Large Enveloped RNA Viruses
1. This family consists of large viruses with an enveloped, helical nucleocapsid and (–) RNA genome.
B Shared pathogenic properties
• Viral attachment proteins bind to sialic acid or protein receptor.
• A fusion (F) protein or activity promotes envelope fusion with target cell membrane and release of nucleocapsid into cytoplasm.
• Epithelial cells of the upper respiratory tract are the site of initial infection by paramyxoviruses.
• Viremic spread of measles virus and mumps virus leads to infection in various sites throughout the body.
• No viremia occurs with parainfluenza virus and RSV, which remain localized to the respiratory tract.
• Measles virus is a strictly human virus with only one serotype. Infection is usually diagnosed clinically.
• Viremic spread from upper respiratory tract and local lymph nodes can lead to infection of the conjunctiva, urinary tract, small blood vessels, lymphatic system, and central nervous system (CNS).
2. Measles clinical manifestations
• This serious febrile illness has an incubation period of 7 to 13 days.
• Prodromal symptoms include cough, coryza (acute rhinitis), and conjunctivitis (3 Cs).
• Koplik’s spots (diagnostic) appear on buccal membrane after 2 days and last for 1 or 2 days.
• Extensive maculopapular rash, appearing 12 to 24 hours after the Koplik spots, starts below the ears and spreads over the body.
3. Complications of measles infection
• Secondary bacterial infections can cause pneumonia, which accounts for 60% of deaths from measles infection.
• Acute postinfectious encephalitis, an immune-mediated demyelinating disease, has a mortality rate of 15%.
• SSPE, a rare, slow viral infection occurring months to years after primary infection, is caused by defective measles virus in the brain.
• Diagnosis usually made from symptoms
• Confirmation by reverse transcriptase–polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR)
• Immunofluorescence of cells in urinary sediment or pharyngeal cells
• Measles, a highly contagious disease, is spread by virion-containing respiratory droplets both before and after symptoms of infection occur.
• Live attenuated vaccine is given at 15 to 24 months of age and again before entering elementary or junior high school as part of the MMR triple vaccine.
a. Use of killed vaccine is associated with more severe, atypical measles infection on exposure to virus.
• Passive immunization with immune serum globulin is effective in protecting unvaccinated immunocompromised children after exposure to measles virus.
• Mumps virus exists as a single serotype and only infects humans.
• Initial infection in the upper respiratory tract spreads to parotid glands.
• Subsequent viremia can spread infection to the testes, ovaries, thyroid, pancreas, and CNS (in 50% of cases).
2. Mumps clinical manifestations
• Infection with mumps virus often is asymptomatic or accompanied by mild nonspecific symptoms.
• Fever, sudden onset of bilateral swelling of the parotid glands (parotitis), and redness and swelling of the ostium of Stensen duct mark acute disease.
• Orchitis, oophoritis, pancreatitis, and CNS infection may occur after a few days.
• Histologic detection of syncytia in cultured cells infected by virions isolated from saliva (or from swabs taken from the pharynx and Stensen duct), urine, or cerebrospinal fluid
• Hemagglutination inhibition, RT-PCR for genome, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) detection of virions, viral antigens, or antibodies to the virus in clinical samples
• Four serotypes of parainfluenza virus infect the upper respiratory tract.
• Spread of infection to lower respiratory tract (without viremia) occurs in about 25% of cases.
2. Diseases due to parainfluenza viruses
• Croup (laryngotracheobronchitis)
a. Infection of the lower respiratory tract caused by serotypes 1 and 2 (primarily in the fall)
b. Most common in children 2 to 5 years of age
c. Characterized by a “seal bark” cough and tracheal swelling that may block the airway
• Bronchiolitis and pneumonia, caused by serotype 3 (year-round), are most common in infants and elderly patients.
• Mild cold-like syndrome of the upper respiratory tract is caused by serotype 4.
• A single serotype of RSV causes localized infection of the upper and lower respiratory tract.
• This family of large viruses with an enveloped, helical nucleocapsid and segmented (–) RNA genome comprises the influenza viruses.
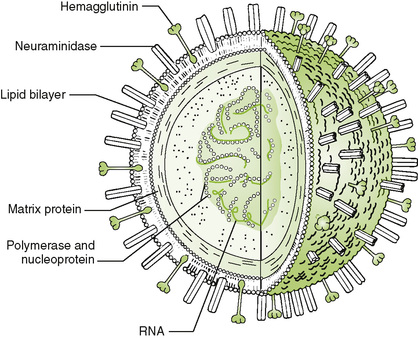
A Key viral proteins (Fig. 24-1)
1. Envelope glycoproteins are the major antigens of influenza virus.
• Hemagglutinin (HA) functions as viral attachment protein and also binds to and aggregates erythrocytes (hemagglutination).
• Neuraminidase (NA), an enzyme that removes sialic acid from virion and host glycoproteins and glycolipids, facilitates release of virions from target cells by minimizing clumping.
