Chapter 44 Late Complications of Hematologic Diseases and Their Therapies
Neuropsychologic Sequelae After Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation in Adults
The few studies describing neurocognitive sequelae in adults undergoing hematopoietic cell transplant (HCT) suggest that these patients are at risk for developing adverse sequelae related to neuropsychologic functioning, such as slowed reaction time, reduced attention and concentration, and difficulties in reasoning and problem solving1; memory impairment2–5; problems with executive functioning and processing speed3; and cognitive impairment.1–3 Reduced memory function is associated with older age, longer interval since HCT, chronic graft-versus-host disease, and long-term cyclosporine use.6 Other predictors include fatigue and poor physical functioning. Lower education level and poorer social functioning appear to impact cognitive performance.3 It is therefore prudent to query post-HCT patients regarding perceived deficits in neuropsychologic functioning and to refer patients with these problems to a neuropsychologist who is experienced in the follow-up care of HCT patients.
Evaluating Survivors for Potential Late Effects
Table 44-1 Late Effects Associated With Conventional Therapy for Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia and Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma
| Common Therapeutic Exposures | Potential Late Effects |
|---|---|
| Vincristine | Peripheral neuropathy, Raynaud phenomenon |
| Corticosteroids | Cataracts, osteopenia, osteoporosis, avascular necrosis |
| Asparaginase | No known late effects |
| Mercaptopurine | Hepatic dysfunction (rare) |
| Thioguanine | Portal hypertension, hepatotoxicity (when used continuously in maintenance therapy) |
| Methotrexate (systemic) | Osteopenia, osteoporosis, osteonecrosis, renal dysfunction (rare), hepatic dysfunction (rare) |
| Methotrexate (intrathecal, high-dose), or cytarabine (high-dose) | Neurocognitive deficits, clinical leukoencephalopathy |
| Cranial or craniospinal irradiation | Neurocognitive deficits, clinical leukoencephalopathy, cataracts, hypothyroidism, second malignant neoplasm in radiation field (e.g., skin, thyroid, brain), short stature, scoliosis or kyphosis, obesity |
| Anthracyclines | Cardiomyopathy, arrhythmias, subclinical left ventricular dysfunction, secondary AML |
| Cyclophosphamide | Hypogonadism, hemorrhagic cystitis, dysfunctional voiding, bladder malignancy, secondary AML or MDS |
| Blood products | Chronic viral hepatitis, HIV |
AML, Acute myeloid leukemia; HIV, human immunodeficiency virus; MDS, myelodysplastic syndrome.
Table 44-2 Late Effects Associated With Conventional Therapy for Acute Myeloid Leukemia
| Common Therapeutic Exposures | Potential Late Effects |
|---|---|
| Anthracyclines | Cardiomyopathy, arrhythmias, subclinical left ventricular dysfunction, secondary acute myeloid leukemia |
| Corticosteroids | Cataracts, osteopenia, osteoporosis, avascular necrosis |
| Asparaginase | No known late effects |
| Cytarabine (high dose) | Neurocognitive deficits, clinical leukoencephalopathy |
| Blood products | Chronic viral hepatitis, human immunodeficiency virus infection |
Table 44-3 Late Effects Associated With Conventional Therapy for Hodgkin Lymphoma
| Common Therapeutic Exposures | Potential Late Effects |
|---|---|
| Anthracyclines | Cardiomyopathy, arrhythmias, subclinical left ventricular dysfunction, secondary AML or MDS |
| Corticosteroids | Cataracts, osteopenia, osteoporosis, avascular necrosis |
| Bleomycin | Pulmonary dysfunction |
| Vincristine, vinblastine | Peripheral neuropathy, Raynaud phenomenon |
| Procarbazine, mechlorethamine, dacarbazine | Hypogonadism, infertility, secondary AML or MDS |
| Cyclophosphamide | Hypogonadism, infertility, hemorrhagic cystitis, dysfunctional voiding, bladder malignancy, secondary AML or MDS |
| Mantle irradiation | Hypothyroidism, premature cardiovascular disease, cardiac valvular disease, cardiomyopathy, arrhythmias, carotid artery disease, scoliosis or kyphosis, second malignant neoplasm in radiation field (e.g., thyroid, breast), pulmonary dysfunction |
| Inverted Y irradiation | Hypogonadism, infertility, adverse pregnancy outcome, second malignant neoplasm in radiation field (e.g., gastrointestinal) |
| Splenectomy | Acute life-threatening infections |
| Blood products | Chronic viral hepatitis, HIV |
AML, Acute myeloid leukemia; HIV, human immunodeficiency virus; MDS, myelodysplastic syndrome.
