Lambrecht, NW. Ménétrier’s disease of the stomach: a clinical challenge. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2011; 13(6):513–517.
Friedman, J, et al. Ménétrier disease. Radiographics. 2009; 29(1):297–301.
Rothenberg, M, et al. Successful use of octreotide to treat Ménétrier’s disease: a rare cause of abdominal pain, weight loss, edema, and hypoalbuminemia. Dig Dis Sci. 2009; 54(7):1403–1407.
Narumi, S, et al. Correspondence between computed tomography and endoscopy in Menetrier’s disease. Pediatr Int. 2008; 50(2):245–247.
Fishman, EK, et al. CT of the stomach: spectrum of disease. Radiographics. 1996; 16(5):1035–1054.
Wolfsen, HC, et al. Menetrier’s disease: a form of hypertrophic gastropathy or gastritis? Gastroenterology. 1993; 104(5):1310–1319.
REESE, DF, et al. Giant hypertrophy of the gastric mucosa (Menetrier’s disease):a correlation of the roentgenographic, pathologic, and clinical findings. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med. 1962; 88:619–626.
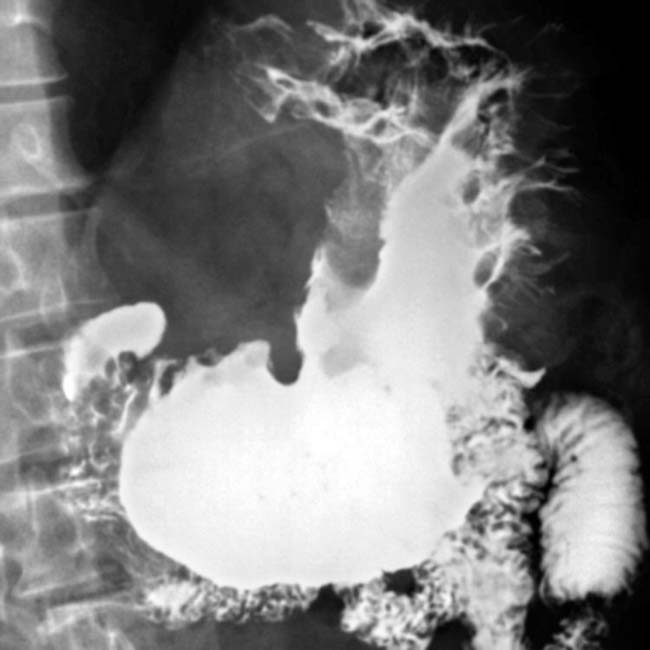
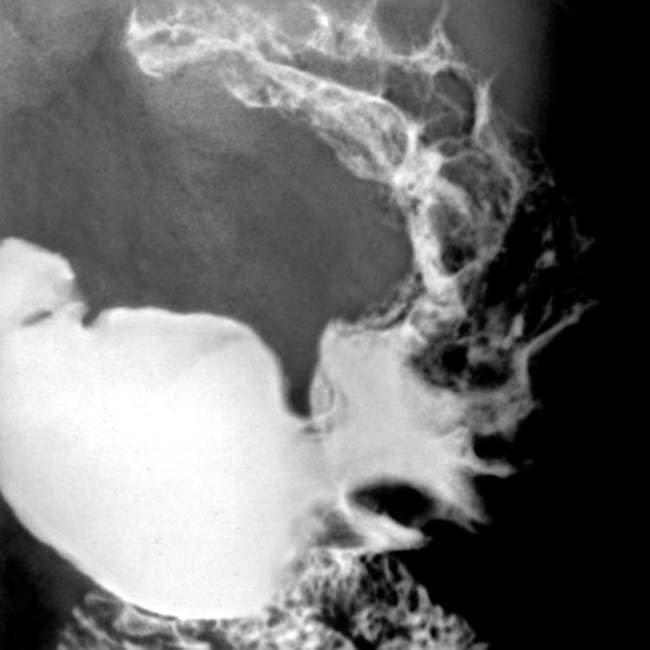
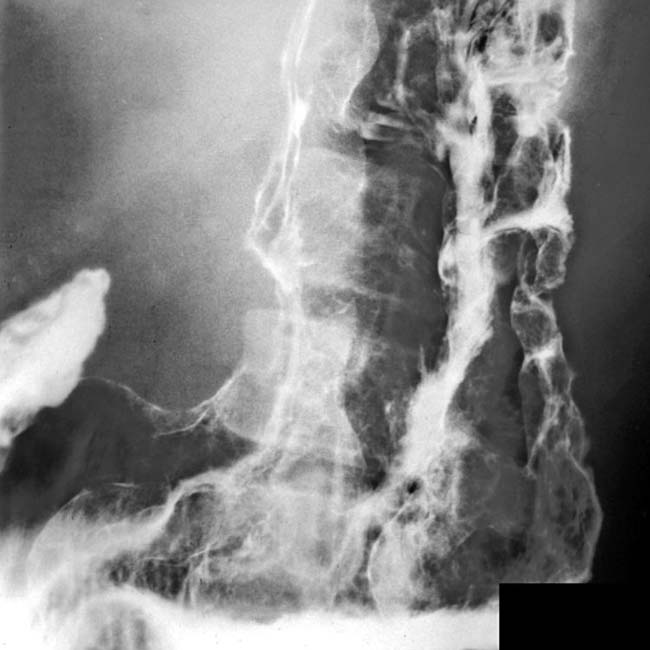
 in the gastric fundus and body, along with engorged gastric vessels
in the gastric fundus and body, along with engorged gastric vessels  . The thick, tortuous folds resemble cerebral convolutions.
