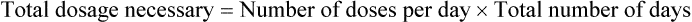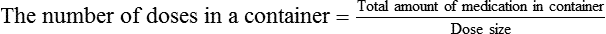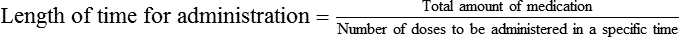Interpreting Physicians’ Orders for Dosages
• Calculate total dosage of medication when quantity is unknown
• Calculate number of doses of medication from total dosage presented on a prescription
• Calculate the number of doses in a prescription if medication is taken according to a physician’s order, including duration in days
• Read and interpret prescriptions to calculate doses and dosages
Pretest
![]() 1 A physician prescribes amoxicillin suspension 250 mg/5 mL 150 mL to be taken 1 teaspoonful three times a day until the entire amount has been taken. A dosespoon is to be included with the prescription.
1 A physician prescribes amoxicillin suspension 250 mg/5 mL 150 mL to be taken 1 teaspoonful three times a day until the entire amount has been taken. A dosespoon is to be included with the prescription.
How many days would the medication last? __________
What total volume of amoxicillin would be administered daily? __________
How many milligrams of antibiotic would the child receive daily? __________
Indicate label directions using a dosespoon. __________
What dose of medication would the person receive with each administration? __________
![]()
![]() 2 A physician prescribes furosemide 20 mg po daily × 1 mo
2 A physician prescribes furosemide 20 mg po daily × 1 mo 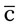 refills × 2. The available medication is furosemide 40 mg/tablet.
refills × 2. The available medication is furosemide 40 mg/tablet.
How many tablets would the patient take daily from the available stock medication? __________
How many tablets would be provided for a month’s supply to the patient from the stock bottle? __________
![]() 3 Using the provided prescription, how many tablets are necessary to fill the prescription? __________
3 Using the provided prescription, how many tablets are necessary to fill the prescription? __________
![]() 4 A physician prescribes NPH insulin 80 units qam. The vial contains 10 ml of NPH insulin U-100. Indicate the amount of medication on the syringe so that you can supply patient instruction for self-administration.
4 A physician prescribes NPH insulin 80 units qam. The vial contains 10 ml of NPH insulin U-100. Indicate the amount of medication on the syringe so that you can supply patient instruction for self-administration.
How many days would this vial of medication last? __________
If the patient needs the insulin for 1 month, how many vials of medication would be necessary? __________
![]() 5 An order is written for the preparation of CEFTIZOXIME 500 mg in 50 mL of D-5-W to be infused at the rate of 50 mg/kg per day. CEFTIZOXIME is available for dilution at 1 g/10 mL of sterile water.
5 An order is written for the preparation of CEFTIZOXIME 500 mg in 50 mL of D-5-W to be infused at the rate of 50 mg/kg per day. CEFTIZOXIME is available for dilution at 1 g/10 mL of sterile water.
How many milliliters of infusion would a patient weighing 88 lb receive per day? __________
If this is to be administered in divided doses q6h, how many milliliters would the patient receive with each dose? __________
How many milligrams would the patient receive per day? __________
How many milligrams would the patient receive with each dose? __________
![]() 6 A physician prescribes Vibramycin 100 mg po tab ii stat and repeat in 12 hours. The prescription then reads to provide the patient with 100 mg/d for one week.
6 A physician prescribes Vibramycin 100 mg po tab ii stat and repeat in 12 hours. The prescription then reads to provide the patient with 100 mg/d for one week.
How many Vibramycin 100 mg tabs would be supplied to fill the prescription? __________
How many milligrams would the patient receive with the first dose? __________
![]() 7 A physician orders AMPICILLIN 0.2 g/kg/d IV in divided doses q6h. The physician wants AMPICILLIN 500 mg to be added to each 100 mL of D-5-W. AMPICILLIN is available in 500 mg vials for reconstitution with 1.2 mL of diluent. The patient weighs 110 lb.
7 A physician orders AMPICILLIN 0.2 g/kg/d IV in divided doses q6h. The physician wants AMPICILLIN 500 mg to be added to each 100 mL of D-5-W. AMPICILLIN is available in 500 mg vials for reconstitution with 1.2 mL of diluent. The patient weighs 110 lb.
How many milliliters of D-5-W would be necessary for the addition for each dose of the AMPICILLIN according to physician orders for dilution? __________
How many milligrams would the patient receive with each dose? __________
How many grams of AMPICILLIN would the patient receive daily? __________
How many total milliliters of fluids would the patient receive daily? __________
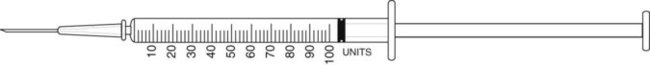
![]() 8 Use the prescription provided to make the necessary calculations. The tablet is available as Toprol-XL 25 mg.
8 Use the prescription provided to make the necessary calculations. The tablet is available as Toprol-XL 25 mg.
How many tablets would be necessary to fill the prescription for a month’s supply? __________
What metric weight of drug would the patient receive with each dose? __________
Interpret the prescription as written. __________
Indicate prescription label directions. __________
![]() 9 A patient weighing 198 lb is to receive chloramphenicol 50 mg/kg/d in divided doses q4h to be administered in D-5-NS 500 mL for a Salmonella typhi infection. The available medication is in 1-g vials at 100 mg/mL.
9 A patient weighing 198 lb is to receive chloramphenicol 50 mg/kg/d in divided doses q4h to be administered in D-5-NS 500 mL for a Salmonella typhi infection. The available medication is in 1-g vials at 100 mg/mL.
Hint: Only full vials are available for use.
How many milliliters of chloramphenicol are in a full vial? __________
How many milliliters of chloramphenicol would be added to each container of fluids for the ordered dose? __________
How many vials of chloramphenicol would be necessary to supply the daily chloramphenicol for the physician’s order? __________
Explain your answer. _____________________________________________________________
![]() 10 A child has a streptococcal infection of the throat. The child weighs 66 lb. The physician tells the pharmacist to supply the accurate amount of medication so that the child receives erythromycin 40 mg/kg/day in divided doses to be administered q6h for 10 days. The medication is available as erythromycin 200 mg chewable tablets.
10 A child has a streptococcal infection of the throat. The child weighs 66 lb. The physician tells the pharmacist to supply the accurate amount of medication so that the child receives erythromycin 40 mg/kg/day in divided doses to be administered q6h for 10 days. The medication is available as erythromycin 200 mg chewable tablets.
What would the prescription label read for the prescription with the medication shown as available? __________
If the parent states that the child will not chew the tablet but will take oral liquids, after obtaining the physician’s permission, what volume of medication would be supplied to the child with each dose if the erythromycin is available as 400 mg/5 mL? __________
How would the label read in household measurements? __________
How many tablets would be necessary to complete the order if chewable tablets are used? __________
How many milliliters of medication would be used to prepare the prescription? __________
Using a choice of utensils for dispensing with the medication, what utensil should be chosen for more exact administration of the medication at home? __________
Hint: Go back to Chapter 7 to see available utensils.
![]() 11 The patient presents the provided prescription for preparation. The patient has no drug insurance coverage and wants 2 months’ supply. The prescription has prn refills for one year. The medication is available in 40-mg capsules.
11 The patient presents the provided prescription for preparation. The patient has no drug insurance coverage and wants 2 months’ supply. The prescription has prn refills for one year. The medication is available in 40-mg capsules.
How many capsules would be prepared for the amount of medication requested? __________
Interpret the prescription as written. __________
Indicate prescription label directions. __________

