Chapter 3 Gastrointestinal tract
Methods of imaging the gastrointestinal tract
Ambrosini R., Barchiesi A., Di Mizio V., et al. Inflammatory chronic disease of the colon: how to image. Eur. J. Radiol.. 2007;61(3):442-448.
Brochwicz-Lewinski M.J., Paterson-Brown S., Murchison J.T. Small bowel obstruction the water soluble follow-through revisited. Clin. Radiol.. 2003;58(5):393-397.
Gasparaitis A.E., MacEneaney P. Enteroclysis and computed tomography enteroclysis. Gastroenterol. Clin. North Am.. 2002;31(3):715-730.
Introduction to Contrast Media
BARIUM
Barium suspension is made up from pure barium sulphate. (Barium carbonate is poisonous.) The particles of barium must be small (0.1–3 µm), since this makes them more stable in suspension. A non-ionic suspension medium is used, for otherwise the barium particles would aggregate into clumps. The resulting solution has a pH of 5.3, which makes it stable in gastric acid.
There are many varieties of barium suspensions in use. Exact formulations are secret. In most situations the preparation will be diluted with water to give a lower density (Table 3.1).
Table 3.1 Barium suspensions and dilutions with water to give a lower density
| Proprietary name | Density (w/v) – use |
|---|---|
| Baritop 100 | 100% – all parts gastrointestinal tract |
| EPI-C | 150% – large bowel |
| E-Z-Cat | 1–2% – computed tomography of gastrointestinal tract |
| E-Z HD | 250% – oesophagus, stomach and duodenum |
| E-Z Paque | 100% – small intestine |
| Micropaque DC | 100% – oesophagus, stomach and duodenum |
| Micropaque liquid | 100% – small and large bowel |
| Micropaque powder | 76% – small and large bowel |
| Polibar | 115% – large bowel |
| Polibar rapid | 100% – large bowel |
Advantages
Disadvantages
Complications
For further complications (e.g. constipation and impaction), see the specific procedure involved.
Water-Soluble Contrast Agents
GASES
Pharmacological Agents
Hyoscine-N-butyl bromide (Buscopan)
Glucagon
This polypeptide hormone produced by the alpha cells of the islets of Langerhans in the pancreas has a predominantly hyperglycaemic effect but also causes smooth muscle relaxation.
General points
CONTRAST SWALLOW
Contrast medium
Equipment
Rapid serial radiography (6 frames per s) or video recording may be required for assessment of the laryngopharynx and upper oesophagus during deglutition.
Patient preparation
None (but as for barium meal if the stomach is also to be examined – see p. 57).
Preliminary film
A control film is advised prior to a water-soluble study if perforation is suspected.
Technique
Modification of technique
Recently, it has been proposed that pull-back studies are not necessary in the majority of children, as tracheo-oesophageal fistulas can usually be demonstrated on standard contrast swallow examination, providing the oesophagus is distended well with contrast media.1 Pull-back studies are still necessary for intubated patients, or those who are at high risk of aspiration. It is important to remember that fistulas are usually quite high, and the orifice can be occluded by an endotracheal tube. This can prevent the fistula being opacified. This can be rectified by altering the patients position, or slightly withdrawing the ET tube.
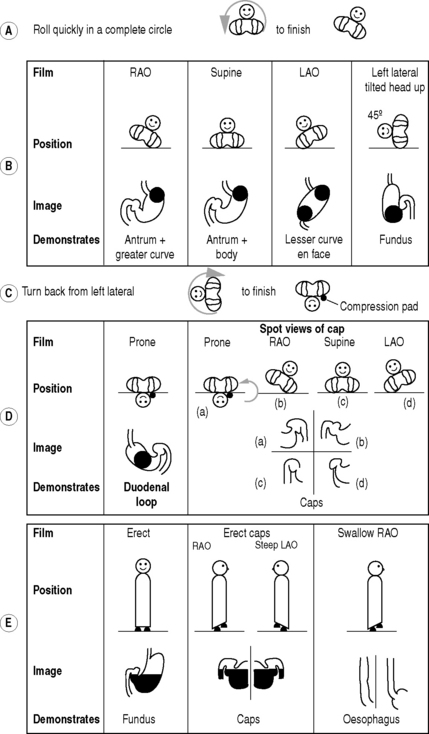
Barium Meal
Technique
The double contrast method (Fig. 3.1):
Films
From the left lateral position the patient returns to a supine position and then rolls onto the left side and over into a prone position. This sequence of movements is required to avoid barium flooding into the duodenal loop, which would occur if the patient were to roll onto the right side to achieve a prone position.
