Pure form: Affects only pancreaticoduodenal groove
• Pancreatic groove is a theoretical space defined by pancreatic head (medially), 2nd portion of duodenum (laterally), 3rd portion of duodenum and IVC (posteriorly), and duodenal bulb (superiorly)
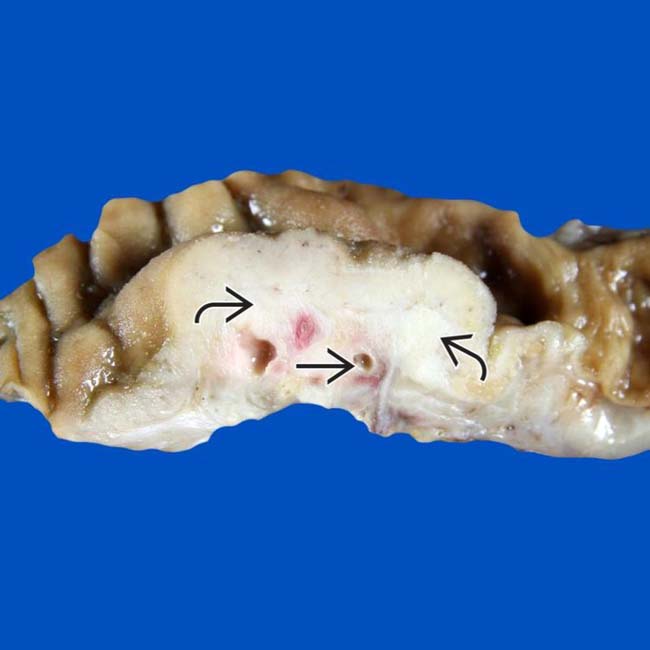
 beneath the duodenal mucosa, representing groove pancreatitis. Note the paraduodenal zone of fibrosis with numerous small cysts
beneath the duodenal mucosa, representing groove pancreatitis. Note the paraduodenal zone of fibrosis with numerous small cysts  .
.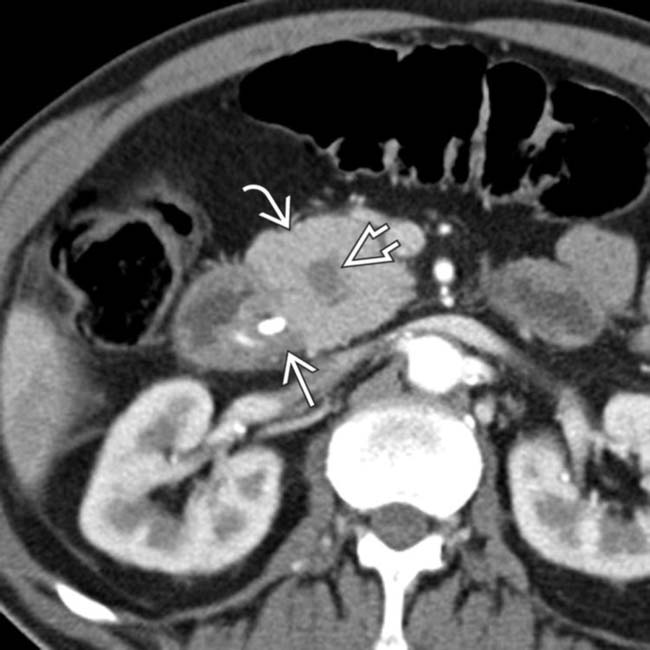
 in the pancreaticoduodenal groove, as well as mass-like pancreatic head
in the pancreaticoduodenal groove, as well as mass-like pancreatic head  enlargement with an internal cyst
enlargement with an internal cyst  . This was found to be segmental (given pancreatic head involvement) groove pancreatitis at surgery.