Late Effects Research: What Is Needed
Issues to Be Considered by Physicians Providing Care to This Population
Future Directions
Research is needed to more clearly define the survivors at greatest risk for specific outcomes.
| Topic | Specific Information to Include |
|---|---|
| Demographics | Name |
| Record number or patient identification number | |
| Date of birth | |
| Sex | |
| Race or ethnicity | |
| Diagnosis | Date or age at diagnosis |
| Referring physician or institution | |
| Treating physician or institution | |
| Presenting symptoms | |
| Past medical history | |
| Family history (including cancer in first- or second-degree relatives) | |
| Physical examination findings at presentation | |
| Initial diagnostics (complete blood cell count, chemistry panel, radiographic studies) | |
| Diagnostic procedures (biopsies, cytologic studies) | |
| Pathology (morphology, histology, cytochemistry, flow cytometry) | |
| Cytogenetics | |
| Central nervous system status (if applicable) | |
| Stage (if applicable) | |
| Metastatic sites (if applicable) | |
| Initial response to therapy (e.g., rapid early response [RER], slow early response [SER], date first complete remission achieved) | |
| Relapse(s) dates, age at relapse(s), relapse site(s) | |
| Treatment | Date of initial treatment (initiated and completed) |
| Date(s) for treatment of relapse (initiated and completed) | |
| Final off-therapy date | |
| Chemotherapy agents received, including route of administration (list all) | |
| Cumulative doses (in mg/m2) and age at treatment for all alkylators, anthracyclines, and heavy metals | |
| Dose ranges for cytarabine and methotrexate (e.g., standard dose versus high dose >1000 mg/m2) | |
