Smooth muscle is replaced by fibrous tissue
• Small bowel
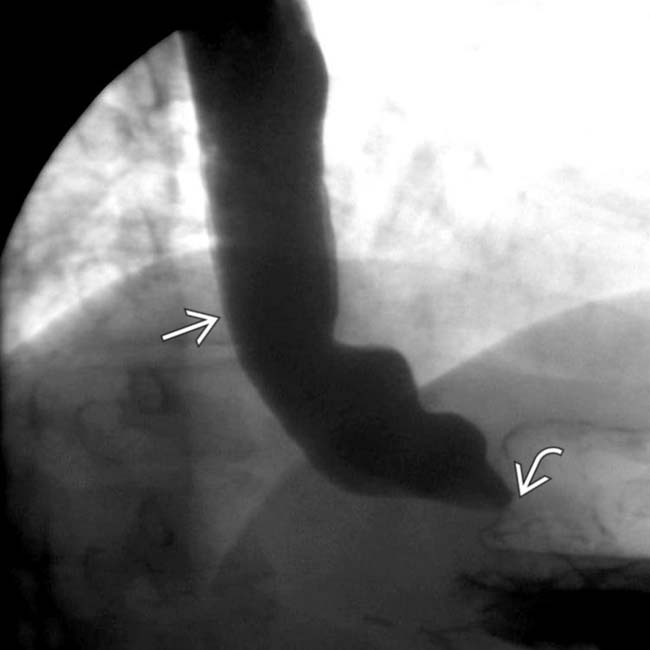
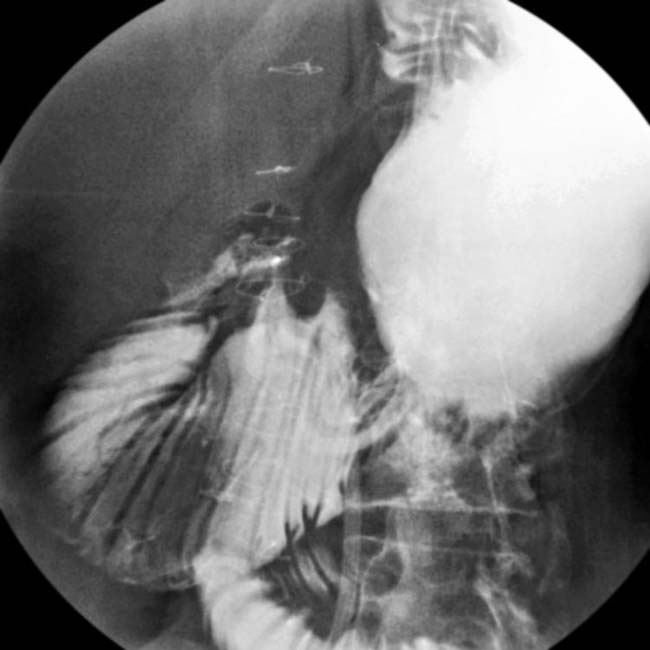
 that is slow to empty due to a distal esophageal, peptic stricture
that is slow to empty due to a distal esophageal, peptic stricture  .
.
 with slow transit. “Pseudo-obstruction” is another descriptive term relevant to this case.
