Mycobacteria
I Shared Mycobacterial Properties
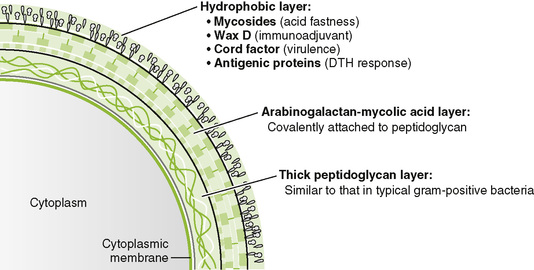
• Mycobacteria are slow-growing, aerobic, facultative intracellular rods with a lipid-rich cell wall that makes them acid fast.
1. Microscopic detection of acid-fast rods in sputum or biopsy specimen
2. Isolation by culturing on egg-based Löwenstein-Jensen medium or on special broth media
3. Serologic tests and DNA probes
• Intradermal injection of purified protein derivative (PPD) from cell wall induces a delayed-type hypersensitivity (DTH) response in those who have been previously exposed to M. tuberculosis or vaccinated.
• Positive reaction is indicated by an area of induration (>15 mm for healthy adults) 48 to 72 hours after PPD injection.
a. Tuberculin skin test is a classic example of a type IV hypersensitivity reaction (DTH).
b. Skin test reactivity usually develops 3 to 4 weeks after infection.
c. False-negative results may occur in those with very recent infection, anergic individuals (especially human immunodeficiency virus [HIV]-infected patients), and older people in whom the DTH response has waned.
d. False-positive results occur in individuals vaccinated with bacille Calmette-Guérin (BCG), the antituberculosis vaccine used in Europe and other countries.
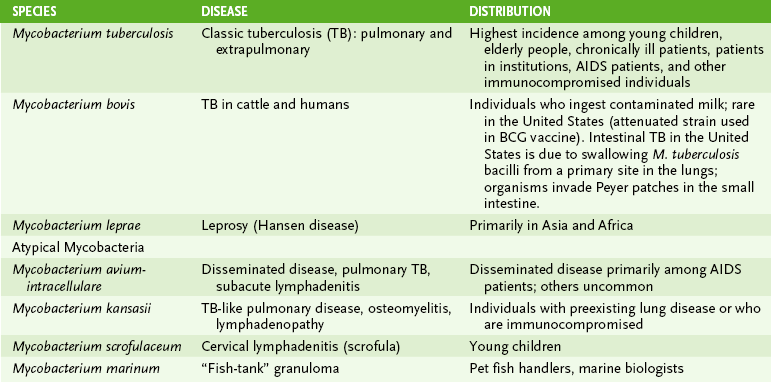
1. Humans are the only natural reservoir of M. tuberculosis
2. Spread of tubercle bacilli through respiratory droplets is promoted by crowded conditions and coughing.
3. Young children, elderly people, and immunocompromised individuals have the highest risk for developing active tuberculosis (TB).
• Infection with M. tuberculosis may involve any organ, but the lungs are the initial and most common sites affected.
1. Inhaled mycobacteria are engulfed by alveolar macrophages and replicate freely in these cells.
• Cell wall components prevent bacterial destruction in macrophage lysosomes.
• Intracellular growth protects mycobacteria from antibody-mediated elimination.
• Other macrophages are attracted to the site and destroy the infected cells, releasing mycobacteria that can spread through the bloodstream.
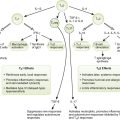
2. Sequence of formation of a tuberculous granuloma (type IV hypersensitivity reaction)
• Tubercle bacilli are phagocytosed by alveolar macrophages.
• Unactivated macrophages cannot kill mycobacteria.
• Other macrophages process and present antigen to CD4 T cells in association with class II antigen sites.
• Macrophages release interleukin-12 (IL-12), which stimulates naïve helper T cells to produce TH1 class memory cells, and IL-1, which causes fever and activates TH1 cells.
• TH1 cells release IL-2 (stimulates lymphocyte proliferation), interferon-γ (activates macrophages to kill tubercle bacillus, called epithelioid cells), and migration inhibitory factor (causes macrophages to accumulate).
• Lipids from killed tubercle bacillus lead to caseous necrosis.
• Activated macrophages fuse, become multinucleated giant cells, and wall off infection.
3. Lack of a host response (e.g., lack of CD4 T cells in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome [AIDS]) leads to dissemination of disease without the formation of granulomas.
