9 Glaucoma
Anatomy/physiology
Ciliary body (CB)
Functions
Outflow Pathways
Trabecular meshwork (traditional pathway)
The pore size of the meshwork decreases towards Schlemm’s canal:
Angle Structures
Visible only by gonioscopy because of total internal reflection at the air/cornea interface (Figure 9-1)
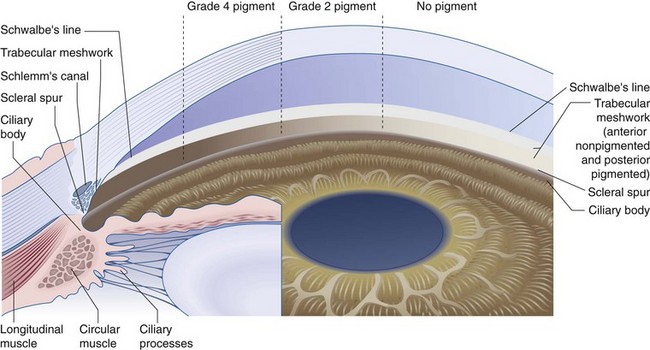
Figure 9-1 Composite drawing of the microscopic and gonioscopic anatomy.
(From Becker B, Shaffer RN: Diagnosis and Therapy of the Glaucomas, St Louis, Mosby, 1965.)
Angle Abnormalities
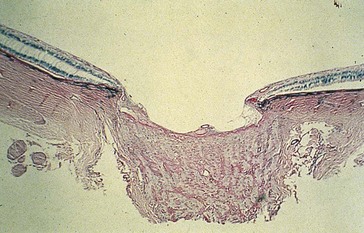
Cyclodialysis cleft
Optic Nerve (Figure 9-2)
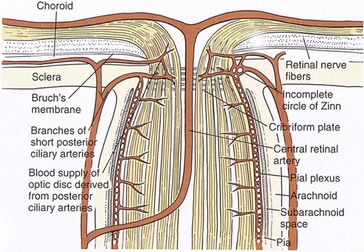
Figure 9-2 Vascular supply and anatomy of the anterior optic nerve.
(From Hart WM Jr: In Podos SM, Yanoff M [eds]: Textbook of Ophthalmology, vol 6, London, Mosby, 1994.)
Testing
Intraocular Pressure
Goldmann equation
IOP = F/C + EVP relates 3 factors important in determination of IOP
Tonometry
IOP measurement can be performed with a variety of devices (tonometers)
Indentation
Applanation
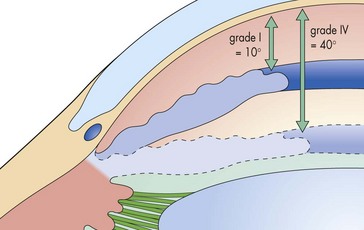
Gonioscopy
Classification systems
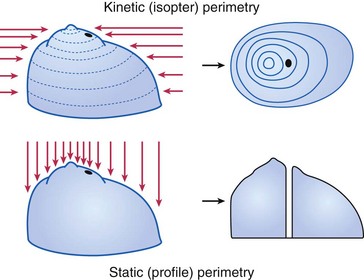
Visual Fields
Central field tests points only within a 30° radius of fixation
Types
Goldmann (kinetic and static)
Humphrey (static)
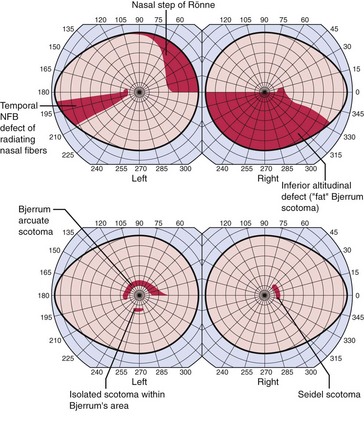
VF defect
a scotoma is an area of partial or complete blindness
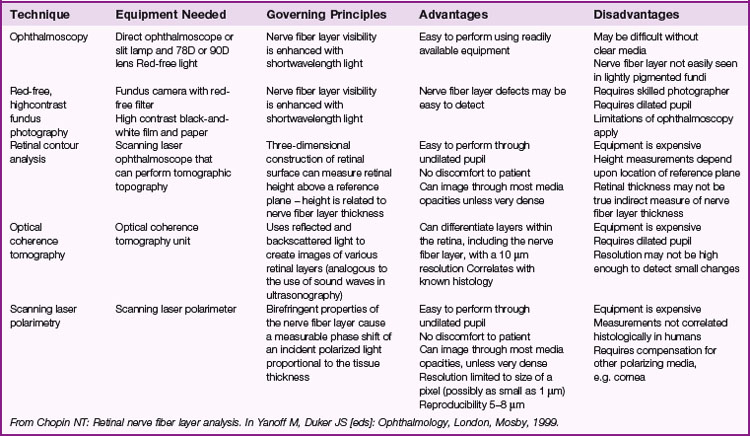
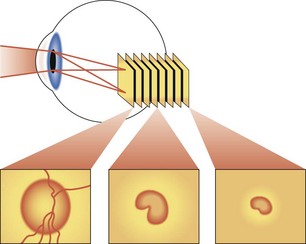
Optic Nerve Head (ONH) Analyzers
Various digital and video cameras that capture ONH image; computer then calculates cup area in an attempt to objectively quantify ONH appearance (Table 9-1)
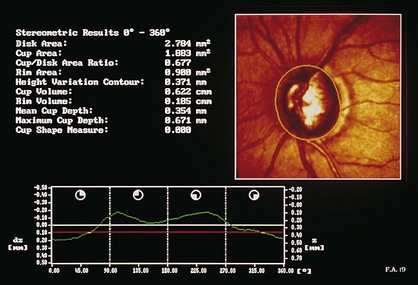
Confocal scanning laser ophthalmoscopy (CSLO; Heidelberg retinal tomograph [HRT]; TopSS)
