Bones
1.1
Generalized increased bone density
1.2
Solitary sclerotic bone lesion
1.3
Multiple sclerotic bone lesions
Developmental
2. Osteopoikilosis – asymptomatic. 1–10 mm, round or oval densities in the appendicular skeleton and pelvis. Ribs, skull and spine are usually exempt. Tend to be parallel to the long axis of the affected bones and are especially numerous near the ends of bones.
3. Osteopathia striata (Voorhoeve’s disease) – asymptomatic. Linear bands of dense bone parallel with the long axis of the bone. The appendicular skeleton and pelvis are most frequently affected; skull and clavicles are spared.
Neoplastic
1. Metastases (see 1.18) – most commonly prostate or breast.
4. Multiple healed or healing benign or malignant bone lesions – e.g. lytic metastases following radiotherapy or chemotherapy, eosinophilic granuloma and brown tumours.
5. Multiple myeloma* – sclerosis in up to 3% of cases.
1.4
Bone sclerosis with a periosteal reaction
Idiopathic
1. Infantile cortical hyperostosis (Caffey’s disease) – in infants up to 6 months of age. Multiple bones involved at different times, most frequently mandible, ribs and clavicles; long bones less commonly; spine, hands and feet are spared. Increased density of bones is caused by massive periosteal new bone. In the long bones the epiphyses and metaphyses are spared.
2. Melorheostosis – cortical and periosteal new bone giving the appearance of molten wax flowing down a burning candle. The hyperostosis tends to extend from one bone to the next. Usually affects one limb but both limbs on one side may be affected. Sometimes it is bilateral but asymmetrical. Skull, spine and ribs are seldom affected.
1.6
Conditions involving skin and bone
1.8
Skeletal metastases – most common radiological appearances
1.9
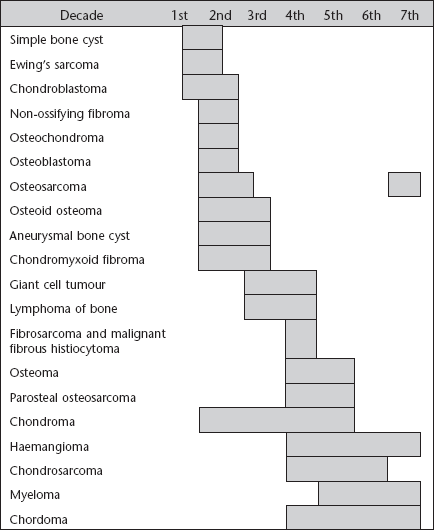
Sites of origin of primary bone neoplasms
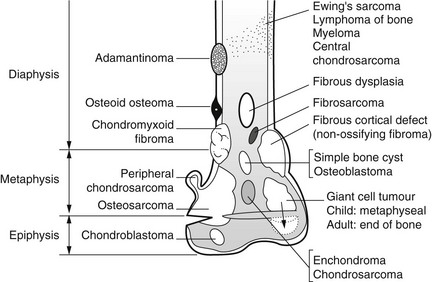
(A composite diagram modified from Madewell et al., 1981.)
1.11
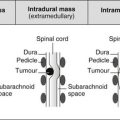
Lucent bone lesion in the medulla – well-defined, marginal sclerosis, no expansion

1.13
Lucent bone lesion in the medulla – ill-defined

Heyning, F. H., Kroon, H. M., Hogendoorn, P. C., et al. MR imaging characteristics in primary lymphoma of bone with emphasis on non-aggressive appearance. Skeletal Radiol. 2007; 36(10):937–944.
Nichols, R. E., Dixon, L. B. Radiographic analysis of solitary bone lesions [Review]. Radiol Clin North Am. 2011; 49(6):1095–1114.
1.16
Subarticular lucent bone lesion
Arthritides
1. Osteoarthritis – may be multiple ‘cysts’ in the load-bearing areas of multiple joints. Surrounding sclerotic margin. Joint-space narrowing, subchondral sclerosis and osteophytes.
2. Rheumatoid arthritis* – no sclerotic margin. Begins periarticularly near the insertion of the joint capsule. Joint-space narrowing and juxta-articular osteoporosis.
3. Calcium pyrophosphate arthropathy (see Calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate deposition disease*) – similar to osteoarthritis but frequently larger and with more collapse and fragmentation of the articular surface.
4. Gout – ± erosions with overhanging edges and adjacent soft-tissue masses.
1.17
Lucent bone lesion – containing calcium or bone
1.18
‘Moth-eaten bone’ in an adult

1.19
Regional osteopenia
Decreased bone density confined to a region or segment of the appendicular skeleton.
1. Disuse – during the immobilization of fractures, in paralysed segments and in bone and joint infections. Usually appears after 8 weeks of immobilization. The patterns of bone loss may be uniform (commonest), spotty (mostly periarticular), band-like (subchondral or metaphyseal) or endosteal cortical scalloping and linear cortical lucencies.
