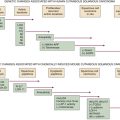
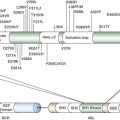
Table 35-1
Frequent Molecular Alterations in Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma
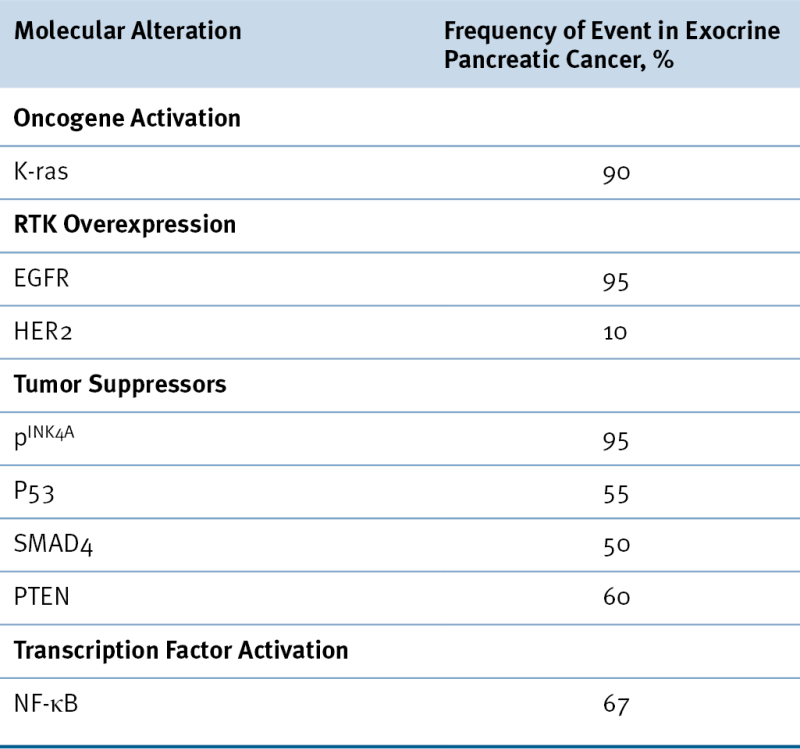
RTK, Receptor tyrosine kinase.
Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor
Activation of Nuclear Transcription Factors
Nuclear Factor κB
Loss of Tumor Suppressors
INK 4 A and ARF Tumor Suppressors
p53
SMAD4
PTEN
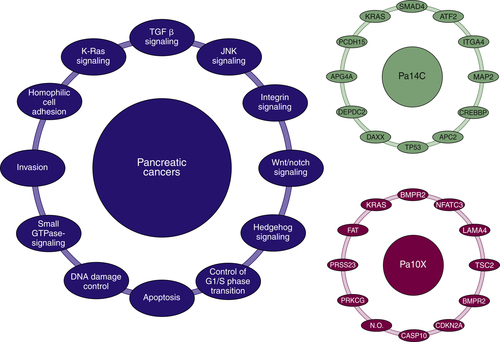
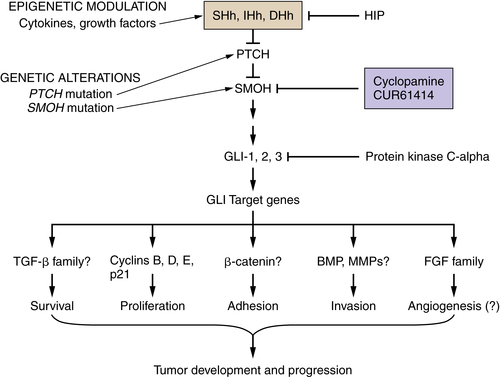
Reactivation of Developmental Biology Pathways
Hedgehog, Notch, and Wnt Pathways
Downstream Events
Desmoplastic Reaction (Tumor Stroma)
Cytokine Production
Conclusion
1. Multicomponent analysis of the pancreatic adenocarcinoma progression model using a pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia tissue microarray . Mod Pathol . 2003 ; 16 : 902 – 912 .
2. Core signaling pathways in human pancreatic cancers revealed by global genomic analyses . Science . 2008 ; 321 : 1801 – 1806 .