![]() 12 A physician prescribes amoxicillin 62.5 mg po tid for 10 days for a child weighing 44 lb. Available is amoxicillin 125 mg/5 mL in 100-mL and 150-mL containers.
12 A physician prescribes amoxicillin 62.5 mg po tid for 10 days for a child weighing 44 lb. Available is amoxicillin 125 mg/5 mL in 100-mL and 150-mL containers.
Which container of amoxicillin would be provided for the prescription? __________
What quantity of the medication would the parents give to provide the correct dose? __________
How much medication would be discarded if the orders are followed correctly? __________
Indicate prescription label directions for the prescription using household measurements. ___________________________________________________________________
![]() 13 A physician writes a prescription for Humulin N 65 units subcutaneously qam and qpm. The prescription also contains an order for Humulin R 25 units subcutaneously with the afternoon dose.
13 A physician writes a prescription for Humulin N 65 units subcutaneously qam and qpm. The prescription also contains an order for Humulin R 25 units subcutaneously with the afternoon dose.
How many 10-mL vials of Humulin N (100 units/mL) are necessary for a month’s supply? __________
How many 10-mL vials of Humulin R (100 units/mL) are necessary for a month’s supply? __________
What size insulin syringes should be supplied to administer both injections? __________
Indicate the volume of medication to be administered in am and in pm on the appropriate syringe. Label the time for the appropriate syringe.
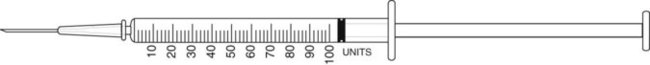
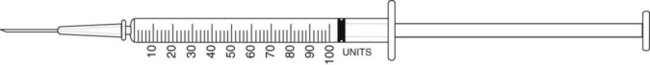
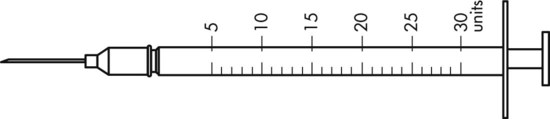
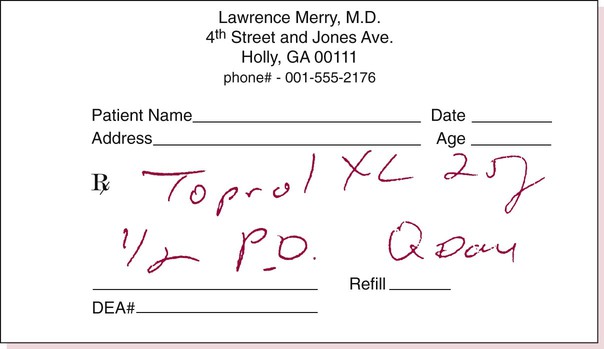
![]() 14 A physician prescribes atenolol 75 mg po qam and 25 mg po at bedtime. The available stock medication is atenolol 50 mg.
14 A physician prescribes atenolol 75 mg po qam and 25 mg po at bedtime. The available stock medication is atenolol 50 mg.
How many tablets would be necessary for a 30-day supply? __________
Indicate prescription label directions. _____________________________________________
![]() 15 A physician prescribes ibuprofen liquid 10 mg/kg to be administered po qid prn for pain for a child who weighs 66 lb. The available medication is 100 mg/5 mL. The volume of medication to be dispensed is 8 ounces.
15 A physician prescribes ibuprofen liquid 10 mg/kg to be administered po qid prn for pain for a child who weighs 66 lb. The available medication is 100 mg/5 mL. The volume of medication to be dispensed is 8 ounces.
How many milliliters of medication would be needed for one day? __________
How many milliliters of medication would be administered to the child with each dose? __________
How many doses of medication are available in this prescription? __________
Indicate the prescription label directions. __________________________________________
Preparing Medications When The Quantity For Dispensing Is Unknown
< ?xml:namespace prefix = "mml" />
Example 14-1
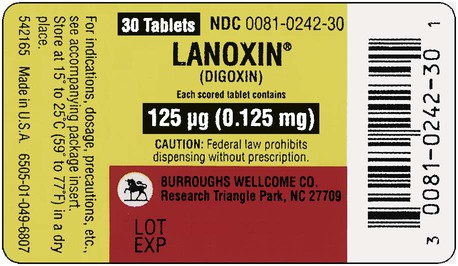
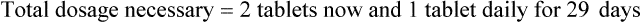
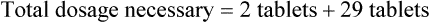
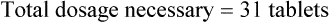
Prescription label directions: Take two tablets now then one tablet daily
Practice Problems A
1. ![]() A physician prescribes phenobarbital gr
A physician prescribes phenobarbital gr 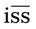 po q6h for epilepsy. The order is to provide a month’s supply with each prescription refill.
po q6h for epilepsy. The order is to provide a month’s supply with each prescription refill.