2. Sudeck’s atrophy (reflex sympathetic dystrophy syndrome) – is mediated via a neurovascular mechanism and associated with post-traumatic and postinfective states, myocardial infarction, calcific tendinosis and cervical spondylosis. It most commonly affects the shoulder and hand and develops rapidly. Pain and soft-tissue swelling are clinical findings.
3. Transient osteoporosis of the hip – a severe, progressive osteoporosis of the femoral head and, to a lesser degree, of the femoral neck and acetabulum. Full recovery is seen in 6 months.
4. Regional migratory osteoporosis – pain, swelling and osteoporosis affect the joints of the lower limbs in particular. The migratory nature differentiates it from other causes. Marrow oedema in affected areas is seen as low signal on T1W and high signal on T2W MRI.
1.20
Generalized osteopenia
1. Osteoporosis – diminished quantity of normal bone.
2. Osteomalacia* – normal quantity of bone but it has an excess of uncalcified osteoid.
3. Hyperparathyroidism* – increased bone resorption by osteoclasts.
4. Diffuse infiltrative bone disease – e.g. multiple myeloma and leukaemia.
1.21
Osteoporosis
2. Cortical thinning with a relative increase in density of the cortex and vertebral end-plates. Skull sutures are relatively sclerotic.
3. Relative accentuation of trabecular stress lines because of resorption of secondary trabeculae.
4. Brittle bones with an increased incidence of fractures, especially compression fractures of vertebral bodies, femoral neck and wrist fractures.
1.22
Renal disease
1. Glomerular disease (renal osteodystrophy*).
(b) Fanconi syndrome – osteomalacia or rickets, growth retardation, RTA, glycosuria, phosphaturia, aminoaciduria and proteinuria. It is most commonly idiopathic in aetiology but may be secondary to those causes of RTA given above.
(c) Vitamin D-resistant rickets (familial hypophosphataemia, X-linked hypophosphataemia) – short stature developing after the first 6 months of life, genu varum or valgum, coxa vara, waddling gait. Radiographic changes are more severe in the legs than the arms.
1.23
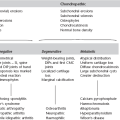
Periosteal reactions – types
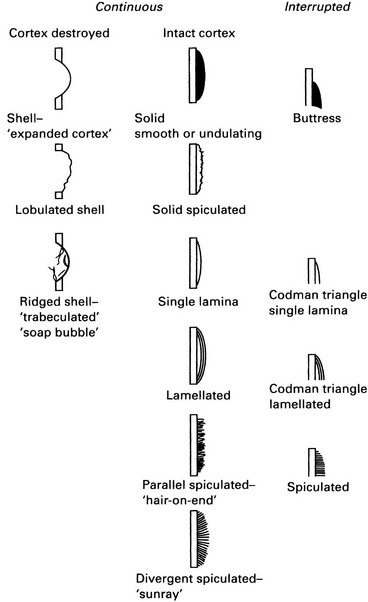
(Modified from Ragsdale et al., 1981.)
1.28
Excessive callus formation
1. Steroid therapy and Cushing’s syndrome*.
2. Neuropathic arthropathy* – including congenital insensitivity to pain.
1.29
Stress fractures – sites and causations
| Site | Activity |
| Lower cervical/upper thoracic spinous processes | Clay shovelling |
| Pars interarticularis | Ballet; heavy lifting; scrubbing floors |
| Obturator ring | Stooping; bowling; gymnastics |
| Ribs | Carrying heavy pack; coughing; golf |
| Coracoid process of scapula | Trap shooting |
| Humerus – distal shaft | Throwing a ball |
| Hamate | Golf; tennis; baseball |
| Ulna – coronoid | Pitching a ball |
| Ulna – shaft | Pitchfork worker; propelling a wheelchair |
| Femur – neck | Ballet; marching; long-distance running; gymnastics |
| Femur – shaft | Ballet; long-distance running |
| Patella | Hurdling |
| Fibula – proximal shaft | Jumping; parachuting |
| Fibula – distal shaft | Long-distance running |
| Tibia – proximal shaft | Running |
| Tibia – mid and distal shaft | Ballet; long-distance running |
| Calcaneus | Jumping; parachuting; prolonged standing |
| Navicular | Marching; long-distance running |
| Metatarsal – shaft | Marching; prolonged standing; ballet |
| Sesamoids of metatarsals | Prolonged standing |
(Modified from Daffner, 1978.)
1.30
Avascular necrosis
Toxic
1. Steroids* – probably does not occur with less than 2 years of treatment.
2. Alcohol – possibly because of fat emboli in chronic alcoholic pancreatitis.
4. Anti-inflammatory drugs – indometacin and phenylbutazone.
1.33
Focal rib lesion (solitary or multiple)
Neoplastic
Secondary more common than primary. Primary malignant more common than benign.
