV. The precise dosage varies according to the body weight and postnatal age of the affected infant. The optimal selection of antibiotics is determined when definitive bacteriological diagnosis is known and by the resistances of the infecting organism. Repeated sampling of CSF is required to ensure response to treatment. Parenteral antibiotic treatment is usually maintained for 21 days or at least 2 weeks after sterilization of CSF. A repeat CSF examination should be performed 48 hours after discontinuation of antibiotic therapy.
In addition to antimicrobial therapy, supportive measures such as maintenance of fluid and electrolyte balance and control of blood pressure and blood gases are essential. Because the syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion is common, fluids should be restricted to 30 to 40 mL/kg/day during the first few days of illness. Seizures are a common complication and should be treated with phenobarbital, phenytoin, or both (see Table 80.2). Serial measurements of head circumference and cranial US scans may assist with early diagnosis of potential complications of ventriculitis, hydrocephalus, and subdural effusion.
Ventriculitis commonly causes hydrocephalus, either during the acute phase of the illness or subsequently (Fig. 80.5). Meningitic hydrocephalus may require treatment by external ventricular drainage, often with a reservoir for intermittent draining of CSF, instillation of antibiotics in selected infants if active infection is present, or both. Most newborns require a permanent ventriculoperitoneal shunt after the infection has been eradicated.
Viral and Parasitic Infections
Congenital Rubella
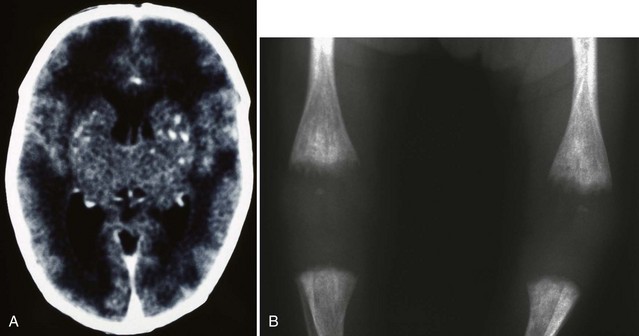
Although the incidence of congenital rubella infection has diminished markedly since widespread use of the rubella vaccination, it remains a significant problem in many parts of the world (Reef et al., 2002; Zerr et al., 2001). The congenital rubella syndrome occurs when the fetus is infected before 20 weeks’ gestation. Clinical features in the newborn include low birth weight, jaundice, hepatosplenomegaly, petechial rash, congenital heart disease, cataracts, sensorineural deafness, microcephaly, bone lesions, and thrombocytopenia (Fig. 80.6). Less severely affected infants appear normal at birth and later show features of neurological and ocular defects, deafness, and congenital heart disease. Infected infants are highly infectious, may shed virus for several years, and must be considered a hazard to nonimmune women. Diagnosis is confirmed by culture of virus (throat swab and urine) and demonstration of rubella-specific immunoglobulin M (IgM) in neonatal plasma. Neuroimaging may reveal periventricular calcifications, subependymal cysts, or PVL. The only effective management is prevention by universal immunization. Antiviral treatment is unavailable. Infants who survive may develop progressive sensorineural hearing loss, behavioral-emotional problems, growth failure, or diabetes mellitus later in childhood.
Cytomegalovirus
Most asymptomatic newborns with congenital CMV infection develop normally. However, a percentage develop progressive neurological problems including impaired intellectual function, progressive hearing loss, microcephaly, chorioretinitis, ataxia, and seizures. The mortality rate in symptomatic newborns is 20% to 30%, and most survivors have multiple severe neurological sequelae (Noyola et al., 2001).