Using the provided label, how many tablets would be provided for the patient? __________
What is the dose q6h in tablets? __________
What is the dose in milligrams? __________
Indicate prescription label directions. _____________________________________________
2. ![]() A physician prescribes Voltaren 50 mg po tid with meals or snack. How many tablets are necessary to fill this prescription for a month? __________
A physician prescribes Voltaren 50 mg po tid with meals or snack. How many tablets are necessary to fill this prescription for a month? __________

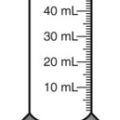
3. ![]() A physician prescribes cephalexin oral suspension 62.5 mg po q6h × 10 days. Indicate the dose on the available utensil below.
A physician prescribes cephalexin oral suspension 62.5 mg po q6h × 10 days. Indicate the dose on the available utensil below.

What volume of medication would be administered with each dose? __________
Would the label shown provide adequate medication to fulfill the prescription? __________
If this is adequate, what volume of medication would be discarded? __________
If the amount is inadequate, how many more milliliters of medication would be necessary for the prescription? __________
What would be the dose in household measurements? __________
Indicate prescription label directions using an oral dose syringe. __________
__________________________________________________________________________________
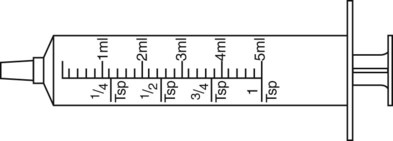
4. ![]()
![]() A physician prescribes Macrodantin 0.1 g to be given po qid for a month for a severe urinary tract infection.
A physician prescribes Macrodantin 0.1 g to be given po qid for a month for a severe urinary tract infection.

Using the provided label, how many capsules would be necessary to complete the order? __________
Indicate the prescription label directions. __________________________________________
5. ![]() Using the provided prescription, how many tablets would be necessary to fill the prescription? __________
Using the provided prescription, how many tablets would be necessary to fill the prescription? __________
Interpret the prescription. _________________________________________________________
Indicate prescription label directions. _____________________________________________

6. ![]() Using the provided prescription, what volume of medication must be supplied to fill the order? __________
Using the provided prescription, what volume of medication must be supplied to fill the order? __________
Interpret the prescription. _________________________________________________________
The medication is available in 80 mL, 100 mL, and 150 mL containers. Which container should be chosen to prepare the medication? __________
What volume of medication should be discarded by the patient if the medication is taken correctly? __________
Indicate prescription label directions using household measurements. ______________

7. ![]() During a severe influenza epidemic, the physician writes the provided prescription as a prophylactic in an older adult with COPD. The only amoxicillin in stock is amoxicillin 250 mg/capsule.
During a severe influenza epidemic, the physician writes the provided prescription as a prophylactic in an older adult with COPD. The only amoxicillin in stock is amoxicillin 250 mg/capsule.
How many capsules should be given to the patient to complete this order? _________
Interpret the prescription. _________________________________________________________
Indicate the prescription directions that would be on the label. _____________________

8. ![]() Using the provided prescription, what volume of medication must be provided to fulfill this order? __________
Using the provided prescription, what volume of medication must be provided to fulfill this order? __________
9. ![]() A patient presents the provided prescription for preparation. __________________
A patient presents the provided prescription for preparation. __________________
How many patches does the patient need for a month’s supply? __________
Interpret the prescription. _________________________________________________________
Indicate the prescription label directions. __________________________________________

10. ![]() On Friday a nurse orders medication to be sent to the floor for the weekend using the provided medication label. The patient is to receive cimetidine 300 mg IM q6h.
On Friday a nurse orders medication to be sent to the floor for the weekend using the provided medication label. The patient is to receive cimetidine 300 mg IM q6h.

How many vials of medication would be sent to the floor for Friday noon through the weekend with sufficient amount to provide the medication on Monday 6 am? __________
11. ![]() A physician orders Solu-Cortef 150 mg IM q8h for a patient with severe allergic dermatitis.
A physician orders Solu-Cortef 150 mg IM q8h for a patient with severe allergic dermatitis.

How many vials of medication would be sent to the floor for administration in 1 day using the provided label? __________
12. ![]() A physician prescribes cyanocobalamin 1.5 mg subcutaneously for administration twice a week for a month. Use 4 weeks for a month with this calculation.
A physician prescribes cyanocobalamin 1.5 mg subcutaneously for administration twice a week for a month. Use 4 weeks for a month with this calculation.

