5 History and Physical Examination of the Aging Spine
KEY POINTS
Past Medical History
History
Neurological History
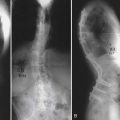
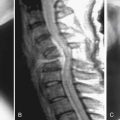
History of weakness, falls, gait abnormalities, difficulty with fine motor movement, bowel or bladder dysfunction, and/or sexual dysfunction are all potential signs of myelopathy. This should be obtained in the initial history, which should also include questions about grip strength, dropping items such as coffee cups, or burning the fingers. Upper extremity weakness or pain needs to be noted, along with any associated radicular symptoms into the arms or legs.
Physical Examination
Specific Cervical Neurological Levels
C7 Neurological Findings
The reflex exam of the C7 nerve root can be assessed with the triceps reflex.
L2 to L4 Neurological Findings
The motor exam of the L2 to L4 nerve roots is best examined with the quadriceps muscle group and the hip adductor muscle group. The quadriceps muscle group, which is innervated by L2 to L4 nerve roots (femoral nerve), is tested with resisted knee extension in a sitting position, while the hip adductor group, also innervated by the L2 to L4 nerve groups, is tested with resisted hip adduction from an abducted position, either sitting or supine. The sensory distribution of the L2 and L3 nerve roots has been described above, and the sensory distribution and reflex exam of L4 will be described below.
L4 Neurological Findings
The sensory distribution of the L4 nerve root is best tested over the anteromedial lower leg.