Herpes Simplex
Neonatal herpes simplex infection is acquired during passage through an infected birth canal in the vast majority of newborns. The incidence of this infection in the newborn is increasing, which reflects the high prevalence of herpes infection in adults in the United States, reported to be between 25% and 65% (Corey and Wald, 2009). It may present as localized oral, cutaneous, or ophthalmic disease; localized disease of the CNS, such as meningitis; or disseminated disease with hepatosplenomegaly, severe disseminated intravascular coagulation, renal failure, and meningoencephalitis. Any infant with CSF suggestive of encephalitis should be considered to have herpes simplex infection until proven otherwise. Intranuclear inclusions may be detected in vesicular fluid, CSF, or conjunctival scrapings. A throat swab, as well as urine and stool samples, should be cultured. Negative culture results do not exclude the diagnosis. Studies of the CSF usually are consistent with viral meningoencephalitis, and diagnosis may be established quickly using PCR (see Chapter 57B). PCR assay is the best technique to identify the virus rapidly in the CSF (Kimberlin, 2004). MRI, especially diffusion-weighted MRI, or CT are useful for delineating the extent and severity of brain injury. In term newborns, a 21-day course of acyclovir (60 mg/kg/day, given in evenly divided doses every 8 hours) should be started even before the results of cultures are known. Dosage should be reduced in premature infants and infants who have impaired renal function, or the dosing interval may need to be increased. Antiviral therapy should be continued until weekly CSF HSV DNA PCR testing is negative. Acyclovir may improve outcome but is not as effective as in postnatally acquired infection (Kimberlin, 2007). Even after successful parenteral treatment, recurrence of HSV can occur and may be a lifelong problem.
Toxoplasmosis
Antibody screening for neonatal infection may suggest congenital toxoplasmosis, but test results for Toxoplasma-specific IgM often are negative. Examination of the CSF may show lymphocytosis, high protein content, and trophozoites. PCR performed on amniotic fluid or placenta appears to be more sensitive (Bessieres et al., 2009). Diffuse intracerebral calcifications may be seen on skull radiography, CT, and US.
Spiramycin, pyrimethamine, and sulfadiazine with folinic acid are used to treat the infected mother and her infant during the first year. Specific doses and regimens are beyond the scope of this discussion. In severe meningoencephalitis, the use of corticosteroids may be considered (MacLeod et al., 2009). Approximately one-third of infected infants are symptomatic, and their mortality rate is 25%. Most survivors have significant neurological sequelae. In contrast, asymptomatic newborns have a good prognosis.
Human Immunodeficiency Virus
Although the rate of mother-to-child transmission has been reduced to less than 2% from 25% to 30% in the developed world by screening and management of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) in pregnancy, overall the number of newborns worldwide who are seropositive for HIV is increasing (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2006). Transmission may occur in utero, during labor and delivery, or postnatally by breastfeeding. Most infected newborns are asymptomatic but later develop opportunistic systemic infections (e.g., CMV, Pneumocystis), dementia with cerebral atrophy, and acquired microencephaly caused by viral infection of the brain. The management of HIV-infected women to prevent maternal-infant transmission is beyond the scope of this discussion. Studies have shown that the risk for transmission may be reduced by a program of prenatal, perinatal, and postnatal antiretroviral therapy and may be decreased further by elective cesarean section and avoidance of breastfeeding (Chasela et al., 2010; Mofensen, 2010).
Mechanical Trauma to Extracranial, Central, and Peripheral Nervous System Structures
Intracranial Hemorrhage
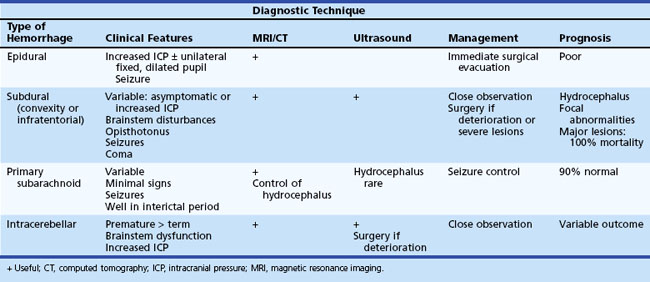
Other types of intracranial hemorrhage such as primary subarachnoid, epidural, subdural, and intracerebellar hemorrhage are usually associated with traumatic delivery or a bleeding diathesis and occur less commonly than PIVH. Subdural hemorrhage occurs in both premature and term newborns and results from laceration of major veins and sinuses. It is often related to excessive molding of the head. MRI or CT are the investigational techniques of choice for diagnosis of subdural hemorrhage. Convexity subdural hematoma, especially if associated with midline shift, may require decompression by craniotomy or subdural tap. Subarachnoid hemorrhage can also be of venous origin but is usually self-limited, originating from small vessels in the leptomeningeal plexus or bridging veins within the subarachnoid space. Infants may be asymptomatic with minor subarachnoid hemorrhage or present with seizures. Diagnosis may be suspected on the basis of uniformly blood-stained or xanthochromic CSF and confirmed by MRI or CT scans. In the absence of severe trauma or major hypoxic-ischemic injury, normal outcome is seen in 90% of patients. Table 80.7 summarizes the clinical features, management, and outcome of these types of intracranial hemorrhage.