| Radiation fields, doses, shielding, age at treatment | |
| Surgical procedure(s) | |
| Transfusion(s), including all blood or serum products | |
| Stem cell transplantation(s), including donor source, preparative regimen, GVHD prophylaxis or treatment | |
| Acute complications | Significant therapy-related complications (e.g., tumor lysis, septic shock, typhlitis, acute GVHD) |
| Significant treatment required for complications (e.g., hemodialysis, amphotericin, aminoglycosides) | |
| Complications after therapy | Significant complications after completion of therapy (e.g., herpes zoster, acute life-threatening infection after splenectomy) |
GVHD, Graft-versus-host disease.
Modified from Children’s Oncology Group Summary of Cancer Treatment, 2008. http://www.survivorshipguidelines.org.
Table 44-5 Monitoring for Potential Late Effects
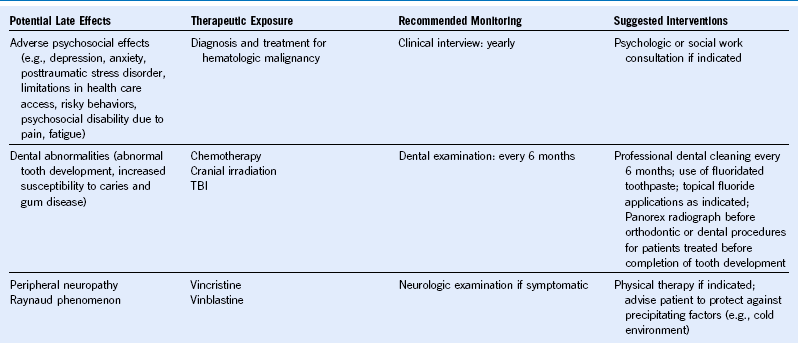
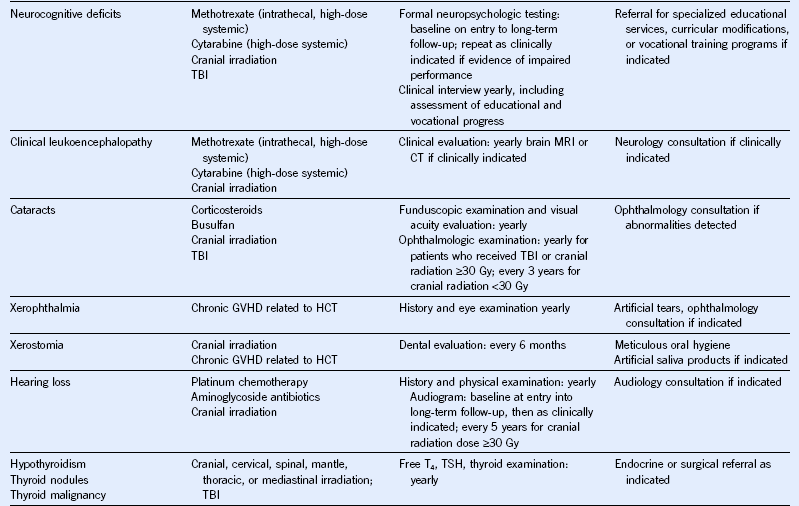
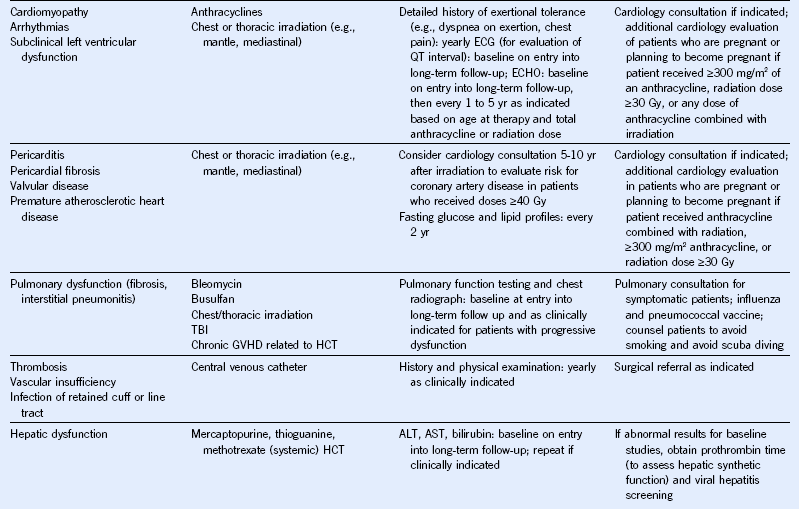
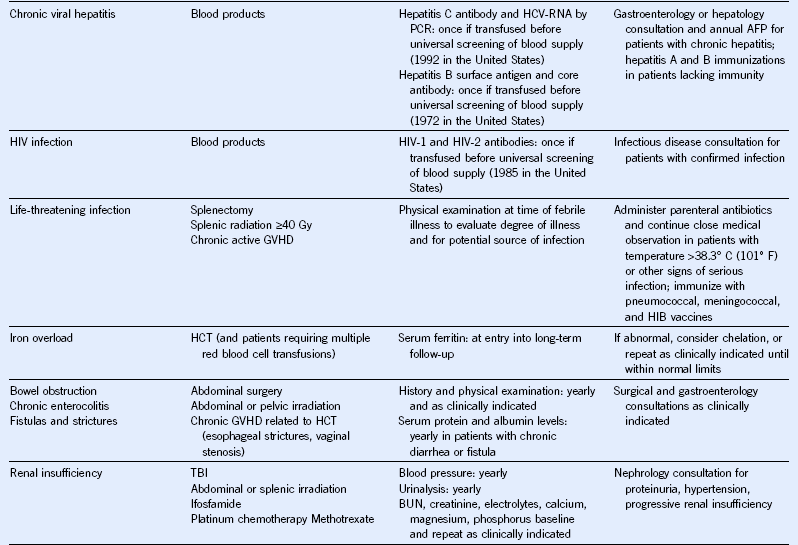
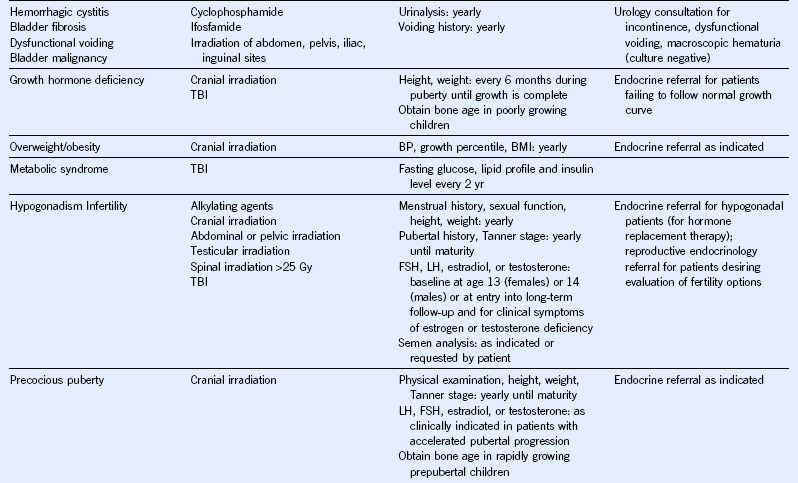
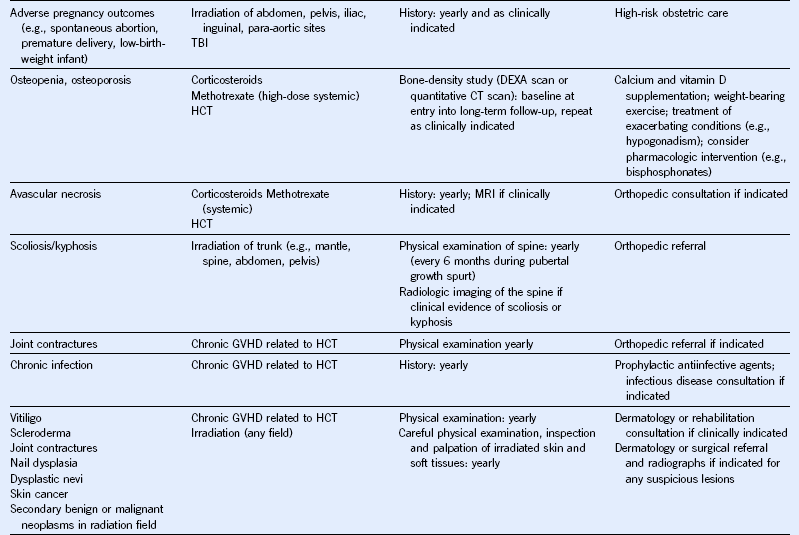
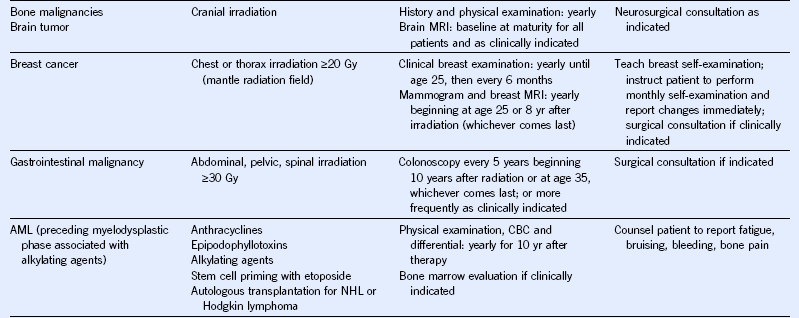
AFP, α-Fetoprotein; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; AML, acute myeloid leukemia; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; BMI, body mass index; BP, blood pressure; BUN, blood urea nitrogen; CBC, complete blood cell count; CT, computed tomography; DEXA, dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry; ECG, electrocardiogram; ECHO, echocardiogram; FSH, follicle-stimulating hormone; GFR, glomerular filtration rate; GVHD, graft-versus-host disease; HCT, hematopoietic cell transplantation; HCV, hepatitis