Chapter 22 Infectious Mononucleosis and Other Epstein-Barr Virus–Associated Diseases
Part 2
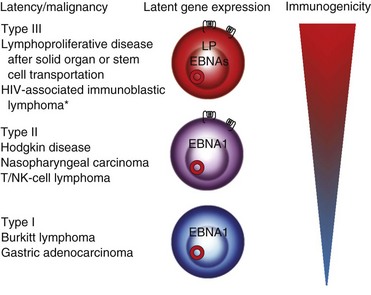
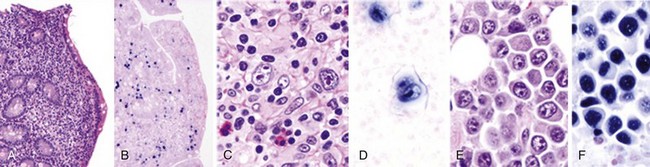
Figure 22-1 EBV-LATENT GENE EXPRESSION AND IMMUNOGENICITY OF COMMON EBV-ASSOCIATED MALIGNANCIES.
EBNA, Epstein-Barr nuclear antigen; LP, leader protein. For an explanation of symbols, see Fig. 21-1. *Not all lymphomas are latency type III.
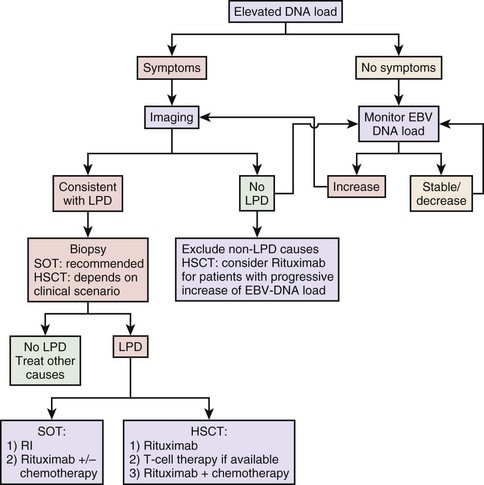
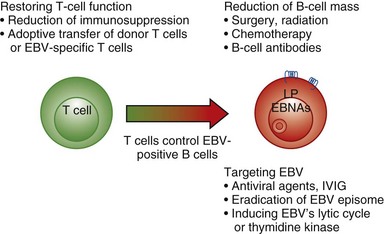
EBV-Associated Malignancies
| Malignancy | EBV Frequency |
|---|---|
| Hodgkin disease | ≈40% |
| Non-Hodgkin lymphomas | |
| Burkitt lymphoma | 20%-95% |
| Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and CD30+ Ki-1+ anaplastic large cell lymphoma | 10%-35% |
| Lymphomatoid granulomatosis | 80%-95% |
| T-cell-rich B-cell lymphoma | 20% |
| Angioimmunoblastic lymphoma | >80% |
| T-cell, NK cell, and T/NK-cell lymphomas | 30%-90% |
| Nasopharyngeal carcinoma | >95% |
| Gastric adenocarcinoma | 5%-10% |
| Pyothorax-associated lymphoma | >95% |
| Leiomyosarcoma in immunocompromised patients | >95% |