Extracranial Hemorrhage
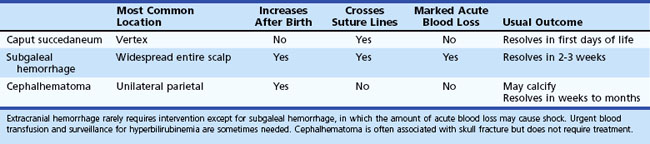
The classification of extracranial hemorrhage is according to the tissue planes involved. Caput succedaneum is superficial bleeding between the skin and the epicranial aponeurosis. Subgaleal hemorrhage, which is often associated with delivery by vacuum extraction, is located between the aponeurosis and the periosteum of the skull, and cephalhematoma occurs in the deepest plane between the periosteum and cranial bones. The major clinical features and the usual outcome for extracranial hemorrhages are summarized in Table 80.8.
Spinal Cord Injury
Spinal cord injury of fetuses in the breech position can be minimized by cesarean delivery of all fetuses with a hyperextended head. Unfortunately, cesarean section does not entirely eliminate the risk because some fetuses sustain injuries in utero, perhaps caused by vertebral artery occlusion. Cord injury after vertex delivery may be a rare complication of forceps rotation. The diagnosis of spinal cord injury is made on the basis of the clinical features. Ultrasonography, radiography, and MRI of the spine are sometimes indicated to exclude surgically correctable lesions such as spinal dysraphism or extramedullary compression. Because the cord injury is a tear or intraparenchymal hemorrhage, surgical decompression and laminectomy generally are not helpful. Supportive management consists of adequate ventilation and prevention of urinary tract infection, decubitus ulcers, and contractures. High-dose corticosteroids have not been used in controlled trials in spinal cord injury in the newborn age group (Brand, 2006).
Traumatic Injury to the Peripheral Nervous System
Brachial Plexus Injury
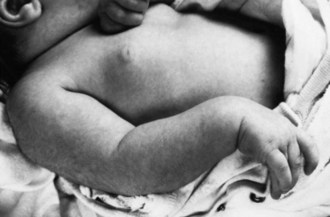
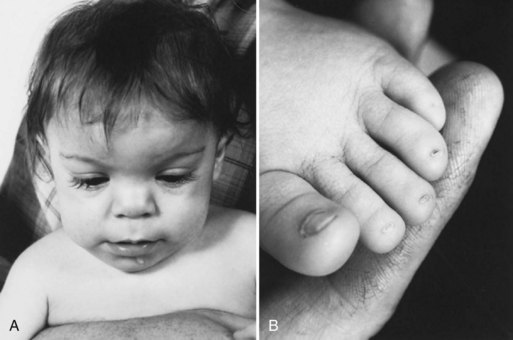
Brachial plexus injury occurs in 0.5 to 2.6 per 1000 live term births. The injury almost always occurs in large newborns with shoulder dystocia who are difficult to deliver (Fig. 80.7) (Gurewitsch et al., 2006). The upper roots of the brachial plexus are involved most commonly (Erb palsy). In other instances, lesions may involve the lower nerve roots down to the first thoracic root (Klumpke palsy). Approximately 5% of cases have been associated with diaphragmatic paralysis caused by injury of the third to fifth cervical roots. Such paralysis may result in tachypnea and hypoventilation, with consequent cyanosis and hypercapnia. Brachial plexus injury also may be associated with Horner syndrome, a fractured clavicle or humerus, subluxation of the shoulder or cervical spine, cervical cord injury, and facial palsy.
The neurological features of brachial plexus injury may be deduced from an understanding of the function of the involved cervical roots. Thus, involvement of the upper cervical roots results in loss of shoulder abduction and external rotation as well as loss of elbow flexion and supination, with variable impairment of wrist and finger extension (see Fig. 80.7). Absence of the biceps reflex on the affected side and an impaired abduction phase of the Moro reflex are demonstrable. With involvement of the lower roots, paralysis extends to intrinsic hand muscles and includes an absent grasp reflex. Horner syndrome occurs in one-third of such patients. Deficits of motor function and reflexes are usually more striking than sensory deficits.