. This was found to be segmental (given pancreatic head involvement) groove pancreatitis at surgery.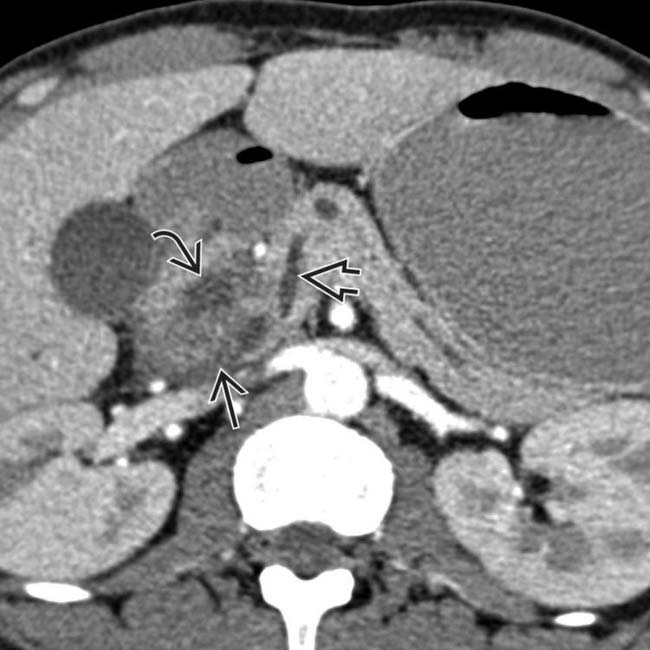
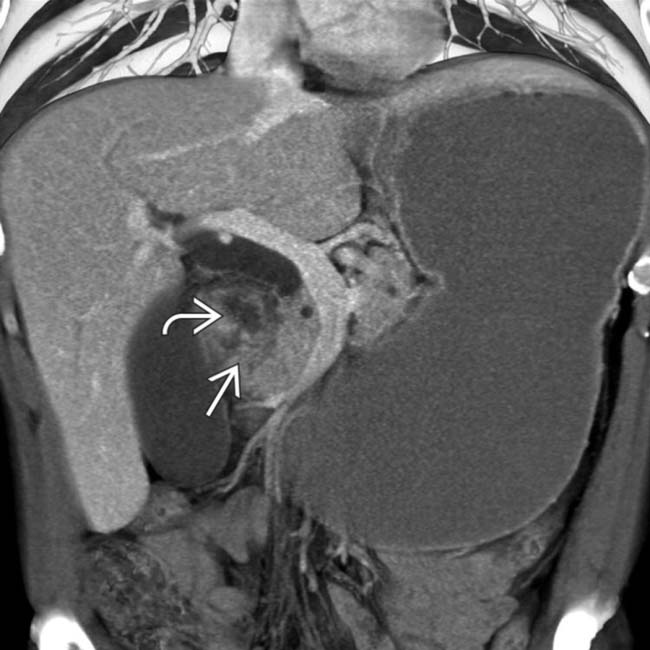
 in the pancreaticoduodenal groove with associated cystic spaces
in the pancreaticoduodenal groove with associated cystic spaces  , resulting in upstream pancreatic ductal dilatation
, resulting in upstream pancreatic ductal dilatation  .
.
 in the pancreaticoduodenal groove with associated cystic spaces
in the pancreaticoduodenal groove with associated cystic spaces  . Initially suspected to represent malignancy, this was found to be groove pancreatitis at surgery.
. Initially suspected to represent malignancy, this was found to be groove pancreatitis at surgery.IMAGING
General Features
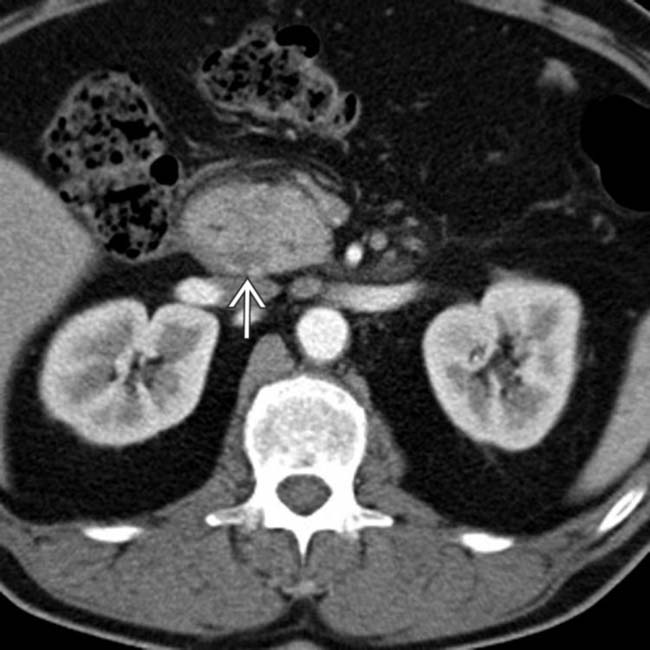
 in the pancreaticoduodenal groove, which persisted on follow-up examinations.