Using the provided label, how many vials of cyanocobalamin would be provided to the patient for this order? __________
What syringe should be provided with the prescription to meet this prescription? __________
Indicate the amount of medication that should be shown as patient education on the appropriate syringe.
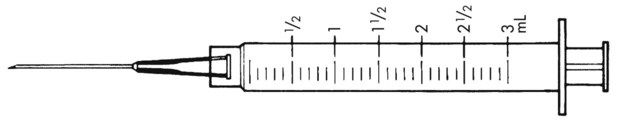
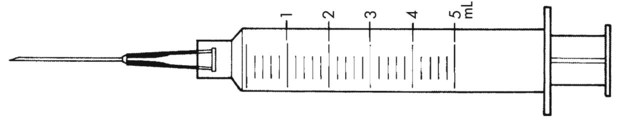
13. ![]() A physician prescribes Keflex 500 mg to be given po qid.
A physician prescribes Keflex 500 mg to be given po qid.
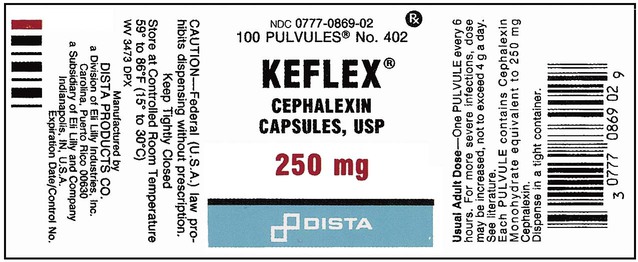
Using the provided label for available medication, how many capsules would be supplied for 2 weeks? __________
Interpret the prescription. _________________________________________________________
Indicate the prescription label directions. __________________________________________
14. ![]() How many tablets would be necessary to supply this medication for 2 weeks? __________
How many tablets would be necessary to supply this medication for 2 weeks? __________
Interpret the prescription. _________________________________________________________
Indicate the prescription label directions. __________________________________________

15. ![]() How many tablets are necessary for a month’s supply of the provided prescription? __________
How many tablets are necessary for a month’s supply of the provided prescription? __________
If each refill is for a month’s supply, how many total tablets would the patient receive over the period of the prescription for 3 months? __________
Interpret the order. _______________________________________________________________
Indicate the prescription label directions. __________________________________________

16. ![]() The physician orders phenobarbital gr 1/4 po q8h for seizures.
The physician orders phenobarbital gr 1/4 po q8h for seizures.
How many tablets would be provided for one week’s supply? __________
Indicate prescription label directions. _____________________________________________

17. Four prescriptions are written as shown in the provided illustration. Determine how many tablets of each medication would be necessary for the prescription as written.

![]() Depakote 500-mg tablet is available.
Depakote 500-mg tablet is available.
Depakote to be supplied: __________
Interpret the order for this medication. ____________________________________________
Indicate label directions. __________________________________________________________
![]() Desyrel 50-mg tablet is available.
Desyrel 50-mg tablet is available.
Desyrel to be supplied: __________
Interpret the order for this medication. ____________________________________________
Indicate label directions. __________________________________________________________
![]() Xanax 0.5-mg tablet is available.
Xanax 0.5-mg tablet is available.
Xanax to be supplied: __________
Interpret the order for this medication. ____________________________________________
Indicate label directions. __________________________________________________________
![]() Zoloft 100-mg tablet is available.
Zoloft 100-mg tablet is available.
Zoloft to be supplied: __________
Interpret the order for this medication. ____________________________________________
Indicate label directions. __________________________________________________________
18. ![]() A physician prescribes Cardizem 120 mg qid.
A physician prescribes Cardizem 120 mg qid.

Using the provided label, how many tablets are necessary to fill the order for 5 days? __________
Indicate the prescription label directions. _________________________________________
19. ![]() A patient who has difficulty swallowing tablets is to receive Mellaril 45 mg bid.
A patient who has difficulty swallowing tablets is to receive Mellaril 45 mg bid.

How many milliliters of medication are necessary for a month’s supply using 30 days as a month? __________
How many milliliters are necessary for a week’s supply? __________
What size medication bottle in ounces would be necessary to hold the month’s supply? __________
What is the daily am dose in household measurements using a medicine dropper calibrated in 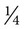 tsp increments? __________
tsp increments? __________
20. ![]()
![]() A physician prescribes Lasix 80 mg po stat, then Lasix 40 mg po daily thereafter.
A physician prescribes Lasix 80 mg po stat, then Lasix 40 mg po daily thereafter.

Calculating The Number of Medication Doses In A Given Container
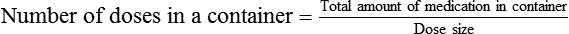
Example 14-2
A physician orders a dose for 1 tsp of an antibiotic from a bottle containing 120 mL.
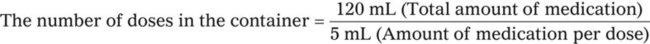
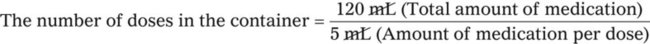
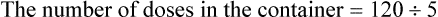
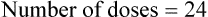
Does the container of medication contain adequate doses for 10 days if the medication is given tid?
Practice Problems B
1. ![]() How many full doses are available with this prescription? __________
How many full doses are available with this prescription? __________
Interpret the prescription. ________________________________________________________
Indicate prescription label directions. _____________________________________________

2. ![]() A physician prescribes Keflex Suspension 125 mg q6h for 10 days.
A physician prescribes Keflex Suspension 125 mg q6h for 10 days.

Using the label supplied, how many doses are in the container? __________
Will one container be sufficient for the prescription? __________
If not, how many containers would be needed if the medication provided on the label is the available medication? __________
Indicate the prescription label directions in household measurements. ______________
__________________________________________________________________________________
3. ![]()
![]() A patient is to take furosemide 80 mg po daily.
A patient is to take furosemide 80 mg po daily.