with slow transit. “Pseudo-obstruction” is another descriptive term relevant to this case.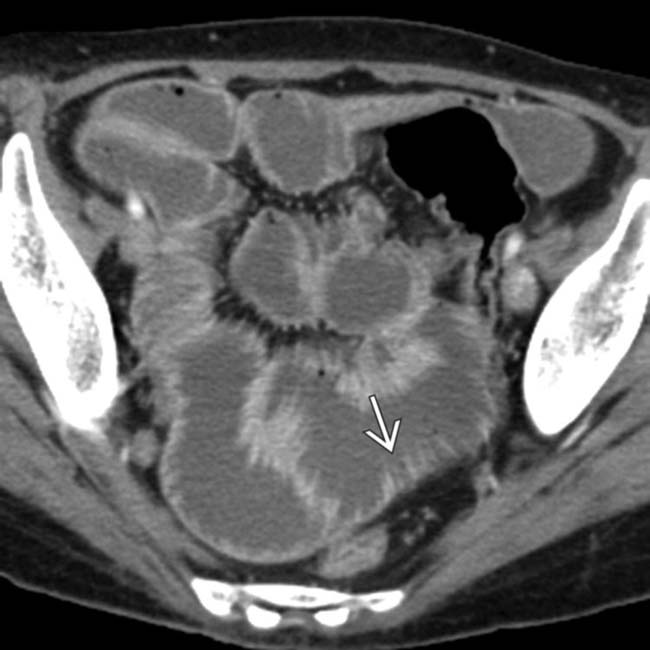
 and diffusely dilated lumen, classic features of scleroderma with pseudo-obstruction.
and diffusely dilated lumen, classic features of scleroderma with pseudo-obstruction.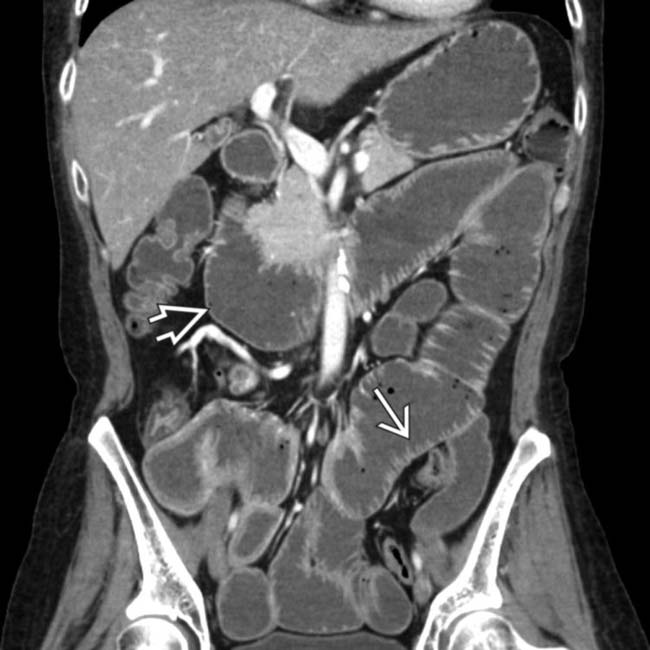
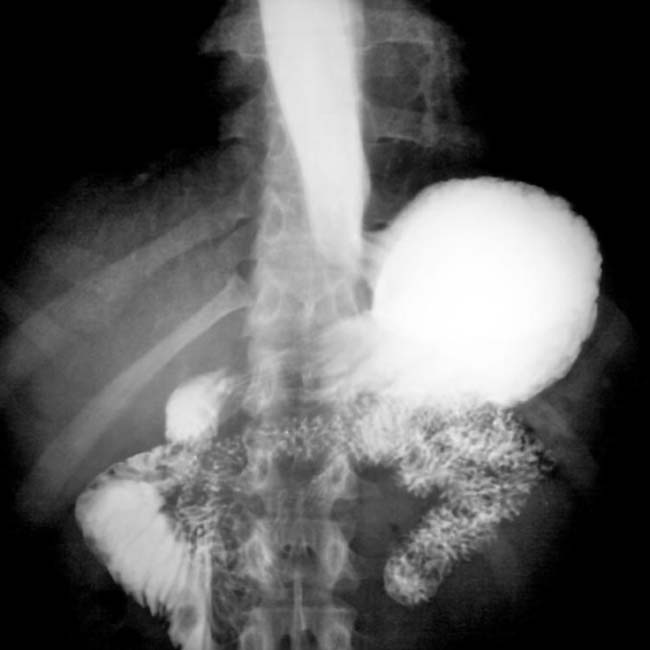
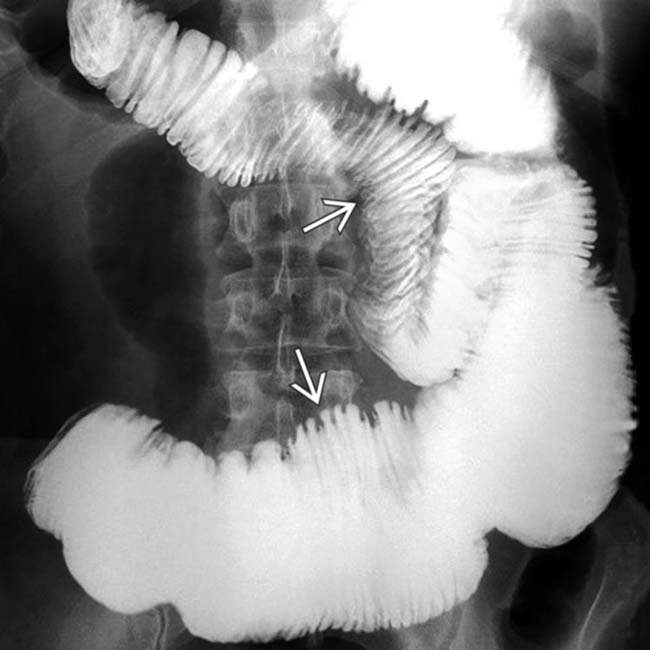