Modification of technique for young children
In newborn infants with upper intestinal obstruction, e.g. duodenal atresia, the diagnosis may be confirmed if 20 ml of air is injected down the nasogastric tube (which will almost certainly have already been introduced by the medical staff). If the diagnosis remains in doubt, it can be replaced by a positive contrast agent (dilute barium or LOCM if the risk of aspiration is high).
Aftercare
BARIUM FOLLOW-THROUGH
Contraindications
Contrast medium
In situations where barium is contraindicated, non-ionic water-soluble solutions have been shown to be a satisfactory alternative.1
Films
Ha H.K., Shin J.H., Rha S.E., et al. Modified small bowel follow through: use of methylcellulose to improve bowel transradiance and prepare barium suspension. Radiology. 1999;211:197-201.
Summers D.S., Roger M.D., Allan P.L., et al. Accelerating the transit time of barium sulphate suspensions in small bowel examinations. Eur. J. Radiol.. 2007;62(1):122-125.
Small-Bowel Enema
Indications and Contraindications
These are the same as for a barium follow-through. In some departments it is only performed in the case of an equivocal follow-through.
Equipment
Patient preparation
Immediately before the examination the pharynx is anaesthetized with lidocaine spray.
Technique
Cirillo L.C., Camera L., Della Noce M., et al. Accuracy of enteroclysis in Crohn’s disease of the small bowel: a retrospective study. Eur. Radiol.. 2000;10(12):1894-1898.
Minordi L.M., Vecchioli A., Guidi L., et al. Multidetector CT enteroclysis versus barium enteroclysis with methylcellulose in patients with suspected small bowel disease. Eur. Radiol.. 2006;16(7):1527-1536.
Nolan D.J. The true yield of the small intestinal barium study. Endoscopy. 1997;29:447-453.
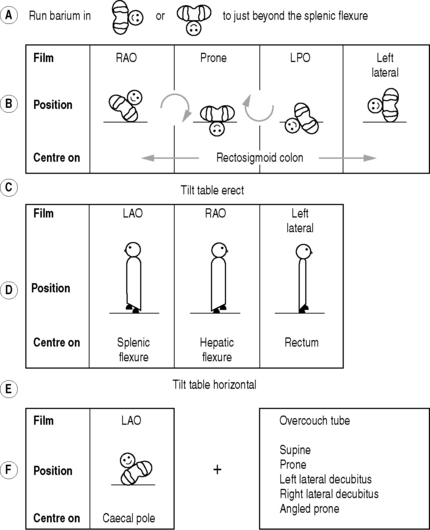
Barium Enema
Contraindications
Patient preparation
Many regimes for bowel preparation exist. A suggested regime is as follows:
Technique
The double-contrast method (Fig. 3.2):
Films
Aftercare
1 Marion J.F., Present D.H. The modern medical management of acute severe ulcerative colitis. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol.. 1997;9:831-835.
2 Low V.H. What is the current recommended waiting time for performance of a gastrointestinal barium study after endoscopic biopsy of the upper or lower gastrointestinal tract? Am. J. Roentgenol.. 1998;170:1104-1105.
3 Taylor P.N., Beckly D.E. Use of air in double contrast barium enema: is it still acceptable? Clin. Radiol.. 1991;44:183-184.
Cittadini G., Sardanelli F., De Cicco E., et al. Bowel preparation for the double contrast barium enema: how to maintain coating with cleansing? Clin. Radiol.. 1999;54:216-220.
Ferrucci J.T. Double-contrast barium enema: use in practice and implications for CT colonography. Am. J. Roentgenol.. 2006;187(1):170-173.
Martin C.J. A review of factors affecting patient doses for barium enemas and meals. Br. J. Radiol.. 2004;77(922):864-868.