How many doses are in the provided container? __________
Indicate the prescription label directions. __________________________________________
4. ![]() A physician orders Humulin 70/30 63 units subcutaneously daily.
A physician orders Humulin 70/30 63 units subcutaneously daily.
How many doses are in the provided vial? __________
How many vials would be necessary for a month’s supply? __________
How many packages of insulin syringes would be necessary per month if each package contains 10 syringes? __________
Indicate the prescription label directions. __________________________________________
Indicate the volume of medication to be administered on the correct syringe.

5. ![]() A physician orders EryPed 200 mg qid for a child with acute bronchitis.
A physician orders EryPed 200 mg qid for a child with acute bronchitis.

How many doses are in the provided container? __________
How many days would this container provide the necessary medication? __________
If this is the size of container of medication available, how many containers would be necessary for 2 weeks? __________
Indicate prescription label directions. _____________________________________________
Indicate the approximate volume of medication to be administered on the dosespoon below.

6. ![]() A physician desires that a patient receive heparin 2500 units IV q8h. The vial of medication available is shown as follows.
A physician desires that a patient receive heparin 2500 units IV q8h. The vial of medication available is shown as follows.
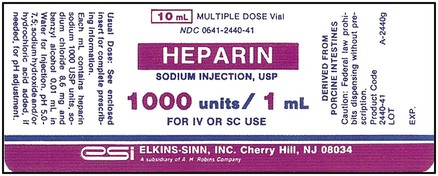
How many doses of heparin are in this vial? __________
How many vials would be necessary for a 3-day supply? __________
Indicate the prescribed amount on the correct syringe.
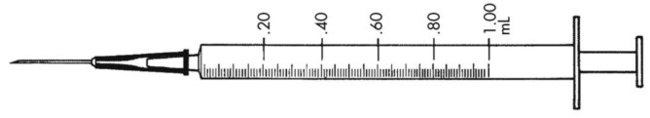
7. ![]() How many doses of medication are in this prescription? __________
How many doses of medication are in this prescription? __________
What metric strength of Omnicef is the patient receiving with each dose? __________
Indicate the prescription label directions using an oral dose syringe. _______________
__________________________________________________________________________________

8. ![]() A physician prescribes Halcion 0.25 mg hs prn sleep.
A physician prescribes Halcion 0.25 mg hs prn sleep.

How many doses are in the container shown? __________
If the patient has taken Halcion 125 mcg for 3 doses, how many full doses are left in the prescription? __________
Indicate prescription label directions. _____________________________________________
9. ![]() A physician prescribes rifampin 600 mg daily 1 hr ac for tuberculosis.
A physician prescribes rifampin 600 mg daily 1 hr ac for tuberculosis.

How many full doses of medication are found in the container with the provided label? __________
How many containers would be necessary for a month’s supply? __________
Indicate the prescription label directions. __________________________________________
10. ![]() A physician orders digoxin 0.25 mg stat and in am and then digoxin 125 mcg daily.
A physician orders digoxin 0.25 mg stat and in am and then digoxin 125 mcg daily.
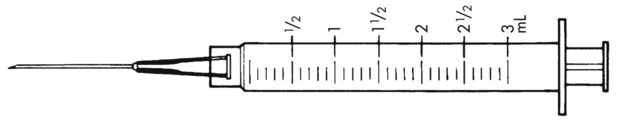
11. ![]() A physician orders Procanbid 1 g stat and repeat in 30 min. Then give Procanbid 500 mg q12h as a maintenance dose to control atrial fibrillation.
A physician orders Procanbid 1 g stat and repeat in 30 min. Then give Procanbid 500 mg q12h as a maintenance dose to control atrial fibrillation.

How many total doses are available of Procanbid in the container following the administration of the two initial doses? __________
The physician prescribes the stock bottle with the label shown for the patient to take with the orders for the daily dose as given previously. Ten days after starting the medication, the physician changes the dose to be Procanbid 1 g qam and 0.5 g qpm. How long in days would the prescription last until needing to be refilled? __________
How many stock containers of medication would be needed to be sure the patient has sufficient medication for 90 days using the last order for the medication? __________
12. ![]() A physician orders Lopid 600 mg qam and 300 mg qpm.
A physician orders Lopid 600 mg qam and 300 mg qpm.

How many days can the patient expect the prescription to last using the provided label? __________
Indicate the prescription label directions. __________________________________________
13. ![]()
![]() A vial of Compazine with the provided label has been provided to the medical floor for a patient with postoperative emesis.
A vial of Compazine with the provided label has been provided to the medical floor for a patient with postoperative emesis.

14. ![]() Using the provided prescription, the pharmacist supplies 50 mL of the medication on the prescription. The dropper holds 1 mL. Round to whole doses.
Using the provided prescription, the pharmacist supplies 50 mL of the medication on the prescription. The dropper holds 1 mL. Round to whole doses.

How many doses of medication are in the 50-mL container? __________
Interpret the prescription. _________________________________________________________
Indicate the prescription label directions. __________________________________________
15. ![]() As the pharmacy technician, you are checking the floor narcotics for the amount of meperidine that has been administered. Meperidine 50 mg has been given to four patients over the past 24 hours. The floor stocks a box of 75 mg/mL ampules in a floor locked cabinet, as labeled below.
As the pharmacy technician, you are checking the floor narcotics for the amount of meperidine that has been administered. Meperidine 50 mg has been given to four patients over the past 24 hours. The floor stocks a box of 75 mg/mL ampules in a floor locked cabinet, as labeled below.