in the pancreaticoduodenal groove, which persisted on follow-up examinations.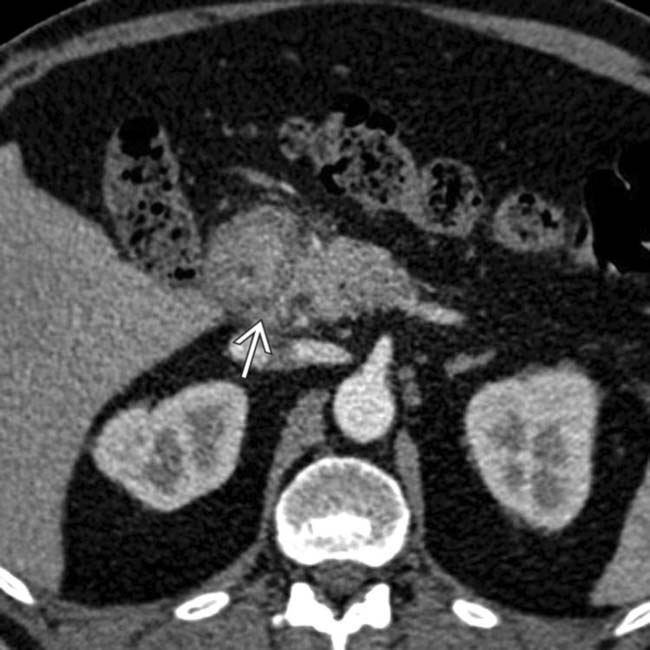
 in the pancreaticoduodenal groove. Initially suspected to represent a duodenal malignancy, this was found to be groove pancreatitis at surgery.
in the pancreaticoduodenal groove. Initially suspected to represent a duodenal malignancy, this was found to be groove pancreatitis at surgery.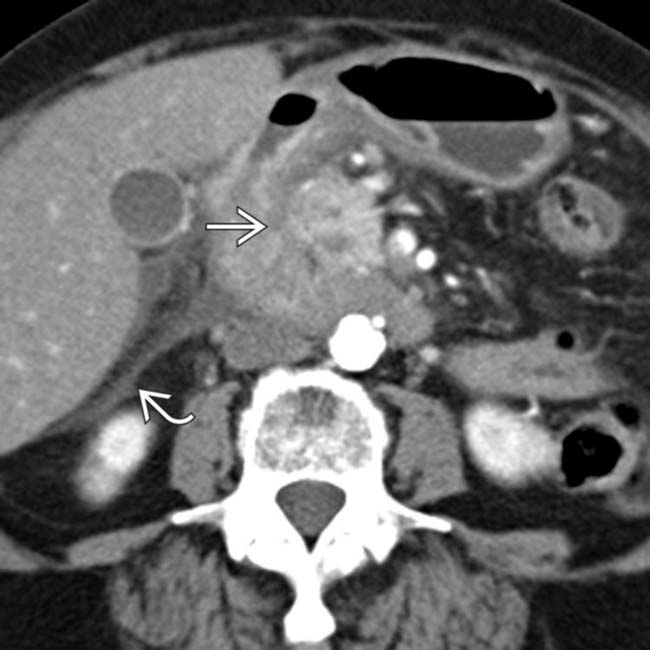
 in the pancreaticoduodenal groove, which persisted over multiple follow-up studies. There is also some fluid
in the pancreaticoduodenal groove, which persisted over multiple follow-up studies. There is also some fluid  tracking from the groove into the right anterior pararenal space.