2. Nucleoprotein and RNA-dependent RNA polymerase associate with genomic segments to form helical nucleocapsids.
3. M1 (matrix) protein surrounds the nucleocapsid and is involved in virion assembly.
4. M2 (membrane) protein, which forms a proton channel that facilitates uncoating and assembly, is a target for amantadine and rimantadine antiviral drugs.
B Types and genetic changes in influenza viruses
• Of the three types of influenza virus (A, B, and C), type A is the only one that infects animals (zoonosis) and humans.
• Influenza A and B are significant human pathogens; influenza C is less important.
• Only influenza A undergoes antigenic shift.
• Major changes that result from reassortment of genome segments from different human and animal strains
• Random mixing and packaging of genome segments into virions occurs after coinfection with different strains of viruses, producing new hybrid viruses.
• For example, reassortment of swine influenza virus (genome segments S1 to S8) and human influenza virus (segments H1 to H8) could create a new, distinct hybrid strain that contains some swine and some human segments and is capable of infecting humans.
• After HA binds to sialic acid–containing receptors on epithelial cells, virions enter by endocytosis.
2. Fusion with endosome and uncoating
• Release of the nucleocapsid from internalized virion is facilitated by acidification of the endosome and M2 proton channel.
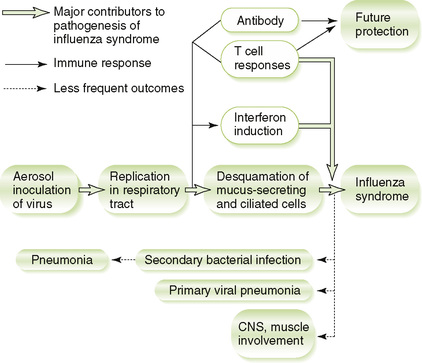
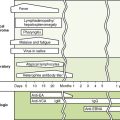
D Pathogenesis and host response (Fig. 24-2)
1. Killing of ciliated and mucus-secreting epithelial cells results from initial infection of upper respiratory tract.
2. Action of viral NA thins out mucous secretions, compromising airway clearance and promoting viral spread to the lungs, as well as secondary bacterial infection.
3. Interferons produced in response to infection help control viral spread but are largely responsible for typical flu-like symptoms.
4. Strain-specific antibody response to HA and NA antigens provides protection against the same but not different strains.
5. Cell-mediated response, which recognizes peptides from less variable proteins (e.g., nucleoprotein), provides more general protection that can help reduce subsequent disease by different strains.
E Diseases due to influenza virus
• Classic acute influenza in adults (Box 24-1)
(1) Malaise and headache during prodrome are followed by myalgia, fever, and nonproductive cough.
(2) Secondary bacterial infection (e.g., sore throat) may occur in the second week.
(1) Disease may be asymptomatic to severe, depending on the degree of existing immunity to the infecting influenza strain and other factors.
(2) Severe illness occurs most often in pregnant women and in patients with immunodeficiencies or cardiorespiratory disease.
1. ELISA and other immunoassays to detect viral antigens in nasal secretions
2. Hemadsorption and hemagglutination to detect the influenza virus in infected cultured cells
3. Hemagglutination inhibition to detect antibodies induced by prior exposure to a specific strain of virus or to identify the virus type, depending on how the assay is set up
1. Respiratory droplets are primary means of spreading influenza virus.
2. Local outbreaks (epidemics) due to antigenic drift (change in viral antigenicity) occur every few years.
3. Widespread outbreaks (pandemics) due to antigenic shift (appearance of new strains) occur about every 10 years.
1. Vaccines consisting of the predicted endemic strains are produced each year.
• Inactivated whole virus or detergent-extracted vaccine
a. Vaccine is produced in embryonated eggs and should not be given to individuals with allergies to eggs.
• Live attenuated aerosol vaccine for patients aged 2 to 49 years.
2. Amantadine and rimantadine, which block uncoating of endocytosed virions, are approved for use against influenza A in unimmunized individuals but are ineffective against influenza B or C.
3. Zanamivir and oseltamivir inhibit neuraminidase and are effective against both influenza A and influenza B.
4. Acetaminophen (not aspirin) can reduce symptoms of influenza.
1. This family consists of large, enveloped viruses with a (+) RNA genome.
2. Virions have a corona-like appearance in electron micrographs.
3. Transmission occurs through respiratory droplets, with infection localized primarily to the respiratory tract.
B Common cold (most common presentation)
1. The disease is similar to that caused by rhinoviruses but with a longer incubation period (3 days).
2. Infection occurs mainly in infants and children, with sporadic outbreaks in winter and spring.
C Gastrointestinal tract infection (uncommon)
• Coronavirus-like particles are occasionally seen in the stools of patients with diarrhea, gastroenteritis, or neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis.
D Severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) (uncommon)
1. An outbreak of this very lethal disease started in China in 2002, and good public health action limited geographic spread.
2. First transmitted to humans through contact with masked palm civets (China) and then from human-to-human contact through respiratory secretions (e.g., hospitals, families).
3. One third of patients improve, and the infection resolves.
4. Diagnose with viral detection by PCR or detection of antibodies