How many ampules should be left in the 75 mg/mL ampule box if the floor stock supply had not been used except for these injections? __________
Explain your answer. _____________________________________________________________
16. ![]() Using the provided prescription, how many doses of Brovex would be supplied to the patient? __________
Using the provided prescription, how many doses of Brovex would be supplied to the patient? __________
Interpret the prescription. _________________________________________________________
Indicate the prescription label directions. __________________________________________

17. ![]() How many doses of amoxicillin are found with this prescription? __________
How many doses of amoxicillin are found with this prescription? __________
How many milligrams of amoxicillin is the patient receiving with each dose? __________
Interpret the prescription. __________
Indicate the prescription label directions using household utensils. __________

18. ![]()
![]() The physician prescribes ibuprofen 0.8 g tid pc for a patient with osteoarthritis.
The physician prescribes ibuprofen 0.8 g tid pc for a patient with osteoarthritis.
How many doses are in the bottle shown with the provided label? __________
Indicate the prescription label directions. __________________________________________
19. ![]() A physician prescribes amoxicillin 250 mg to be taken tid.
A physician prescribes amoxicillin 250 mg to be taken tid.
How many doses are available using the provided label? __________
If the medication is available as amoxicillin 250 mg/5 mL in a 150-mL bottle, how many doses would be available? __________
Indicate prescription label directions using a dose syringe. _________________________
20. ![]() A physician orders Lincocin 0.6 g IM q12h.
A physician orders Lincocin 0.6 g IM q12h.

Determining The Length Of Time A Prescription Will Last
The time that the prescription should last may be determined using the following equation:

Example 14-3

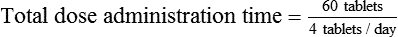
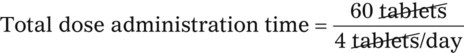
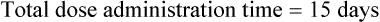
Practice Problems C
1. ![]() How long would the provided prescription last? __________
How long would the provided prescription last? __________
Interpret the prescription. ________________________________________________________
Indicate prescription label directions. _____________________________________________

2. ![]() How long would the medication in the provided prescription last? __________
How long would the medication in the provided prescription last? __________
3. ![]() A physician writes a prescription for minoxidil 0.04 g to be administered po daily. The pharmacist fills the prescription with 40 tablets of the medication shown on the provided label.
A physician writes a prescription for minoxidil 0.04 g to be administered po daily. The pharmacist fills the prescription with 40 tablets of the medication shown on the provided label.

How many days would this prescription last? __________
How many tablets would be necessary for a month’s supply? __________
Indicate prescription label directions. _____________________________________________
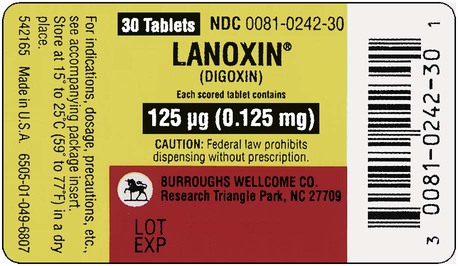
4. ![]() A physician writes a prescription for Lanoxin 0.125 mg tablets #40. The patient is to take Lanoxin 0. 5 mg stat and 0.375 mg in am and then to take tab i daily.
A physician writes a prescription for Lanoxin 0.125 mg tablets #40. The patient is to take Lanoxin 0. 5 mg stat and 0.375 mg in am and then to take tab i daily.
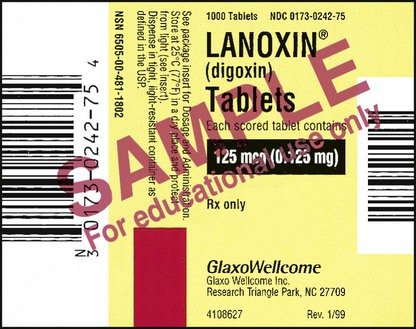
How long would this prescription last after the two initial doses? __________
Indicate prescription label directions. _____________________________________________
5. ![]() Using the provided prescription, how long would the medication last? _________
Using the provided prescription, how long would the medication last? _________
Interpret the prescription. ________________________________________________________
Indicate prescription label directions. _____________________________________________

6. ![]() How long would the medication in the provided prescription last if taken appropriately? __________
How long would the medication in the provided prescription last if taken appropriately? __________
Interpret the prescription. ________________________________________________________
Indicate prescription label directions. _____________________________________________

7. ![]() A physician prescribes erythromycin ethylsuccinate 200 mg tid using the label provided.
A physician prescribes erythromycin ethylsuccinate 200 mg tid using the label provided.

How many days would the medication last if taken as ordered? __________
How many doses of medication are available in the container? __________
Indicate prescription label directions using household utensils. __________
8. ![]() How long would the provided prescription last if taken appropriately? __________
How long would the provided prescription last if taken appropriately? __________
Interpret the prescription. ________________________________________________________
Indicate prescription label directions. _____________________________________________

9. ![]() How long would the provided prescription last if taken appropriately? __________
How long would the provided prescription last if taken appropriately? __________
Interpret the prescription. ________________________________________________________
Indicate prescription label directions. _____________________________________________

10. ![]() How long would this medication last if taken as specified on the provided prescription? __________
How long would this medication last if taken as specified on the provided prescription? __________
Interpret the prescription. _________________________________________________________
Should this prescription be refilled? _________ Explain your answer ________________
Indicate the prescription label directions. __________________________________________

11. ![]() How long would the provided prescription last if taken appropriately? __________
How long would the provided prescription last if taken appropriately? __________
Interpret the prescription. _________________________________________________________
Indicate the prescription label directions. __________________________________________