tracking from the groove into the right anterior pararenal space.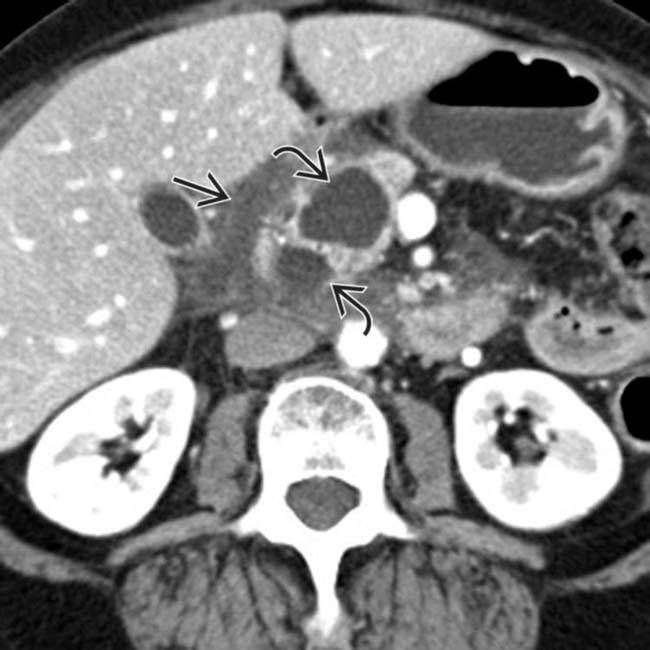
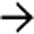 in the groove, with several cysts
in the groove, with several cysts 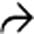 present in the pancreatic head. This was found to be groove pancreatitis at surgery, but the presence of fluid tracking in the retroperitoneum is atypical and more common with acute edematous pancreatitis.
present in the pancreatic head. This was found to be groove pancreatitis at surgery, but the presence of fluid tracking in the retroperitoneum is atypical and more common with acute edematous pancreatitis.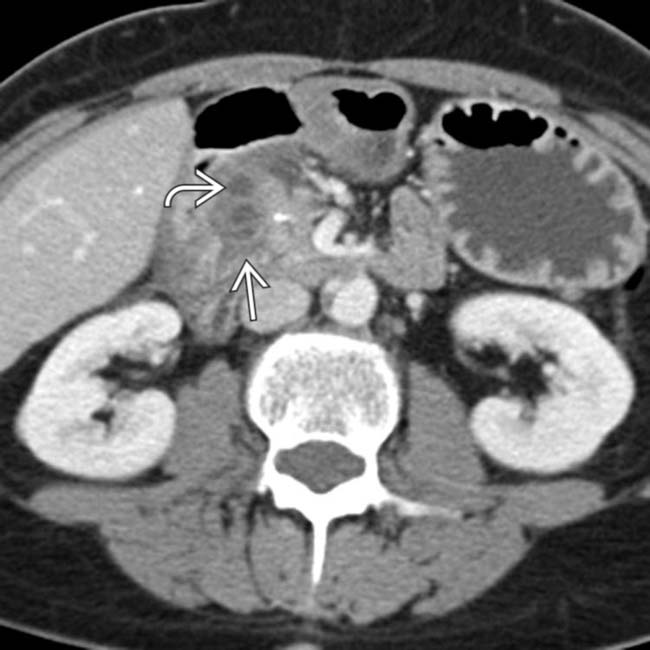
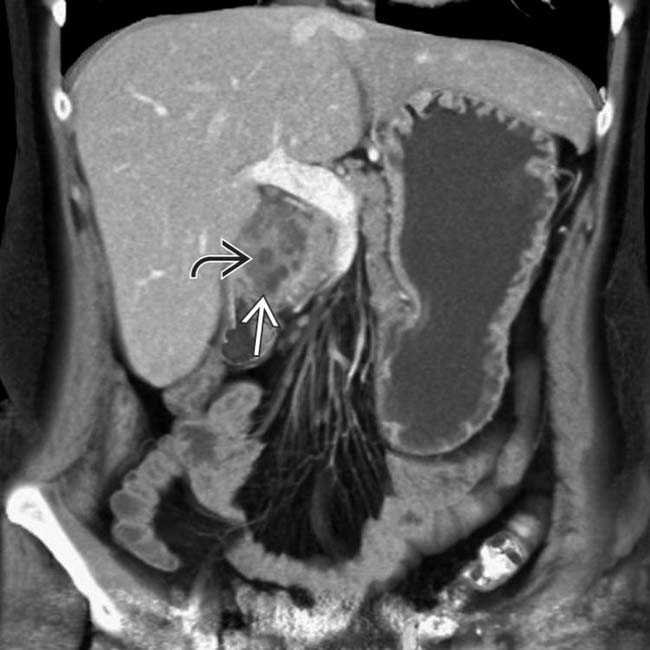
 in the pancreaticoduodenal groove with multiple internal cystic spaces
in the pancreaticoduodenal groove with multiple internal cystic spaces  .