low-power laser produces digital 3D picture of ON head by integrating coronal scans of increasing tissue depth; indirectly measures nerve fiber layer (NFL) thickness (Figures 9-6, 9-7)
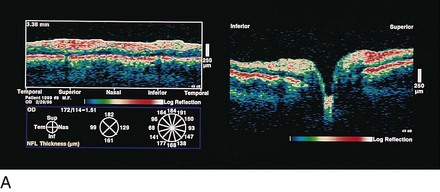
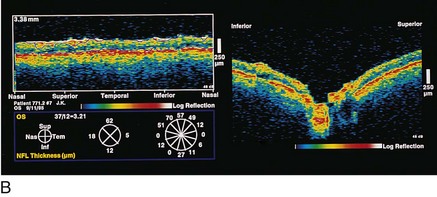
Optical coherence tomography (OCT)
measures optical backscattering of light to produce high-resolution, cross-sectional image of the NFL (Figure 9-8)
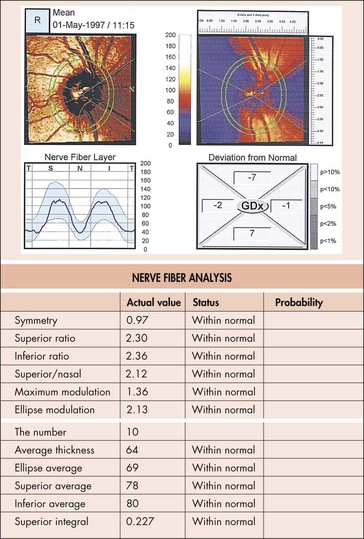
Scanning laser polarimetry (SLP; Nerve Fiber Analyzer, GDx)
uses a confocal scanning laser ophthalmoscope with an integrated polarimeter to detect changes in light polarization from axons to measure the NFL thickness; quantitative analysis of NFL thickness to detect early glaucomatous damage (Figure 9-9)
Pathology
Glaucoma
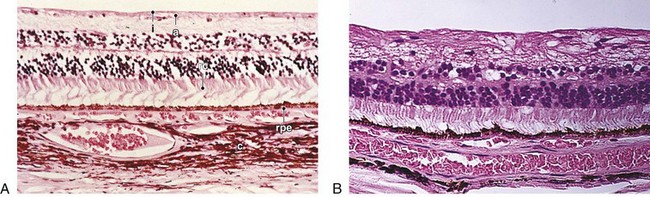
Dropout of ganglion cells, replacement of NFL with dense gliotic tissue and some glial cell nuclei; partial preservation of inner nuclear layer with loss of Müller’s and amacrine cells (normal 8–9 cells high; in glaucoma, 4–5 cells high); earliest histologic changes occur at level of lamina cribrosa; advanced cases may show backward bowing of lamina or ‘beanpot’ appearance (Figures 9-11, 9-12)
Disorders
Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma (POAG)
Secondary Open-Angle Glaucoma
Mechanism/Etiology
Pigmentary glaucoma (PG) (AD)
Mapped to chromosome 7q35-q36 (GLC1F)
Findings
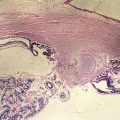
halos and blurry vision with IOP spikes (pigment may be released with exercise); Krukenberg spindle (melanin phagocytized by corneal endothelium); heavy TM pigmentation; iridodonesis; iris transillumination defects (radial midperipheral spoke-like appearance); associated with lattice degeneration (20%) and retinal detachment (5%) (Figure 9-14)
Pseudoexfoliation glaucoma (PXG)
Mapped to chromosome 15q24 (LOXL1).