3. DPC4 gene status of the primary carcinoma correlates with patterns of failure in patients with pancreatic cancer . J Clin Oncol . 2009 ; 27 : 1806 – 1813 .
4. Genetics and biology of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma . Genes Dev . 2006 ; 20 : 1218 – 1249 .
5. Most human carcinomas of the exocrine pancreas contain mutant c-K-ras genes . Cell . 1988 ; 53 : 549 – 554 .
6. Preinvasive pancreatic neoplasia of ductal phenotype induced by acinar cell targeting of mutant Kras in transgenic mice . Cancer Res . 2003 ; 63 : 2016 – 2019 .
7. Preinvasive and invasive ductal pancreatic cancer and its early detection in the mouse . Cancer Cell . 2003 ; 2 : 437 – 450 .
8. Endogenous oncogenic K-ras(G12D) stimulates proliferation and widespread neoplastic and developmental defects . Cancer Cell . 2004 ; 5 : 375 – 387 .
9. Activated Kras and Ink4a/Arf deficiency cooperate to produce metastatic pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma . Genes Dev . 2003 ; 17 : 3112 – 3126 .
10. Trp53R172H and KrasG12D cooperate to promote chromosomal instability and widely metastatic pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma in mice . Cancer Cell . 2005 ; 7 : 469 – 483 .
11. Oncogenic Kras maintains pancreatic tumors through regulation of anabolic glucose metabolism . Cell . 2012 ; 149 : 656 – 670 .
12. Cetuximab, a monoclonal antibody targeting the epidermal growth factor receptor, in combination with gemcitabine for advanced pancreatic cancer: a multicenter phase II trial . J Clin Oncol . 2004 ; 22 : 2610 – 2616 .
13. Transforming growth factor alpha expression drives constitutive epidermal growth factor receptor pathway activation and sensitivity to gefitinib (Iressa) in human pancreatic cancer cell lines . Cancer Res . 2006 ; 66 : 3802 – 3812 .
14. Erlotinib plus gemcitabine compared with gemcitabine alone in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer: a phase III trial of the National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group . J Clin Oncol . 2007 ; 25 : 1960 – 1966 .
15. The nuclear factor-kappa B RelA transcription factor is constitutively activated in human pancreatic adenocarcinoma cells . Clin Cancer Res . 1999 ; 5 : 119 – 127 .
16. PTEN is a major tumor suppressor in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and regulates an NF-kappaB-cytokine network . Cancer Discov . 2011 ; 1 : 158 – 169 .
17. Potential role of Jun activation domain-binding protein 1 as a negative regulator of p27kip1 in pancreatic adenocarcinoma . Cancer Res . 2006 ; 66 : 8581 – 8589 .
18. Role of Sp proteins in regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor expression and proliferation of pancreatic cancer cells . Cancer Res . 2004 ; 64 : 6740 – 6749 .
19. Celecoxib inhibits vascular endothelial growth factor expression in and reduces angiogenesis and metastasis of human pancreatic cancer via suppression of Sp1 transcription factor activity . Cancer Res . 2004 ; 64 : 2030 – 2038 .
20. Stat3 activation regulates the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and human pancreatic cancer angiogenesis and metastasis . Oncogene . 2003 ; 22 : 319 – 329 .
21. Tolfenamic acid and pancreatic cancer growth, angiogenesis, and Sp protein degradation . J Natl Cancer Inst . 2006 ; 98 : 855 – 868 .
22. Concordant loss of MTAP and p16/CDKN2A expression in pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia: evidence of homozygous deletion in a noninvasive precursor lesion . Mod Pathol . 2005 ; 18 : 959 – 963 .
23. Both p16(Ink4a) and the p19(Arf)-p53 pathway constrain progression of pancreatic adenocarcinoma in the mouse . Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A . 2006 ; 103 : 5947 – 5952 .
24. Expression of p53 protein in precursor lesions and adenocarcinoma of human pancreas . Am J Pathol . 1994 ; 145 : 1291 – 1295 .
25. DPC4/SMAD4 gene alterations in human cancer, and their functional implications . Ann Oncol . 1999 ; 10 ( suppl 4 ) : 56 – 59 .