.
 in the pancreaticoduodenal groove with multiple internal cystic spaces
in the pancreaticoduodenal groove with multiple internal cystic spaces 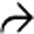 . While this was suspected to represent groove pancreatitis, Whipple procedure was performed to exclude underlying malignancy, a common outcome in these cases.
. While this was suspected to represent groove pancreatitis, Whipple procedure was performed to exclude underlying malignancy, a common outcome in these cases.
 secondary to gastric outlet obstruction. Note the band-like soft tissue thickening
secondary to gastric outlet obstruction. Note the band-like soft tissue thickening 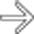 in the groove between the 2nd duodenum and the pancreas, characteristic of groove pancreatitis.
in the groove between the 2nd duodenum and the pancreas, characteristic of groove pancreatitis.
 is markedly narrowed by the adjacent soft tissue, and there is a small cyst
is markedly narrowed by the adjacent soft tissue, and there is a small cyst  in the pancreatic groove.
in the pancreatic groove.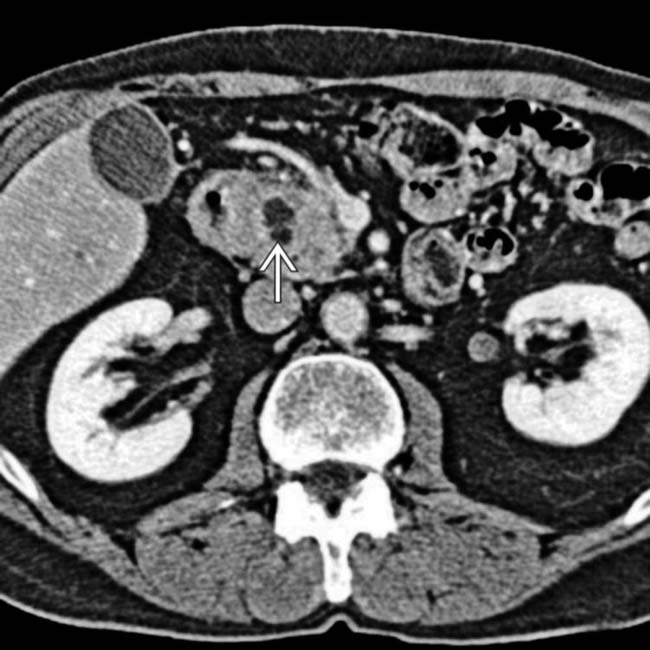
 . This was found to represent groove pancreatitis at surgery.
. This was found to represent groove pancreatitis at surgery.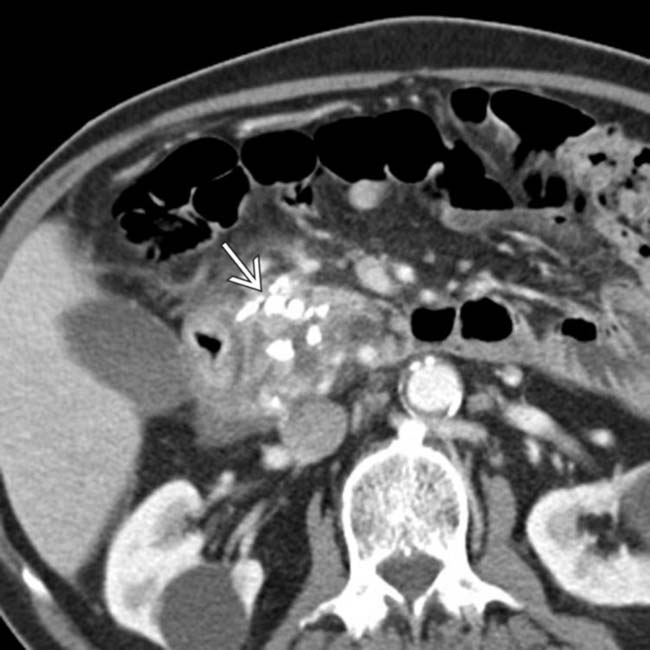
 centered in the groove. Groove pancreatitis in the chronic setting, as in this case, can appear very similar to traditional chronic pancreatitis (including the presence of calcifications).