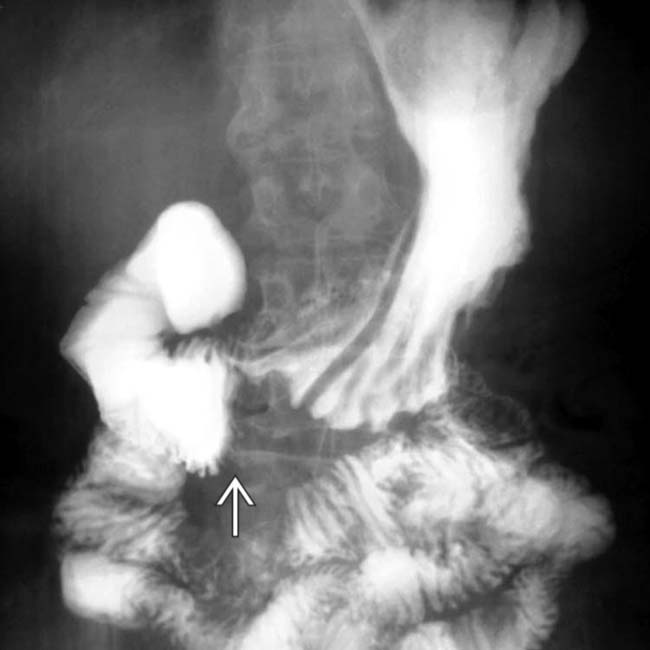
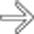
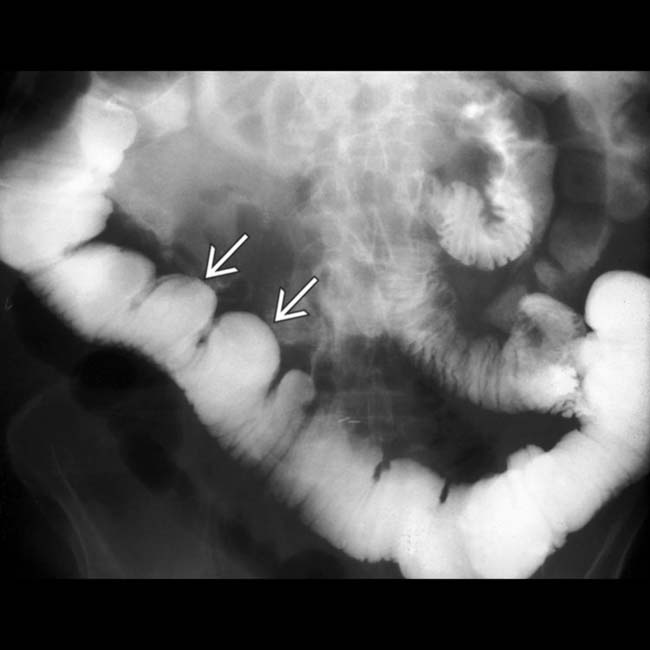
 (particularly in the jejunum), a characteristic feature of scleroderma. Also note the disproportionate dilation of the duodenum
(particularly in the jejunum), a characteristic feature of scleroderma. Also note the disproportionate dilation of the duodenum  , another common feature of scleroderma.
