CHAPTER 2: The Cellular and Molecular Basis of Inheritance
CHAPTER 3: Chromosomes and Cell Division
CHAPTER 4: DNA Technology and Applications
CHAPTER 5: Mapping and Identifying Genes for Monogenic Disorders
CHAPTER 6: Developmental Genetics
CHAPTER 7: Patterns of Inheritance
CHAPTER 8: Mathematical and Population Genetics
CHAPTER 9: Polygenic and Multifactorial Inheritance
CHAPTER 10: Hemoglobin and the Hemoglobinopathies
CHAPTER 11: Biochemical Genetics
CHAPTER 15: Genetic Factors in Common Diseases
CHAPTER 16: Congenital Abnormalities and Dysmorphic Syndromes
CHAPTER 17: Genetic Counseling
CHAPTER 18: Chromosome Disorders
CHAPTER 19: Single-Gene Disorders
CHAPTER 20: Screening for Genetic Disease
CHAPTER 21: Prenatal Testing and Reproductive Genetics
CHAPTER 23: Treatment of Genetic Disease

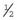
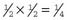 , for girls the same; therefore the chance of being the same sex is
, for girls the same; therefore the chance of being the same sex is 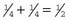 (0.5)
(0.5)