In the majority of infants, diagnosis is based primarily on careful neurological examination and confirmed, if necessary, by showing electromyographic evidence of denervation 2 to 3 weeks after the injury (Joyner et al., 2006). Clinical suspicion of diaphragmatic paralysis requires confirmation by either fluoroscopy or US scanning. This complication necessitates careful surveillance of respiratory status and perhaps ventilatory support or surgical plication of the affected diaphragm. Other traumatic or bony lesions should be excluded by radiography of the cervical spine, clavicles, and humerus (Piatt, 2005).
Management
The affected arm is usually painful and should be immobilized across the upper abdomen for 7 to 10 days. Passive range-of-motion exercises are then initiated to prevent contractures. Supportive wrist splints are important. The value of electrical stimulation techniques is controversial. Prognosis relates largely to the severity of the injury and to the time of onset and rate of initial improvement. Evidence of improved arm function within 2 weeks is a favorable prognostic sign. Although spontaneous recovery as high as 75% to 95% has been cited in the literature, more recent reports indicate that only about two-thirds of infants have spontaneous recovery (Foad et al., 2009). Surgical reconstruction of the plexus (e.g., nerve grafts, neuroma excision) should be considered in infants with no evidence of spontaneous recovery at 4 months (Birch et al., 2005; Strombeck et al., 2000).
Effects of Drugs and Toxins
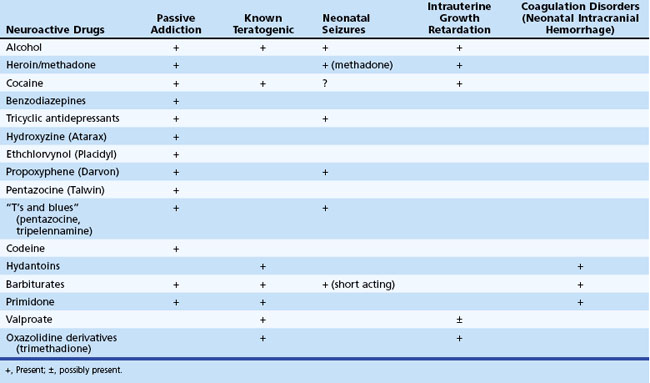
Table 80.9 lists the major adverse effects of the most commonly used neuroactive agents taken during pregnancy. Prevention is the most important aspect of management, and women of childbearing age must be advised of the risks to the fetus of noxious agents before conception, because the risk for malformations is greatest during the early weeks of gestation.
Teratogenic Effects and Intrauterine Growth Retardation
Congenital malformations and intrauterine growth retardation often are associated. In general, maternal alcohol abuse causes growth retardation and intellectual deficits, whereas anticonvulsant drugs cause congenital heart disease and cleft lip and palate. Exposure to valproate during the first weeks of gestation is associated with a 5% risk for neural tube defects. This risk may be diminished to some degree by preconceptional and periconceptional maternal folate supplementation. Because neural tube defects originate very early during pregnancy (5-6 weeks’ gestation), folate administered after confirmation of pregnancy is not helpful in this regard. Distinct syndromes of growth retardation, developmental delay, dysmorphism, and distal limb abnormalities are attributed to fetal exposure to phenytoin (Fig. 80.8), barbiturates, alcohol, trimethadione, and valproate (Kaneko et al., 1999; Report of Quality Standards Subcommittee, 1998). Additional studies are needed to fully delineate the teratogenic potential of newer anticonvulsants. Recent reports from animal studies of neuronal apoptosis following exposure to anticonvulsants in utero raises further concerns (Motamedi and Meador, 2006).
Passive Addiction and Withdrawal Syndrome
The initial features of withdrawal reflect CNS overactivity: jitteriness, irritability, disturbed sleep/wake patterns, shrill cry, and frantic sucking. These may be accompanied by gastrointestinal disturbances such as poor feeding, vomiting, and diarrhea, and less commonly by sneezing, tachypnea, and excessive sweating. Fever and seizures are uncommon manifestations of the neonatal withdrawal syndrome (see the exceptions listed in Table 80.9) and suggest the possibility of sepsis or other serious neonatal disorders.