, another common feature of scleroderma.IMAGING
General Features
Radiographic Findings
• Small bowel follow-through
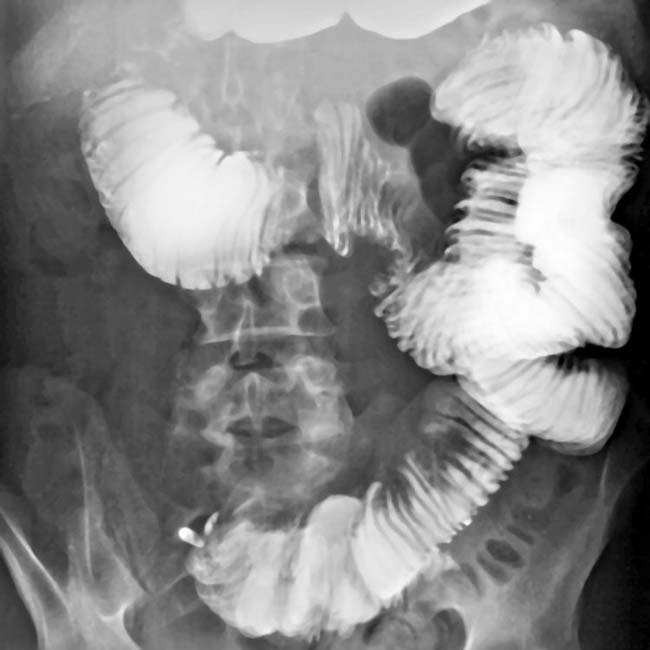
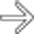
 Marked dilatation of small bowel (particularly 2nd and 3rd parts of duodenum and jejunum)
Marked dilatation of small bowel (particularly 2nd and 3rd parts of duodenum and jejunum)
 Marked dilatation of small bowel (particularly 2nd and 3rd parts of duodenum and jejunum)
Marked dilatation of small bowel (particularly 2nd and 3rd parts of duodenum and jejunum)
 as it crosses the spine.
as it crosses the spine.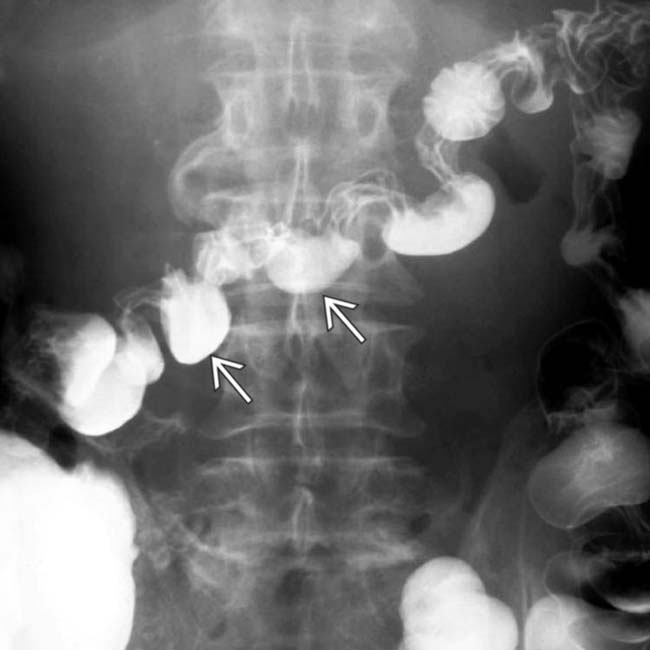
 along the mesenteric border. These reflect the muscle atrophy within the bowel wall and its replacement by collagen and fibrosis.
along the mesenteric border. These reflect the muscle atrophy within the bowel wall and its replacement by collagen and fibrosis.
