Gram-Positive Cocci
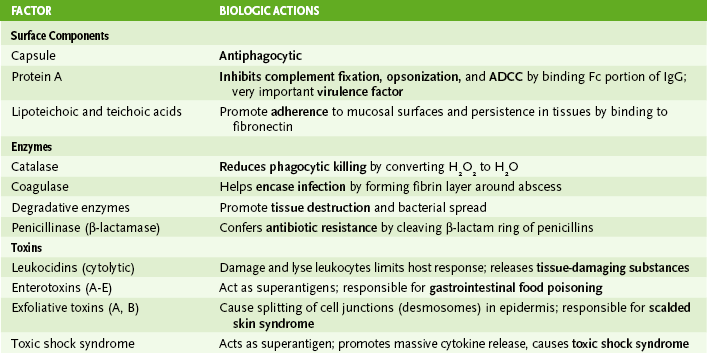
• Three staphylococcal species commonly cause human disease: S. aureus (most virulent), S. epidermidis, and S. saprophyticus.
A Shared staphylococcal properties
1. Gram-positive cocci in grape-like clusters
2. Catalase positive; growth in 7.5% salt
3. Ubiquitous distribution; part of normal flora; responsible for many nosocomial infections
B Coagulase-positive staphylococci (S. aureus)
• S. aureus is normal flora of skin and the anterior nares.
2. Diseases caused by S. aureus (Box 9-1)
• Community-acquired methicillin resistant S. aureus (CA-MRSA) carries resistance plasmids that also have the Panton valentine leukocidin gene and may be more virulent.
• Inflammatory diseases mediated by pyogenic and necrotic activities of S. aureus
• Person-to-person contact and via fomites
• Endogenous spread via blood or aspiration of nasal secretions
• Most staphylococci produce penicillinase (a β-lactamase) and are commonly treated with a penicillinase-resistant β-lactam penicillin derivative, such as nafcillin, oxacillin, or methicillin.
• MRSA strains (hospital acquired) are treated with vancomycin, linezolid, daptomycin, tigecycline, trimethoprim sulfa, or clindamycin.
• CA-MRSAs are becoming more common.
• Methicillin- and vancomycin-resistant S. aureus was acquired from an Enterococcus plasmid.
C Coagulase-negative staphylococci (S. epidermidis and S. saprophyticus)
1. These bacteria are normally benign colonizers of the skin.
2. They are less virulent than S. aureus, although their virulence factors are similar (except for lack of coagulase).
3. S. epidermidis can adhere to artificial heart valves, vascular catheters, shunts, and prosthetic joints, colonizing the implant area and causing tissue destruction mediated by degradative enzymes.
4. S. saprophyticus is a frequent cause of urinary tract infections (UTIs) in sexually active young women.
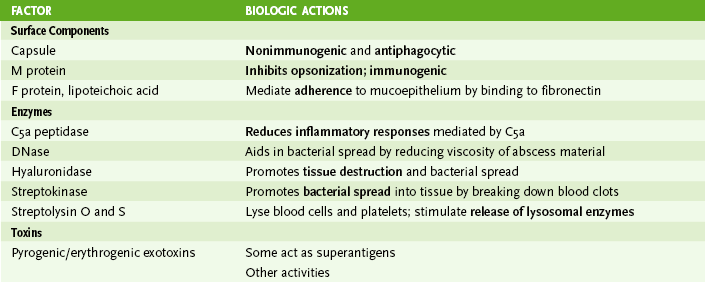
• Most common streptococcal pathogens in humans are S. pyogenes, S. agalactiae, viridans group, and S. pneumoniae.
A Shared streptococcal properties
1. Gram-positive spherical or football-shaped cocci in pairs or chains
3. Species-dependent hemolysis in blood agar (Table 9-2)
TABLE 9-2
| Hemolytic reaction | Organism | Differentiating property |
| α (Incomplete) hemolysis | S. pneumoniae | Optochin sensitive |
| (greenish zone around colony) | Viridans streptococci | Optochin resistant |
| Enterococcus (some) | — | |
| β (Complete) hemolysis | S. pyogenes (group A) | Bacitracin sensitive |
| (clear zone around colony) | S. agalactiae (group B) | Bacitracin resistant |
| γ (No) hemolysis | Enterococcus (some) | — |
B Group A streptococci (S. pyogenes)
• Sensitive to bacitracin (A disk)
• Hyaluronic acid–containing capsule
• Antibodies to streptolysin O appearing 3 or 4 weeks after primary infection
• Table 9-3 summarizes the major contributors to the virulence of S. pyogenes and other group A streptococci.
3. Group A streptococcal diseases (Box 9-2)
• Localized suppurative diseases: pharyngitis (strep throat), skin infections, postsurgical cellulitis, puerperal (at childbirth) sepsis
C Group B streptococci (S. agalactiae)
• S. agalactiae is a normal inhabitant of the gastrointestinal and lower genital tracts.
• Antiphagocytic capsule is immunogenic.
• Anticapsular antibodies are important in host defense.
• Hemolysins and various degradative enzymes mediate cellular and tissue destruction.
3. Group B streptococcal diseases
• Early-onset neonatal disease begins within 7 days of birth.
a. Acquired in utero or at delivery (infection in mother’s vagina)
• Late-onset neonatal disease begins 1 week to 3 months after birth.
• Postpartum sepsis is usually acquired via wound inflicted during parturition.
• Wound infections occur in other adults, especially immunocompromised patients.
D Viridans streptococci (S. mutans, S. sanguis)
• These constitute a major part of normal flora of the mouth and teeth.
2. Viridans streptococcal diseases
• Streptococcal endocarditis occurs most commonly in patients with damaged heart valves, to which bacteria adhere.
E S. pneumoniae (pneumococcus)
• S. pneumoniae is normally present in the throat and nasopharynx.
• Sensitive to Optochin (P disk)
• Positive quellung reaction (capsular swelling in the presence of specific anticapsular antibody)
• Aspiration of nasopharyngeal secretions into lower airways leads to rapid growth of pneumococci in alveolar spaces.
a. Reduced clearance of airways due to disruption of ciliated epithelium in upper respiratory tract by viral infection or smoking promotes aspiration.
• Antiphagocytic capsule is required for virulence (See Box 9-4).
• Pneumolysin (similar to streptolysin O) lyses cells.
• Pneumococcal immunoglobulin A (IgA) protease cleaves secretory IgA, increasing adherence to mucosal surfaces.
• Neuraminidase (spreading factor) promotes bacterial spread into tissue.
• Typical community-acquired pneumonia
a. Marked by abrupt onset, high fever (102° to 105°F), rigor, productive cough, and pleuritic chest pain from pleural inflammation from either bronchopneumonia (patchy pneumonia) or lobar pneumonia (involvement of one or more lobes)
• Bacteremia, found in 25% to 30% of pneumonia patients, may lead to pneumococcal meningitis.
• Most common cause of acute otitis media and sinusitis
• Most common cause of sepsis in children with sickle cell disease and dysfunctional spleen
• Most common cause of spontaneous peritonitis in children with nephrotic syndrome and ascites
4. Epidemiology of pneumococcal infection
• Transmission of pneumococci occurs via aerosol droplets from infected person followed by aspiration into lower airways. Infection is most common in winter and spring.
• At-risk groups include young children, elderly people, asplenic patients (Box 9-4), and other immunocompromised individuals.