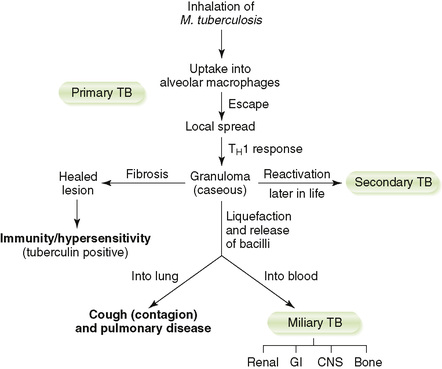
D Clinical course of TB (Fig. 16-2)
a. Active disease occurs within 2 years of infection in 5% to 10% of cases (primary) and recurs later in life in a small number of these cases (secondary).
b. The remainder of infected individuals never develops active TB.
• Localized infection foci form within lung after inhalation of M. tuberculosis.
a. CD4 TH1 cell–macrophage response restricts intracellular proliferation of mycobacteria to the mid to lower lung region and encloses them within tubercles.
b. Subpleural lesion of caseous necrosis is called a Ghon focus.
c. Lymphatic spread to the hilar lymph nodes is called a Ghon complex.
• Clinical manifestations of active TB (Box 16-2)
a. Nonspecific symptoms include malaise, weight loss, cough, night sweats, and hemoptysis.
b. Active disease is marked by pneumonitis and hilar lymphadenopathy.
c. Calcification of healed primary lesions leaves scars that appear as spots on the lung in radiographs.
d. Individuals with latent tuberculosis, infection without active disease, are not infectious but can develop active TB later in life.
• Surveillance programs using the PPD skin test (Mantoux test) identify previously infected individuals, followed by chest radiograph of individuals with positive response.
• Prophylactic isoniazid may be given to those at high risk for developing active disease (e.g., latent TB).
• Live, attenuated BCG vaccine is somewhat effective.
• BCG-immunized individuals test weakly positive in PPD screening programs.
3. Prophylaxis after exposure to drug-resistant TB includes pyrazinamide plus either ethambutol or levofloxacin.
III “Atypical” Mycobacteria: Nontuberculosis Mycobacteria (NTB)
• Numerous Mycobacterium species causing TB-like diseases are classified based on their rate of growth and pigment production.
A Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare complex (MAC)
1. Major mycobacterial pathogen in AIDS patients, causing disseminated TB-like disease
2. Usually produces asymptomatic infection in healthy adults but may cause pulmonary disease
3. Acquired by ingestion of contaminated food or water or by inhalation
4. MAC are resistant to anti-TB drugs and are treated with clarithromycin or azithromycin plus ethambutol and rifampin.
B Mycobacterium kansasii and Mycobacterium scrofulaceum (see Table 16-1)
• M. leprae causes leprosy (Hansen disease), which is characterized by skin lesions, nerve damage, and extensive tissue destruction in some cases.
1. TH1 response (DTH, interferon-γ, macrophage activation) → milder tuberculoid leprosy
2. TH2 response (humoral antibody) → more severe lepromatous leprosy
B Clinical presentations (Table 16-2)
TABLE 16-2
Clinical and Immunologic Manifestations of Leprosy
| Property | Tuberculoid | Lepromatous |
| Appearance of skin lesions | Few erythematous or hypopigmented and atrophic plaques with flat centers and raised demarcated borders | Many erythematous macules, papules, or nodules accompanied by extensive tissue damage to nose cartilage, bone, testicles |
| Histopathology of skin lesions | Granulomatous with Langerhans cells and epithelioid cells surrounded by lymphocytes | Predominantly “foamy” macrophages with few lymphocytes and no Langerhans cells |
| Nerve involvement | Early peripheral nerve damage with complete sensory loss; visible nerve enlargement (ulnar nerve, greater auricular nerve); autoamputation of the digits | Late diffuse nerve damage with patchy sensory loss; no nerve enlargement |
| Acid-fast bacilli | Few or none present in skin lesions or nerves | Abundant in skin lesions, nerves, and internal organs |
| Infectivity | Low | High |
| Immune responses | ||
| DTH reaction to lepromin | Yes | No |
| Immunoglobulin levels | Normal | Hypergammaglobulinemia |
| Lepromin skin test | Positive (intact cellular immunity) | Negative (absent cellular immunity) |
• Many skin lesions with large numbers of M. leprae at the site of the lesion
• Nodular lesions on the face (“leonine” facies)
• Negative lepromin skin test (shows lack of cellular immunity)
• New skin lesions with small numbers of M. leprae at the site of the lesion
• Hypopigmented skin lesions with lack of sensation
• Positive lepromin skin test (shows intact cellular immunity)
3. Dimorphic leprosy: lesions ranging between the tuberculoid and lepromatous forms