12. ![]() A physician prescribes Humulin R 50 units subcutaneously at breakfast and 40 units subcutaneously before the evening meal.
A physician prescribes Humulin R 50 units subcutaneously at breakfast and 40 units subcutaneously before the evening meal.
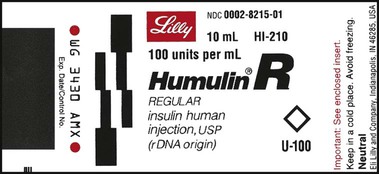
How long would the vial last? __________
How many vials of Humulin R would be necessary for a month’s supply for this patient if injected according to physician’s order? __________
Select the correct syringe for each dose and label am and pm as appropriate. Show the amount on selected syringes.
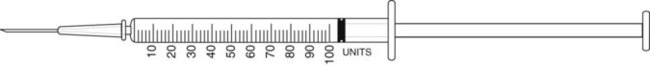


13. ![]() A physician prescribes penicillin G potassium 200,000 units bid. The medication has been diluted with 1.6 mL of diluent.
A physician prescribes penicillin G potassium 200,000 units bid. The medication has been diluted with 1.6 mL of diluent.

How many doses can be obtained from this vial of medication? __________
How many vials of medication would be provided for a 24-hour supply? __________
What is the powder volume of the container? __________
What volume of medication should be given for each dose? __________
14. ![]() A physician prescribes 200 mg of Lorabid po bid.
A physician prescribes 200 mg of Lorabid po bid.

How many days would the container with the provided label last? __________
How many containers of Lorabid would be dispensed for a 10-day supply? _________
What is the powder volume of this container? __________
Indicate the prescription label directions in household measurements. ______________
15. ![]() A physician prescribes Dilantin 0.3 g to be taken po each am and Dilantin 100 mg to be taken po at bedtime for epilepsy.
A physician prescribes Dilantin 0.3 g to be taken po each am and Dilantin 100 mg to be taken po at bedtime for epilepsy.

Using the provided label, how many days would that container of medication last? __________
How many extra capsules would be necessary for a month’s supply if the medication is taken as ordered? __________
Indicate the prescription label directions. __________________________________________
16. ![]() A physician prescribes Prozac Liquid 40 mg po qam.
A physician prescribes Prozac Liquid 40 mg po qam.

How many days would the medication shown on the provided label last if it is taken appropriately? __________
Indicate the prescription label directions using household utensils. _________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
17. ![]()
![]() A physician prescribes Benadryl elixir 18.75 mg po tid.
A physician prescribes Benadryl elixir 18.75 mg po tid.

Using the label provided, how many doses of medication are available if the patient takes the medication as ordered? __________
Indicate the label directions using a dose syringe. _________________________________
Indicate the prescription label directions using household utensils. _________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
18. ![]() A physician prescribes Biaxin 500 mg po bid. The available medication is shown on the provided label.
A physician prescribes Biaxin 500 mg po bid. The available medication is shown on the provided label.

19. ![]() The physician prescribes KCl 80 mEq po qam. The medication is supplied in the container with the provided label.
The physician prescribes KCl 80 mEq po qam. The medication is supplied in the container with the provided label.

How many days would the medication last if the patient takes the medication as ordered? __________
How many containers of medication would be needed for a 90-day supply? __________
Indicate the prescription label directions in household measurements. __________
20. ![]() A patient is to take Lantus insulin 35 units qam. Using the syringes below, show the amount of Lantus to be administered on the correct syringe for the order.
A patient is to take Lantus insulin 35 units qam. Using the syringes below, show the amount of Lantus to be administered on the correct syringe for the order.
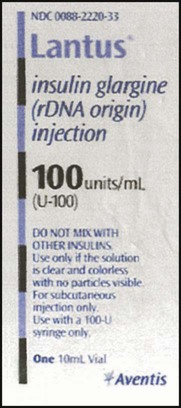

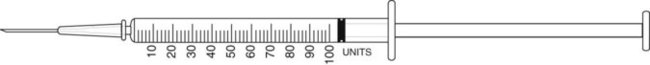
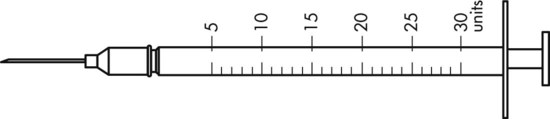
How long would the vial seen here last? __________
How many vials of Lantus would be necessary to provide a month’s supply? __________
Hint: Be sure that you calculate full doses for each day and 1 month is 30 days for this calculation.
How many vials of medication would be needed for a 90-day supply? __________
Review
Posttest
![]() 1 Determine the number of tablets necessary to fill this prescription. __________
1 Determine the number of tablets necessary to fill this prescription. __________
![]() 2 Determine the number of tablets necessary to complete the provided prescription for 30 days. __________
2 Determine the number of tablets necessary to complete the provided prescription for 30 days. __________
Interpret the prescription. ________________________________________________________
Indicate prescription label directions. _____________________________________________

![]() 3 How many Alora patches are necessary for a 30-day supply? __________
3 How many Alora patches are necessary for a 30-day supply? __________
![]()
![]()
![]() 4 A physician writes a prescription for a 1 : 1 : 1 proportion of the following:
4 A physician writes a prescription for a 1 : 1 : 1 proportion of the following:
What is the amount of each component necessary to make 6 oz? __________
How many doses of medication are available if the patient swishes and spits 1 tsp q4h? __________
What percentage of the mouthwash is lidocaine? __________
Indicate the prescription label directions using household utensils. __________
![]() 5 A physician writes a prescription for Decadron as shown on the provided label on a sliding scale of tabs 1 qid × 2 days, tid × 2 days, bid × 2 days, and daily × 4 days.
5 A physician writes a prescription for Decadron as shown on the provided label on a sliding scale of tabs 1 qid × 2 days, tid × 2 days, bid × 2 days, and daily × 4 days.