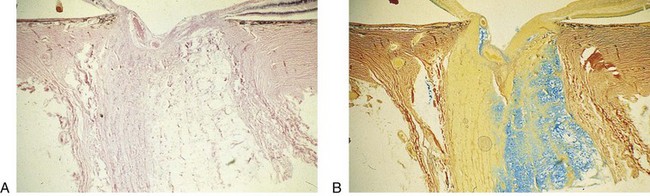
High incidence (up to 50%) of secondary open-angle glaucoma in patients with pseudoexfoliation syndrome (PXS); more common among Scandinavians. Amyloid-like substance deposits in eye and clogs TM, also found in other organs (Figure 9-15)
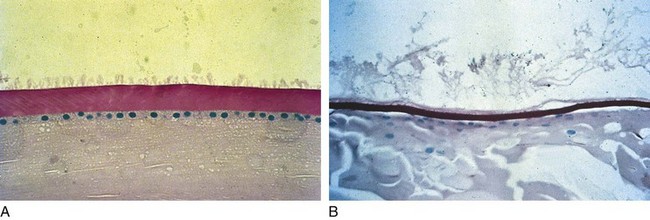
Figure 9-15 Pseudoexfoliative syndrome demonstrating exfoliative material on lens capsule.
(From Samuelson TW, Shah G: Pseudoexfoliative glaucoma. In: Yanoff M, Duker JS [eds]: Ophthalmology, London, Mosby, 1999.)
Corticosteroid-induced
Traumatic
Angle recession
glaucoma develops in 10% of cases with >180° of involvement due to scarring of the angle and TM
Primary Angle-Closure Glaucoma
Acute angle closure
Secondary Angle-Closure Glaucoma
Mechanism/Etiology
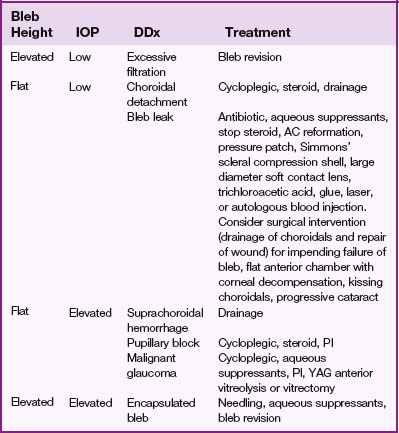
Malignant glaucoma (aqueous misdirection syndrome, ciliolenticular or ciliovitreal block)
Treatment
Normal Tension Glaucoma (NTG)
Glaucoma with open angles and IOP <22 mmHg
Proposed mechanisms
Treatment
Laser
Argon Laser Trabeculoplasty (ALT) (Figure 9-16)
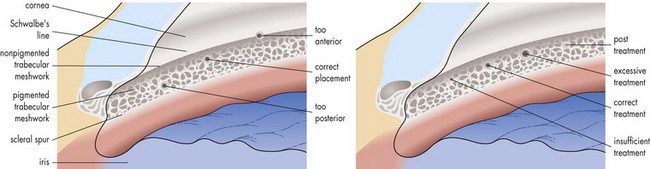
Figure 9-16 ALT.
(From Schwartz AL: Argon Laser Trabeculoplasty in Glaucoma: What’s Happening (Survey Results of American Glaucoma Society Members), J Glaucoma 2:329-336, 1993.)
Anterior burns have poor effect; posterior burns more likely to develop PAS
Surgery
Trabeculectomy
Consider use of antimetabolite in patients at risk for bleb failure
Antimetabolites
Treatment
Drainage Implants (Setons/Tubes)
Seton is from Latin ‘seta’ or bristle (original surgery used horse hair)
Cyclocryotherapy
Surgical Iridectomy
Perform through 3 mm clear corneal wound for angle-closure glaucoma
Indications
Major glaucoma clinical studies
Advanced Glaucoma Intervention Study (AGIS)
Ocular Hypertension Treatment Study (OHTS)
Collaborative Initial Glaucoma Treatment Study (CIGTS)
Early Manifest Glaucoma Trial (EMGT)
Collaborative Normal Tension Glaucoma Study (CNTGS)
Objective: to evaluate whether IOP is a causative factor in NTG
Review Questions (Answers start on page 368)
American Academy of Ophthalmology. Glaucoma, vol 10. San Francisco: AAO; 2012.
Anderson DR, Patella VM. Automated Static Perimetry, 2nd edn. St Louis: Mosby; 1999.
Campbell DG, Netland PA. Stereo Atlas of Glaucoma. St Louis: Mosby; 1998.
Higginbotham EJ, Lee DA. Clinical Guide to Glaucoma Management. Amsterdam: Butterworth-Heinemann; 2003.
Netland PA, Mandal AK. Pediatric Glaucoma. Philadelphia: Elsevier Butterworth-Heinemann; 2006.
Ritch R, Shields MB, Krupin T. The Glaucomas, 2nd edn. St Louis: Mosby; 1996.
Allingham RR, Moroi SE, Shields. Textbook of Glaucoma, 6th edn. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins; 2010.
Weber J, Caprioli J. Atlas of Computerized Perimetry. Philadelphia: WB Saunders; 2000.
Zimmerman TJ, Kooner KS. Clinical Pathways in Glaucoma. New York: Thieme Medical; 2001.