Barkovich A.J., Miller S.P., Bartha A., et al. MR spectroscopy and diffusion tensor imaging of sequential studies in neonates with encephalopathy. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2006;27:533-547.
Bassan H., Benson C., Limperopoulos C., et al. Ultrasonographic features and severity scoring of periventricular hemorrhagic infarction in relation to risk factors and outcome. Pediatrics. 2006;117:2111-2118.
Bassan H., Bental Y., Shany E., et al. Neonatal seizures: dilemmas in workup and management. Pediatr Neurol. 2008;38:415-421.
Bellini, G., Micelli, F., Soldovieri, M.V., et al. 2010. Benign familial neonatal seizures. Gene Reviews [online].
Bessieres M.H., Berrebi A., Cassaing S., et al. Diagnosis of congenital toxoplasmosis: prenatal and neonatal evaluation of methods used in Toulouse University Hospital and incidence of congenital toxoplasmosis. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 2009;104:389-392.
Birch R., Ahad N., Kono H., et al. Repair of obstetric brachial plexus palsy: results in 100 children. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2005;87:1089-1095.
Brand M.C. Part 1: recognizing neonatal spinal cord injury. Adv Neonatal Care. 2006;6:15-24.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Achievements in public health. Reduction in perinatal transmission of HIV infection-United States 1985-2005. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2006;55:592-597.
Chasela C.S., Hudgens M.G., Jamieson D.J., et al. Maternal or infant antiretroviral drugs to reduce HIV-I transmission. N Engl J Med. 2010;362:2271-2281.
Chau V., Poskitt K.J., Sargent M.A., et al. Comparison of computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging scans on the third day of life in term newborns with neonatal encephalopathy. Pediatrics. 2009;123:319-326.
Clancy R. Prolonged encephalogram monitoring for seizures and their treatment. Clin Perinatol. 2006;33:649-665.
Corey L., Wald A. Maternal and neonatal herpes simplex virus infections. N Engl J Med. 2009;361:1376-1385.
Counsell S.J., Tranter S.L., Rutherford M.A. Magnetic resonance imaging of brain injury in the high-risk term infant. Semin Perinatol. 2010;34:67-78.
Dyet L.E., Kennea C., Counsell S.J., et al. Natural history of brain lesions in extremely preterm infants studied with serial magnetic resonance imaging from birth and neurodevelopmental assessments. Pediatrics. 2006;118:536-548.
Foad S.L., Mehlman C.T., Foad M.B., et al. Prognosis following neonatal brachial plexus palsy: an evidence-based review. J Child Orthop. 2009;3:459-463.
Glass H.C., Wirrell E. Controversies in neonatal seizure management. J Child Neurol. 2009;24:591-599.
Glass H.C., Wu Y. Epidemiology of neonatal seizures. J Pediatr Neurol. 2009;7:13-17.
Gurewitsch E.D., Johnson E., Hamzehzadeh S., et al. Risk factors for brachial plexus injury with and without shoulder dystocia. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2006;194:486-492.
Hamrick S.E., Miller S.P., Leonard C., et al. Trends in severe brain injury and neurodevelopmental outcome in premature newborn infants: the role of cystic periventricular leukomalacia. J Pediatr. 2004;145:593-599.
Hanrahan J., Cox I.J., Edwards A.D., et al. Persistent increases in cerebral lactate concentration after birth asphyxia. Pediatr Res. 1998;44:304-311.
Jacobs, S.E., Hunt, R., Tarnow-Mardi, W.O., et al., 2007. Cooling for newborns with hypoxic-ischaemic encephalopathy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 4 Art. No.: CD003311.
Jensen F. Neonatal seizures: an update on mechanisms and management. Clin Perinatol. 2009;36:881-900.
Joyner B., Soto M.A., Adam H.M. Brachial plexus injury. Pediatr Rev. 2006;27:238-239.
Kaneko S., Battino D., Andermann E., et al. Congenital malformations due to antiepileptic drugs. Epilepsy Res. 1999;33:145-158.
Koh E.E., Lerner J., Sankar R., et al. Accuracy of amplitude integrated EEG in a neonatal cohort. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal. 2010;95:F169-F173.