How many tablets are necessary to fill this prescription? __________
How many milligrams of dexamethasone would the patient receive on each day of the sliding scale? _________ Days 1 and 2: _________ Days 3 and 4: _________ Days 5 and 6: __________ Days 7 to 10: __________
![]() 6 How many days would the provided prescription last if the medication is taken as written? __________
6 How many days would the provided prescription last if the medication is taken as written? __________
![]()
![]() 7 How long would the prescription for Gabitril last if taken appropriately? __________
7 How long would the prescription for Gabitril last if taken appropriately? __________
How long would the prescription for Colace last if taken as a daily dose as prescribed prn? __________
Interpret both prescriptions. __________ __________
Indicate the prescription label directions for each medication. __________ __________

![]() 8 How long would the provided prescription last if taken as ordered? __________
8 How long would the provided prescription last if taken as ordered? __________
![]() 9 A physician orders erythromycin ethylsuccinate 300 mg po tid for 10 days.
9 A physician orders erythromycin ethylsuccinate 300 mg po tid for 10 days.

How many milliliters of medication would be necessary for each dose? __________
What total metric strength of erythromycin would be given each day? __________
What total volume of medication would be necessary for the prescription as ordered? __________
Is there sufficient medication in the container as shown on the label given? __________
How should the dose ordered be indicated on an oral dose syringe? __________
Indicate the prescription label directions using an oral dose syringe. __________
__________________________________________________________________________________
Indicate the prescribed amount on the syringe below.
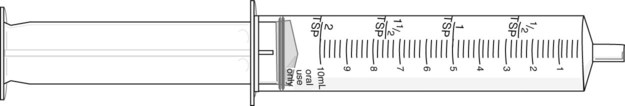
![]() 10 A physician writes an order for Voltaren 50 mg bid with food for 7 days and decrease to daily for a 30 day supply.
10 A physician writes an order for Voltaren 50 mg bid with food for 7 days and decrease to daily for a 30 day supply.

How many Voltaren tablets would be necessary for this prescription? __________
If the person takes the medication at home, what would the label directions be? ______________________________________________________________________________________
![]() 11 If the patient uses the albuterol as ordered on a regular basis and does not skip a dose, how long would the provided medication last? __________
11 If the patient uses the albuterol as ordered on a regular basis and does not skip a dose, how long would the provided medication last? __________
![]() 12 How many capsules would be necessary to provide a 3-month supply? __________
12 How many capsules would be necessary to provide a 3-month supply? __________
After the first month the physician increases the HCTZ to bid. How much longer will the original amount of medication last? __________
Interpret the order as written. __________
Indicate the prescription label directions. __________________________________________

![]() 13 A physician orders Coumadin 5 mg po on Sunday, Tuesday, Wednesday, Friday, and Saturday and Coumadin
13 A physician orders Coumadin 5 mg po on Sunday, Tuesday, Wednesday, Friday, and Saturday and Coumadin 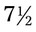 mg po on the other days of the week.
mg po on the other days of the week.


How many tablets would be necessary for a week’s supply? __________
What amount of Coumadin in milligrams would be taken in a week? __________
How many tablets would be necessary for a month’s supply? __________
Using the provided labels, which Coumadin provides the least number of tablets and still allows patient safety with administration? __________
Indicate prescription label directions. _____________________________________________
![]() 14 If the patient takes the medication as ordered at one tablet q4h, as well as before an appointment, how many days would this medication last? __________
14 If the patient takes the medication as ordered at one tablet q4h, as well as before an appointment, how many days would this medication last? __________
Interpret the prescription. _________________________________________________________
Indicate the prescription label directions. __________________________________________

![]() 15 How many days would the provided prescription last if taken as written? ___________
15 How many days would the provided prescription last if taken as written? ___________
Interpret the prescription. _________________________________________________________
Indicate the prescription label directions. __________________________________________

![]() 16 The medication as prescribed is available in a 5-mL container.
16 The medication as prescribed is available in a 5-mL container.

If no medication were wasted, how many days would this medication last? _________
Interpret the prescription. _________________________________________________________
Indicate the prescription label directions. __________________________________________
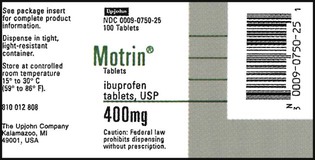
![]()
![]() 17 How many doses of the medication are found in the provided prescription as ordered? _________
17 How many doses of the medication are found in the provided prescription as ordered? _________
What weight of Motrin is the patient receiving with each dose? _________
Interpret the prescription. _________________________________________________________
Indicate the prescription label directions. __________________________________________

![]() 18 A physician prescribes Dilantin 200 mg po bid for 14 days.
18 A physician prescribes Dilantin 200 mg po bid for 14 days.

Using the provided label, how many tablets would be provided to fill the prescription? _________
Indicate the prescription label directions. __________________________________________
![]() 19 A physician writes for Thorazine 50 mg po qam and 75 mg po at bedtime.
19 A physician writes for Thorazine 50 mg po qam and 75 mg po at bedtime.

How many tablets would be necessary for a 21-day supply? _________
What is the total dosage per day of the medication? _________
Indicate the prescription label directions. __________________________________________
![]() 20 How long would the provided medication last if taken as ordered? _________
20 How long would the provided medication last if taken as ordered? _________