In the world of medicine and pharmaceuticals, understanding how drugs work is critical to developing safe and effective treatments. This is where the term MoA comes into play. The MoA medical abbreviation refers to the mechanism of action, specific biochemical interaction through which a drug produces its therapeutic effect. But what is the mechanism of action, really? And how does it differ from other pharmacological concepts?
Whether you’re a healthcare professional, pharmacy student, or curious patient, grasping the mechanism of action meaning is essential. In this article, we’ll break down what a mechanism of action is, explain what MoA means in pharmacology, and explore how it’s used in clinical and research settings.
What is the mechanism of action?
In pharmacology, the mechanism of action refers to how a drug produces its desired effect in the body. It describes the specific biological process or molecular target a medication interacts with to bring about a therapeutic result.
The MoA medical abbreviation is commonly used in both clinical and research settings, and it’s a crucial concept in understanding how drugs work at the cellular or biochemical level. While MoA tells us how a drug works, it is often confused with pharmacodynamics (what a drug does to the body) and pharmacokinetics (how the body processes the drug). It’s important to distinguish between these to fully grasp the MoA meaning in pharmacology.
For example, the mechanism of action of aspirin involves the inhibition of enzymes called COX-1 and COX-2, which reduces inflammation and pain. This is a clear illustration of MoA in medical terms, showing exactly how a drug achieves its effect.
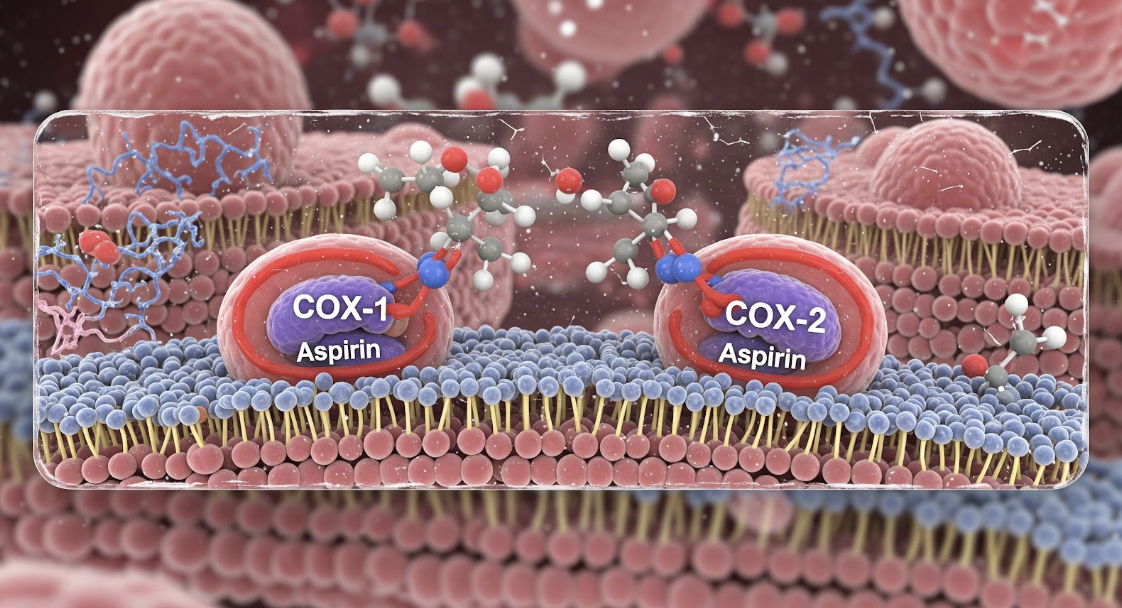
Application of MoA in healthcare settings
Whether in medicine, pharmacy, or hospital settings, applying MoA in medical terms leads to more precise and effective care. Let’s explore its key applications:
How MoA guides treatment decisions in medicine
Understanding the mechanism of action of drugs allows healthcare professionals to choose the most appropriate treatments for individual patients. For example, when selecting an antidepressant, a physician may consider whether the drug acts by inhibiting serotonin reuptake, modulating norepinephrine levels, or affecting multiple neurotransmitters. These different MoAs in medicine help determine which option will offer the most benefit with the fewest side effects for a specific patient. This knowledge leads to more accurate, targeted, and effective treatment strategies.
Beyond psychiatric medications, MoA is used in nearly every medical specialty — from antibiotics that target bacterial cell walls to antiplatelet drugs that prevent clot formation by inhibiting specific receptors. When clinicians understand what MoA is in pharmacology, they can more confidently select medications that align with the pathophysiology of a disease. This ensures that treatments are not just symptom-focused but mechanism-driven, offering better long-term outcomes and a deeper understanding of therapeutic effectiveness.
Educating patients with MoA videos and resources
Patients need to understand how their medications work. Knowing the MoA of different medicines helps patients feel more informed and confident about their treatment. To support this, healthcare providers are increasingly using visual tools like MoA animations and videos, which enhance patient education.
Resources like mechanism of action videos or animated explainers are especially useful in busy clinical settings, where time for in-depth education is limited. A short, clear moa video meaning segment can give patients the confidence to ask better questions and stay committed to their treatment. By using these tools, healthcare professionals bridge the gap between scientific detail and patient understanding, turning the technical moa in healthcare into practical, empowering knowledge that supports better outcomes.
Role of MoA in pharmacy practice
In the pharmacy setting, knowing what MoA is in pharmacology is critical for daily decision-making. Pharmacists use this information to explain drug mechanisms to patients, identify and prevent potential drug interactions, and recommend alternatives when side effects or contraindications arise. The MoA pharmacy abbreviation often appears in drug references, databases, and continuing education resources, allowing pharmacists to quickly identify how a medication works and what risks it may pose in combination with others.
Pharmacists also rely on MoA in pharmacy when supporting medication therapy management (MTM) and performing clinical reviews. For instance, two medications may treat the same condition, but a pharmacist can recommend the better choice based on their distinct mechanisms of action. By understanding MoA, pharmacists play a key role in optimizing medication regimens, reducing adverse events, and supporting evidence-based therapy — all of which contribute to safer, more effective care.
MoA in personalizing patient care
With the rise of personalized and precision medicine, understanding MoA in healthcare has become more important than ever. Clinicians now use molecular and genetic data to guide therapy, often matching a drug’s mechanism of action to the patient’s specific biology. For example, in oncology, targeted therapies are selected based on mutations in tumor cells, ensuring that treatment works on the exact cellular pathways driving the disease. These MoA pharmaceutical strategies not only improve results but also reduce exposure to ineffective or harmful drugs.
Personalizing care based on what is MoA in medicine is also transforming how chronic conditions like diabetes, asthma, and autoimmune diseases are managed. Instead of a one-size-fits-all approach, patients are now offered drugs whose MoA in medical terms aligns with their unique clinical profiles. This results in improved symptom control, fewer side effects, and better patient satisfaction. As diagnostics continue to evolve, the role of MoA in pharma will only grow, becoming a cornerstone of individualized treatment planning.
Wrapping up
Understanding the mechanism of action is essential across all areas of healthcare and pharmaceutical practice. From guiding treatment decisions to improving patient education and driving innovation in drug development, MoA in medicine helps professionals make more informed, precise, and effective choices. Whether you’re a physician, pharmacist, researcher, or patient, knowing what MoA is in pharmacology provides a clearer view of how medications work and why they matter.