Kimberlin D.W. Neonatal herpes simplex infection. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2004;17:1-13.
Kimberlin D.W. Herpes simplex virus infections of the newborn. Semin Perinatol. 2007;31:19-25.
Lamblin A.M., d’Allest A.M., Curzi-Dascalova L., et al. Electroencephalography in premature and full term infants: developmental features and glossary. Neurophysiol Clin. 2010;40:59-124.
MacLeod R., Kieffer F., Sautter M., et al. Why prevent, diagnose and treat congenital toxoplasmosis. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 2009;104:320-344.
Ment L.R., Vohr B., Allan W., et al. The etiology and outcome of cerebral ventriculomegaly at term in very low birth weight preterm infants. Pediatrics. 1999;104:243-248.
Miller S.P., Ferreiro D.M. From selective vulnerability to connectivity: insights from newborn brain imaging. Trends Neurosci. 2009;32:496-505.
Miller S.P., Ramaswamy V., Michelson D., et al. Patterns of brain injury in term neonatal encephalopathy. J Pediatr. 2005;146:453-460.
Mills P.B., Footitt E.J., Mills K.A., et al. Genotypic and phenotypic spectrum of pyridoxine-dependent epilepsy (ALDH7AI deficiency). Brain. 2010;133:2148-2159.
Moers A., Brockmann K., Wang D., et al. EEG features of Glut-1 deficiency syndrome. Epilepsia. 2002;43:941-945.
Mofenson L.M. Protecting the next generation-eliminating perinatal HIV-I infection. N Engl J Med. 2010;362:2316-2318.
Motamedi G.K., Meador K.J. Antiepileptic drugs and neurodevelopment. Cur Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2006;6:341-346.
Noyola D.E., Demmler G.J., Nelson C.T., et al. Early predictors of neurodevelopmental outcome in symptomatic congenital cytomegalovirus infection. J Pediatr. 2001;138:525-531.
Pearl P.L. New treatment paradigms in neonatal metabolic epilepsies. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2009;32:204-213.
Piatt J.H.Jr. Birth injuries of the brachial plexus. Clin Perinatol. 2005;32:39-59.
Reef S.E., Frey T.K., Theall K., et al. The changing epidemiology of rubella in the 1990s: on the verge of elimination and new challenges for control and prevention. JAMA. 2002;287:464-472.
Rennie J., Boylan G. Treatment of neonatal seizures. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal. 2007;92:F148-F150.
Report of Quality Standards Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Practice parameter-management issues for women with epilepsy (summary statement). Neurology. 1998;51:944-948.
Roland E.H. Summary of “Cooling for newborns with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy.”. Evidence-Based Child Health: a Cochrane Review. 2008;3:1116-1117.
Roland E.H., Poskitt K., Rodriquez E., et al. Perinatal hypoxic-ischemic thalamic injury: clinical features and neuroimaging. Ann Neurol. 1998;44:161-166.
Rutherford M.A., Biarge M.M., Allsop J., et al. MRI of perinatal brain injury. Pediatr Radiol. 2010;40:819-833.
Schrag S.J., Zywicki S., Farley M.M., et al. Group B streptococcal disease in the era of intrapartum prophylaxis. N Engl J Med. 2000;342:15-20.
Strombeck C., Kramlinde-Sundholm L., Forssberg H. Functional outcome at 5 years in children with obstetrical brachial plexus palsy with and without microsurgical reconstruction. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2000;42:148-157.
Tekgul H., Gauvreau K., Saul J., et al. The current etiologic profile and neurodevelopmental outcome of seizures in term newborn infants. Pediatrics. 2006;47:1270-1280.
van Rooij L.G.M., Toet M.C., van Huffelen A.C., et al. Effect of treatment of subclinical neonatal seizures detected with aEEG: randomized, controlled trial. Pediatrics. 2010;125:e358-e366.
Volpe J.J. Neurology of the Newborn, fifth ed. Philadelphia: WB Saunders; 2008.
Wu Y.W., Hamrick S.E.G., Miller S.P., et al. Intraventricular hemorrhage in term neonates caused by sinovenous thrombosis. Ann Neurol. 2003;54:123-126.
Zerr D.M., Heath J., Riggert D., Marcuse E.K. Congenital rubella infection control problem. Pediatrics. 2001;108:1389-1390.