C virus; HIB, Haemophilus influenzae type B; HIV, human immunodeficiency virus; LH, luteinizing hormone; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; NHL, non-Hodgkin lymphoma; PCR, polymerase chain reaction; T4, thyroxine; TBI, total body irradiation; TSH, thyroid-stimulating protein; yr, year.
Modified from Children’s Oncology Group: Long-term follow-up guidelines for survivors of childhood, adolescent, and young adult cancers, version 3.0, 2008, Children’s Oncology Group. http://www.survivorshipguidelines.org.
1 Andrykowski MA, Altmaier EM, Barnett RL, et al. Cognitive dysfunction in adult survivors of allogeneic marrow transplantation: Relationship to dose of total body irradiation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1990;6:269.
2 Andrykowski MA, Schmitt FA, Gregg ME, et al. Neuropsychologic impairment in adult bone marrow transplant candidates. Cancer. 1992;70:2288.
3 Harder H, Cornelissen JJ, Van Gool AR, et al. Cognitive functioning and quality of life in long-term adult survivors of bone marrow transplantation. Cancer. 2002;95:183.
4 Syrjala KL, Dikmen S, Langer SL, et al. Neuropsychologic changes from before transplantation to 1 year in patients receiving myeloablative allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplant. Blood. 2004;104:3386.
5 Meyers CA, Weitzner M, Byrne K, et al. Evaluation of the neurobehavioral functioning of patients before, during, and after bone marrow transplantation. J Clin Oncol. 1994;12:820.
6 Padovan CS, Yousry TA, Schleuning M, et al. Neurological and neuroradiological findings in long-term survivors of allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Ann Neurol. 1998;43:627.