Monoamine oxidase inhibitors
MAOIs are classified as either hydrazide or nonhydrazide derivatives. Additionally, they are either selective or nonselective inhibitors of MAO. The MAOIs available for use in the United States include phenelzine, tranylcypromine, isocarboxazid, selegiline, and rasagiline (Table 96-1). Phenelzine, tranylcypromine, and isocarboxazid inhibit the activity of both MAO-A and MAO-B. Selegiline and rasagiline block MAO-B and are used for the treatment of Parkinson disease. Although selegiline and rasagiline are selective inhibitors of MAO-B, they lose their selectivity in a dose-dependent fashion. The lowest strength (6-mg) selegiline patch is efficacious in the treatment of depression without the need for dietary modification. This mode of drug delivery allows selegiline to bypass first-pass hepatic metabolism and be delivered to the brain in a concentration that inhibits both MAO-A and MAO-B.
Table 96-1
Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors Most Commonly Used in the United States
| Drug | Hydrazide vs. Nonhydrazide | Selectivity* | Clinical Use |
| Phenelzine | Hydrazide | A and B | Antidepressant |
| Tranylcypromine | Nonhydrazide | A and B | Antidepressant |
| Isocarboxazid | Hydrazide | A and B | Antidepressant |
| Selegiline—oral | Nonhydrazide | B | Antiparkinsonian |
| Selegiline—patch | Nonhydrazide | A and B | Antidepressant |
| Rasagiline | Nonhydrazide | B | Antiparkinsonian |
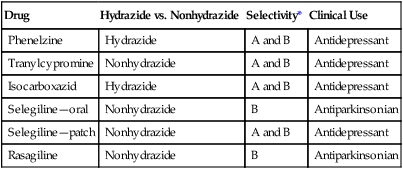
*The two forms of the monoamine oxidase enzyme are designated A and B.
Adverse effects
Orthostatic hypotension
Orthostatic hypotension is the most common adverse effect associated with the use of MAOIs (Box 96-1). Octopamine, a false neurotransmitter, is formed by the β-hydroxylation of tyramine in the sympathetic nerve terminal and is stored within the presynaptic storage vesicle, displacing norepinephrine. Neural impulses that normally would stimulate the release of norepinephrine from these storage vesicles now release less norepinephrine along with some octopamine, which has very little α- and β-receptor activity. When an individual taking MAOIs assumes an upright position, the presence of this false neurotransmitter manifests itself by causing less vasoconstriction than normally would occur, resulting in hypotension.