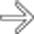 as it crosses the spine. The transverse folds of the jejunum
as it crosses the spine. The transverse folds of the jejunum  are thin and abnormally close together.
are thin and abnormally close together.

































































 and abnormal folds in the small bowel.
and abnormal folds in the small bowel.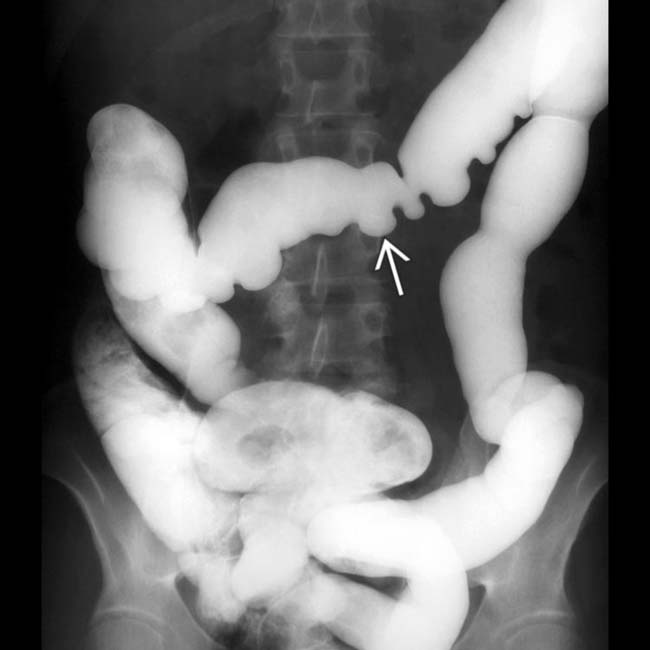
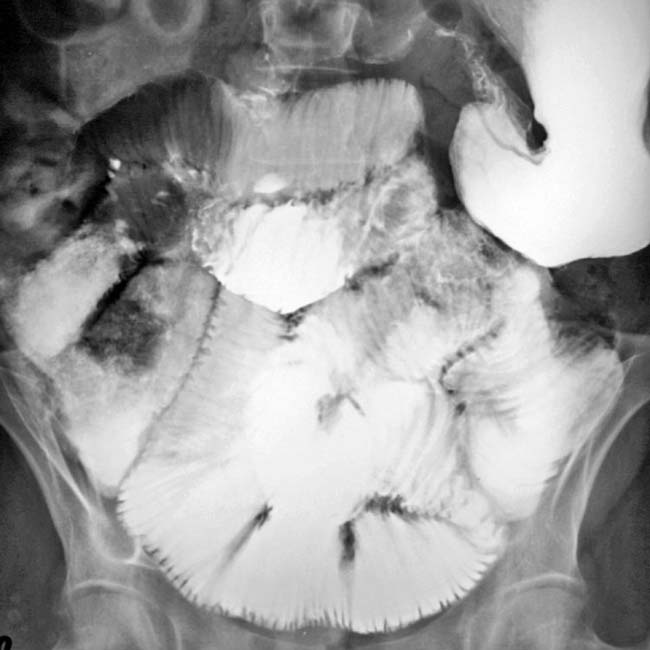
 of the transverse colon and loss of a normal haustral pattern throughout most of the colon, all due to scleroderma.
of the transverse colon and loss of a normal haustral pattern throughout most of the colon, all due to scleroderma.