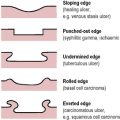
CHAPTER 3 Investigative procedures
Conventional radiology
• A plain radiograph is one where no contrast medium is administered to the patient, e.g. routine CXR.
• A contrast study involves administration of a contrast medium, which outlines or delineates the structure under study, e.g. barium in GI studies or iodinated benzoic acid derivatives in arteriography.
Plain films
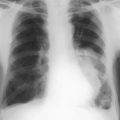
Chest X-ray (CXR)
• Make sure the whole chest and diaphragm are clearly on the film. You may need to count the ribs to exclude a cervical rib.
• Check cardiothoracic ratio. Maximum width of heart divided by maximum ‘bony’ (rib-to-rib) diameter of chest should be <50% in normal adults.
• Check vascular pattern, e.g. reduced in recent pulmonary embolus, distension of upper lobe veins in pulmonary venous hypertension.
Abdominal X-ray (AXR)
• Free intraperitoneal gas (check position in which film was taken, e.g. air under the diaphragm with perforated hollow viscus)
• Abnormal gas patterns, e.g. air in biliary tree with cholecystoduodenal fistula and gallstone ileus, bladder with colovesical fistula
• Calcified calculi – kidney, ureter, bladder, gallbladder; 10% of gallbladder stones are radio-opaque and 85% of renal stones are radio-opaque
• Abnormal calcification, e.g. arteriosclerotic vessels, pancreatic calcification seen with chronic pancreatitis (rarely carcinoma of the pancreas calcifies), uterine fibroids