1.34
Rib notching – inferior surface
Arterial
1. Coarctation of the aorta – rib signs are unusual before 10 years of age. Affects 4th–8th ribs bilaterally; not the upper two if conventional. Unilateral and right-sided if the coarctation is proximal to the left subclavian artery. Unilateral and left-sided if associated with an anomalous right subclavian artery distal to the coarctation. Other signs include a prominent ascending aorta and a small descending aorta with an intervening notch, left ventricular enlargement and possibly signs of heart failure.
2. Aortic thrombosis – usually the lower ribs bilaterally.
3. Subclavian obstruction – most commonly after a Blalock operation (either subclavian-to-pulmonary artery anastomosis) for Fallot’s tetralogy. Unilateral rib notching of the upper three or four ribs on the operation side.
4. Pulmonary oligaemia – any cause of decreased pulmonary blood supply.
1.38
Carpal fusion
1.39
Short metacarpal(s) or metatarsal(s)
As the sole or predominant abnormality.
2. Post-traumatic – iatrogenic, fracture, growth plate injury, thermal or electrical.
3. Postinfarction – e.g. sickle-cell anaemia*.
4. Turner’s syndrome* – 4th ± 3rd and 5th metacarpals.
5. Pseudohypoparathyroidism and pseudopseudohypoparathyroidism* – 4th and 5th metacarpals.
1.40
Arachnodactyly
Arachnodactyly range 8.4–10.4.
1. Marfan’s syndrome* – although arachnodactyly is not necessary for the diagnosis.
2. Homocystinuria* – morphologically resembles Marfan’s syndrome but 60% are mentally handicapped, they have a predisposition to arterial and venous thromboses and the lens of the eye dislocates downward rather than upward.
1.41
Distal phalangeal destruction
NB. Because of reinforced Sharpey’s fibres, periosteal reaction is rare at this site.
Resorption of the tuft
3. Psoriatic arthropathy* – can precede the skin changes.
4. Neuropathic diseases – diabetes mellitus, leprosy, myelomeningocoele, syringomyelia and congenital indifference to pain.
5. Thermal injuries – burns, frostbite and electrical.
9. Porphyria – due to cutaneous photosensitivity leading to blistering and scarring.
10. Phenytoin toxicity – congenitally in infants of epileptic mothers.
11. Snake and scorpion venom – due to tissue breakdown by proteinases.
Poorly defined lytic lesions
1. Osteomyelitis – mostly staphylococcal with diabetics at particular risk. Periosteal reaction is infrequent.
2. Metastases – bronchus is the most common primary site. Bone metastases to the hand are commonest in the terminal phalanx and may be the only metastasis to bone. The subarticular cortex is usually the last to be destroyed.
4. Aneurysmal bone cyst* – rare at this site. Marked thinning and expansion of cortex.
5. Giant cell tumour* – usually involving the base of the phalanx.
6. Leprosy – at any age, but 30% present before 15 years of age.
Well-defined lytic lesions
1. Implantation dermoid/epidermoid cyst – an expanding lesion. 1–20 mm, with minimal sclerosis ± soft-tissue swelling.
3. Sarcoidosis* – associated ‘lace-like’ destruction of phalangeal shaft, subperiosteal erosion leading to resorption of terminal tufts and endosteal sclerosis.
4. Glomus tumour – soft-tissue swelling with disuse osteoporosis because of pain. Bone involvement is uncommon but there may be pressure erosion or a well-defined lytic lesion.
1.43
Increased uptake on bone scans
1. Metastatic disease – multiple, randomly scattered lesions especially in the axial skeleton.
2. Joint disease – commonly degenerative in the cervical spine, hips, hands and knees. Also inflammatory joint disease.
(a) Aligned fractures in ribs are traumatic.
(b) Single lesions elsewhere – always ask if history of trauma.
4. Postsurgery – after joint replacement. Increased uptake lasts 1 year.
5. Paget’s disease* – diffuse involvement with much increased uptake often starting from bone end. Commonly affects the pelvis, skull, femur and spine. Involvement of the whole of the vertebra is typical.
6. Superscan – high uptake throughout the skeleton often due to disseminated secondary disease with poor or absent renal images but often with bladder activity.
7. Metabolic bone disease – high uptake in the axial skeleton, proximal long bones, with prominent calvarium and mandible. Faint or absent kidney images.
8. Dental disease – inflammation, recent extraction.
9. Infection – increased uptake in vascular and blood pool phases also.
1.44
Increased uptake on bone scans not due to skeletal abnormality
Artefacts
1.45
Photopenic areas (defects) on bone scans
1. Artefacts – the commonest cause.
2. Avascular lesions – e.g. cysts.
3. Multiple myeloma* – may show increased uptake.
4. Metastases – lytic: renal, thyroid, lung.
5. Leukaemia – may show increased uptake.
6. Haemangiomas of the spine – occasionally slightly increased uptake.