centered in the groove. Groove pancreatitis in the chronic setting, as in this case, can appear very similar to traditional chronic pancreatitis (including the presence of calcifications).













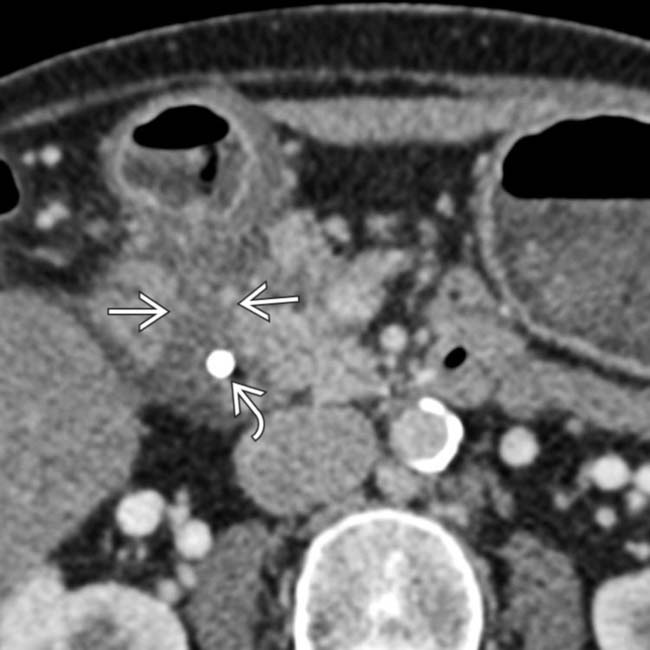
 . Note the stent
. Note the stent  in the common duct placed due to biliary obstruction from the adjacent soft tissue.
in the common duct placed due to biliary obstruction from the adjacent soft tissue.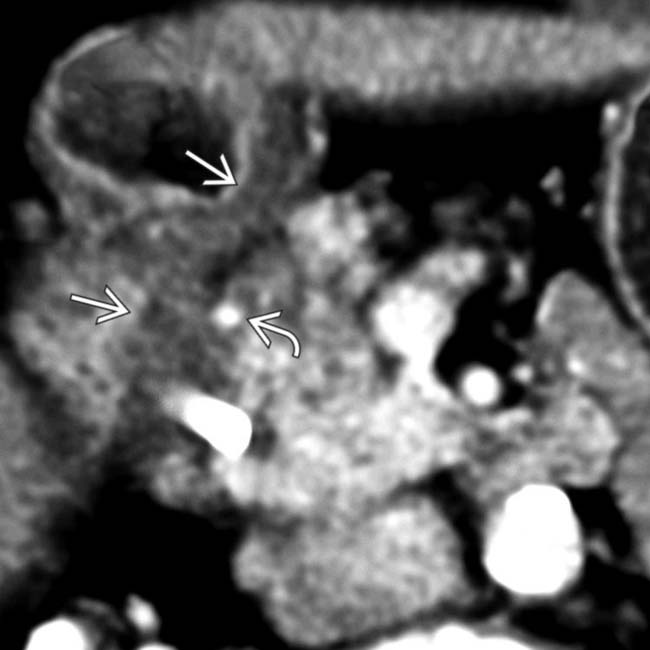
 and thickens the medial wall of the 2nd duodenum
and thickens the medial wall of the 2nd duodenum  .
.