. The thick, tortuous folds resemble cerebral convolutions.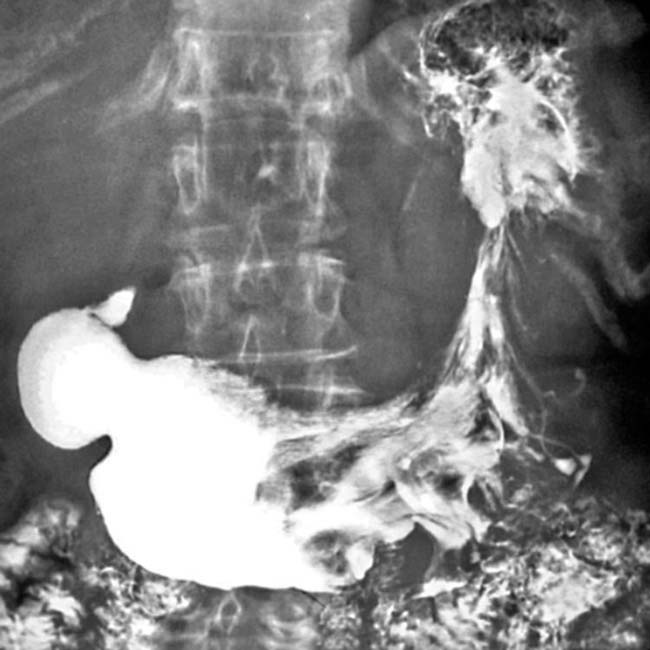
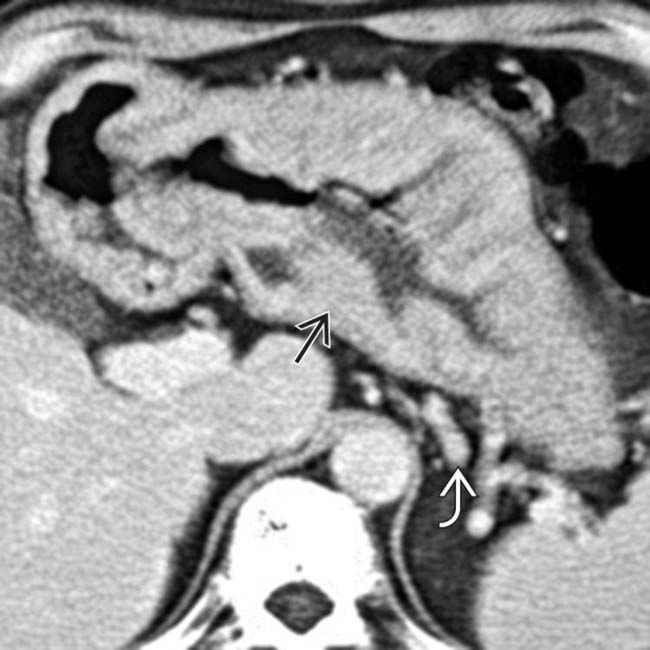
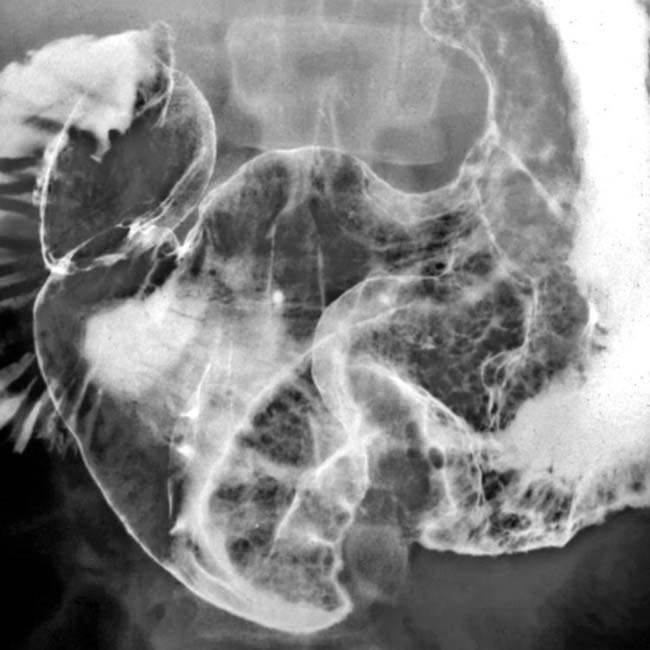
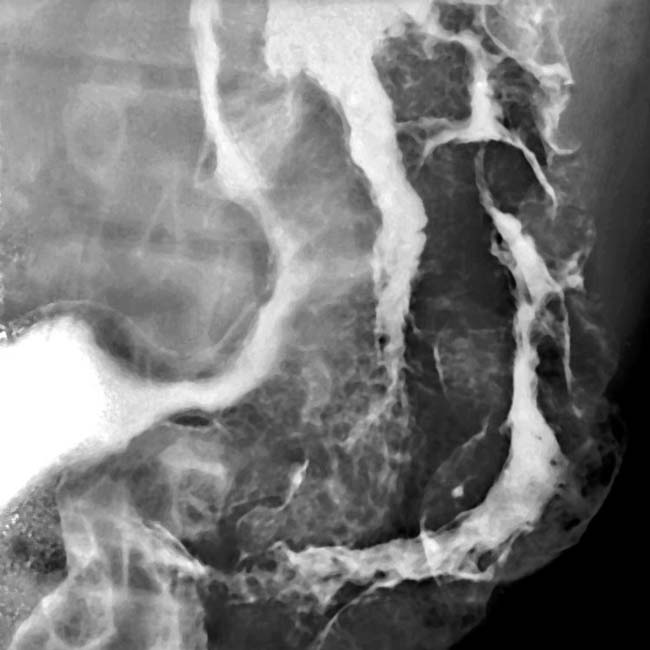
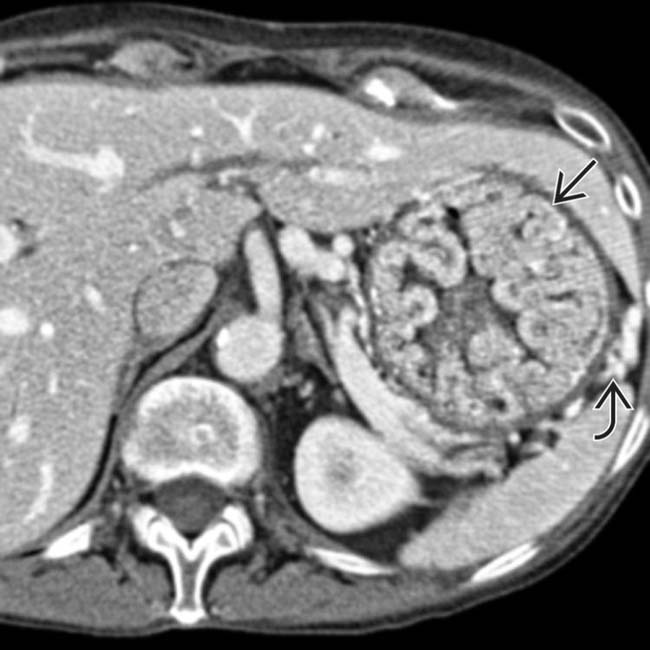
 , but there is no sign of extension into the perigastric tissues. The gastric arterial and venous branches are engorged
, but there is no sign of extension into the perigastric tissues. The gastric arterial and venous branches are engorged  , indicating hyperemia of the stomach.
, indicating hyperemia of the stomach.