26. Role of Smad4 (DPC4) inactivation in human cancer . Biochem Biophys Res Commun . 2003 ; 306 : 799 – 804 .
27. Loss of expression of Dpc4 in pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia: evidence that DPC4 inactivation occurs late in neoplastic progression . Cancer Res . 2000 ; 60 : 2002 – 2006 .
28. The SMAD4 protein and prognosis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma . Clin Cancer Res . 2001 ; 7 : 4115 – 4121 .
29. Tumor suppressor PTEN: modulator of cell signaling, growth, migration and apoptosis . J Cell Sci . 2001 ; 114 : 2375 – 2382 .
30. The PI 3-kinase/Akt signaling pathway is activated due to aberrant Pten expression and targets transcription factors NF-kappaB and c-Myc in pancreatic cancer cells . Oncogene . 2004 ; 23 : 8571 – 8580 .
31. Pten constrains centroacinar cell expansion and malignant transformation in the pancreas . Cancer Cell . 2005 ; 8 : 185 – 195 .
32. Developmental biology informs cancer: the emerging role of the hedgehog signaling pathway in upper gastrointestinal cancers . Cancer Cell . 2003 ; 4 : 245 – 247 .
33. The love-hate relationship between Ras and Notch . Genes Dev . 2005 ; 19 : 1825 – 1839 .
34. Hedgehog is an early and late mediator of pancreatic cancer tumorigenesis . Nature . 2003 ; 425 : 851 – 856 .
35. Sleeping Beauty mutagenesis reveals cooperating mutations and pathways in pancreatic adenocarcinoma . Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A . 2012 ; 109 : 5934 – 5941 .
36. The deubiquitinase USP9X suppresses pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma . Nature . 2012 ; 486 : 266 – 270 .
37. Friends or foes—bipolar effects of the tumour stroma in cancer . Nat Rev Cancer . 2004 ; 4 : 839 – 849 .
38. Quantitative analysis of collagen and collagen subtypes I, III, and V in human pancreatic cancer, tumor-associated chronic pancreatitis, and alcoholic chronic pancreatitis . Pancreas . 1995 ; 11 : 357 – 364 .
39. Distribution of extracellular matrix proteins in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and its influence on tumor cell proliferation in vitro . Pancreas . 1987 ; 2 : 14 – 24 .
40. Extracellular matrix-mediated membrane-type 1 matrix metalloproteinase expression in pancreatic ductal cells is regulated by transforming growth factor-beta1 . Cancer Res . 2006 ; 66 : 7032 – 7040 .
41. Pancreatic carcinoma cells induce fibrosis by stimulating proliferation and matrix synthesis of stellate cells . Gastroenterology . 2005 ; 128 : 907 – 921 .
42. Transforming growth factor-beta1 induces desmoplasia in an experimental model of human pancreatic carcinoma . Cancer Res . 2001 ; 61 : 550 – 555 .
43. Overexpression of TGF-beta by infiltrated granulocytes correlates with the expression of collagen mRNA in pancreatic cancer . Br J Cancer . 2004 ; 91 : 1316 – 1326 .
44. Inhibition of Hedgehog signaling enhances delivery of chemotherapy in a mouse model of pancreatic cancer . Science . 2009 ; 324 : 1457 – 1461 .
45. Proinflammatory cytokines, nutritional support, and the cachexia syndrome: interactions and therapeutic options . Cancer . 1997 ; 79 : 1828 – 1839 .
46. Cytokines in pancreatic carcinoma: correlation with phenotypic characteristics and prognosis . Cancer . 2004 ; 101 : 2727 – 2736 .
47. Cytokine expression profile in human pancreatic carcinoma cells and in surgical specimens: implications for survival . Cancer Immunol Immunother . 2006 ; 55 : 684 – 698 .
48. Role of mononuclear cells and inflammatory cytokines in pancreatic cancer-related cachexia . Clin Cancer Res . 2005 ; 11 : 5802 – 5808 .
49. Transcriptional anti-angiogenesis therapy of human pancreatic cancer . Cytokine Growth Factor Rev . 2006 ; 17 : 147 – 156 .
50. Constitutive and inducible interleukin 8 expression by hypoxia and acidosis renders human pancreatic cancer cells more tumorigenic and metastatic . Clin Cancer Res . 1999 ; 5 : 3711 – 3721 .