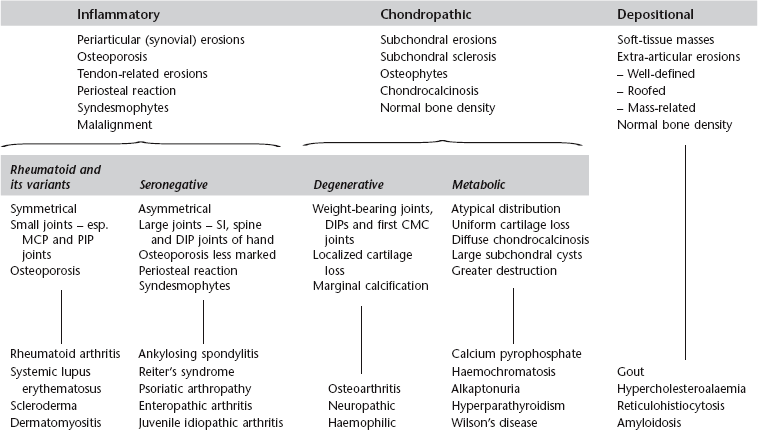
Joints
3.1
Monoarthritis
1. Trauma – pointers to the diagnosis are: (a) the history, (b) the presence of a fracture, and (c) a joint effusion, especially a lipohaemarthrosis.
4. Rheumatoid arthritis* – occasionally. Also juvenile idiopathic arthritis.
5. Pyogenic arthritis – commonest joints affected are the hip, knee and small joints of the hands and feet. 15% of those due to Staphylococcus aureus and 80% of those of gonococcal aetiology involve two or more joints. The joint may be radiographically normal at first presentation.
6. Tuberculous arthritis – insidious onset with radiological changes present at the time of first examination. Erosions first develop at peripheral non-contact points of the joint.
7. Pigmented villonodular synovitis* – most commonly at the knee.
8. Sympathetic – a joint effusion can occur as a response to a tumour in the adjacent bone.
Demertzis, J. L., Rubin, D. A. MR imaging assessment of inflammatory, crystalline-induced, and infectious arthritides [Review]. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am. 2011; 19(2):339–363.
Murphey, M. D., Vidal, J. A., Fanburg-Smith, J. C., Gajewski, D. A. Imaging of synovial chondromatosis with radiologic–pathologic correlation [Review]. Radiographics. 2007; 27(5):1465–1488.
3.3
Arthritis with osteoporosis
2. Juvenile idiopathic arthritis.
3. Systemic lupus erythematosus*.
6. Reiter’s syndrome* – in the acute phase.
3.4
Arthritis with preservation of bone density
2. Calcium pyrophosphate arthropathy – see Calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate deposition disease*.
6. Reiter’s syndrome* – in chronic or recurrent disease.
7. Neuropathic arthropathy* – especially in the spine and extremities.
3.5
Arthritis with a periosteal reaction
1. Juvenile idiopathic arthritis*.
5. Rheumatoid arthritis* – in less than 5% of patients.
3.6
Arthritis with preserved or widened joint space
1. Early infective or inflammatory arthritis – because of joint effusion.
2. Psoriatic arthropathy* – due to deposition of fibrous tissue.
3. Acromegaly* – due to cartilage overgrowth.
3.7
Arthritis with soft-tissue nodules
3.9
Diffuse terminal phalangeal sclerosis
1. Normal variant – in 10% of normal individuals.
2. Rheumatoid arthritis* – most commonly in association with erosive arthropathy but may occur in its absence.
3.10
Calcified loose body (single or multiple) in a joint
1. Detached osteophyte – larger and more variable in size than synovial osteochondromata. Other signs of degenerative arthritis.
3. Osteochondritis dissecans – most commonly the knee, talus and elbow. A corresponding defect in the parent bone may be visible.
4. Neuropathic arthropathy* – joint disorganization.
5. Synovial osteochondromatosis – knee most commonly; hip, ankle, wrist and shoulder less commonly. Multiple small nodules of fairly uniform size. Faintly calcified initially; later ossified. Secondary erosion of intracapsular bone, joint-space narrowing and osteophyte formation may occur later in the disease.
3.12
Sacroiliitis
1. Changes initially in the lower and middle thirds of the joint, and the iliac side is more severely affected than the sacral side.
2. Periarticular osteoporosis, superficial erosions and sclerosis of subchondral bone.
3. Further erosion leads to widening of the joint space.
The most typical patterns of distribution are:
Bilateral symmetrical
1. Ankylosing spondylitis* – may be asymmetrical early in the disease.
2. Inflammatory bowel disease – ulcerative colitis, Crohn’s disease and Whipple’s disease. Identical appearances to ankylosing spondylitis.
3. Psoriatic arthropathy* – ankylosis is less frequent than in ankylosing spondylitis. Occurs in 30–50% of patients with arthropathy. Less commonly is asymmetrical or unilateral.
4. Osteitis condensans ilii – predominantly in young, multiparous women. A triangular segment of bone sclerosis on the inferior aspect of the iliac side of the joint is associated with a well-defined joint margin and a normal joint space.
5. Hyperparathyroidism* – subchondral bone resorption and joint-space widening only.
Bilateral asymmetrical
2. Psoriatic arthropathy* – this pattern in 40% of cases.
3. Rheumatoid arthritis* – rare. Minimal sclerosis and no significant bony ankylosis.
4. Gouty arthritis (see Gout*) – large well-defined erosions with surrounding sclerosis.
5. Osteoarthritis – the articular margins are smooth and well defined. Joint-space narrowing, subchondral sclerosis and anterior osteophytes are observed.
3.13
Protrusio acetabuli
1. Rheumatoid arthritis* – including juvenile idiopathic arthritis.
3. Osteomalacia and rickets (q.v.)*.
6. Osteoarthritis – occasionally.
8. Trauma – acetabular fractures.
10. Marfan’s syndrome* – 45% show evidence of protrusio acetabuli. Of these, 50% are unilateral and 90% have an associated scoliosis.
3.14
Widening of the symphysis pubis
Acquired
1. Pregnancy – resolves by the 3rd postpartum month.
3. Osteitis pubis – one or more months after parturition or pelvic surgery, especially prostatic surgery. It may also be observed as a chronic stress reaction in athletes. Symmetrical bone resorption with subchondral bony irregularity and sclerosis. Ankylosis may be a late finding.
5. Infection – low-grade osteomyelitis shows similar radiological features to osteitis pubis.
6. Ankylosing spondylitis* and rheumatoid arthritis* – early in the disease.
7. Hyperparathyroidism* – due to subperiosteal bone resorption.
3.15
Femoral head and neck abnormalities
Idiopathic
Coxa vara
In coxa vara the femoral angle is reduced so the femoral neck becomes more horizontal.