Rollandi G.A., Biscaldi E., DeCicco E. Double contrast barium enema: technique, indications, results and limitations of a conventional imaging methodology in the MDCT virtual endoscopy era. Eur. J. Radiol.. 2007;61(3):382. –327
The ‘Instant’ Enema
AIR ENEMA
REDUCTION OF AN INTUSSUSCEPTION
This procedure should only be attempted in full consultation with the surgeon in charge of the case and when an anaesthetist with adequate paediatric training and experience, and with paediatric anaesthetic equipment, is available.1,2
Methods
Contraindications
Patient preparation
Preliminary investigations
Technique
Pneumatic reduction
Barium reduction: now rarely used
1 The Royal College of Anaesthetists. Guidelines for the Provision of Anaesthetic Services. Guidance on the Provision of Paediatric Anaesthesia. London: Royal, 1999;24-26.
2 The British Association of Paediatric Surgeons. revised 1995. A Guide for Purchasers and Providers of Paediatric Surgeons. London: British Association of Paediatric Surgeons; 1994.
3 Kirks D.R. Air intussusception reduction: ‘The winds of change’. Pediatr. Radiol.. 1995;25:89-91.
4 Stringer D.A., Ein S.H. Pneumatic reduction: advantages, risks and indications. Pediatr. Radiol.. 1990;20:475-477.
5 Daneman A., Navarro O. Intussusception Part 2: An update on the evolution of management. Paediatr. Radiol.. 2004;34:97-108.
6 Lim H.K., Bae S.H., Lee K.H., et al. Assessment of reducibility of ileocolic intussusception in children: usefulness of color Doppler sonography. Radiology. 1994;191:781-785.
7 Britton I., Wilkinson A.G. Ultrasound features of intussusception predicting outcome of air enema. Pediatr. Radiol.. 1999;29:705-710.
8 Gorenstein A., Raucher A., Serour F., et al. Intussusception in children: reduction with repeated, delayed air enema. Radiology. 1998;206:721-724.
9 Barr L.L., Stansberry S.D., Swischuk L.E. Significance of age, duration, obstruction and the dissection sign in intussusception. Pediatr. Radiol.. 1990;20:454-456.
Contrast Enema in Neonatal Low Intestinal Obstruction
Patient preparation
The baby should already have i.v. access and be well hydrated prior to the procedure.
Contrast medium
Dilute ionic contrast medium as is used for cystography, e.g. Urografin 150. This has the advantage of not provoking large fluid shifts and being dense enough to provide satisfactory images. Non-ionic contrast media and barium offer no advantages and the latter is contraindicated with perforation as a possibility. Infants with meconium ileus or functional immaturity will benefit from a water-soluble contrast enema and so their therapeutic enema commences with the diagnostic study. The non-operative treatment of meconium ileus was first described using the hypertonic agent Gastrografin, which dislodged the sticky meconium by drawing water into the bowel lumen. However, most paediatric radiologists now believe that a hypertonic agent is not necessary for successful treatment.1
Technique
If the enema demonstrates that the entire colon is small (a microcolon; <1 cm in diameter) then the diagnosis is likely to be meconium ileus or ileal atresia. (The microcolon of prematurity and total colonic Hirschsprung’s disease are alternative rare diagnoses.) For the treatment of meconium ileus, the aim is to run the water-soluble contrast medium into the small bowel to surround the meconium. An attempt should be made to get the contrast medium back into dilated small bowel. If successful, meconium should be passed in the next hour. If no result is seen and the infant’s condition deteriorates then surgical intervention will be necessary. If the passage of meconium is incomplete and the clinical condition remains stable, multiple enemas over the succeeding few days will be necessary to ensure complete resolution of the obstruction.
Overall success rate is approximately 50–60%, with a perforation rate of 2%.1
Sinogram
RETROGRADE ILEOGRAM
HERNIOGRAM
Ekberg O. Inguinal herniography in adults: technique, normal anatomy, and diagnostic criteria for hernias. Radiology. 1981;138:31-36.
Ekberg O. Complications after herniography in adults. Am. J. Roentgenol.. 1983;140:490-495.
Garner J.P., Patel S., Glaves J., et al. Is herniography useful. Hernia. 2006;10(1):66-69.
Gwanmesia I.I., Walsh S., Bury R., et al. Unexplained groin pain: safety and reliability of herniography for the diagnosis of occult hernias. Postgrad. Med. J.. 2001;77(906):250-251.
Evacuating Proctogram
Dobben A.C., Wiersma T.G., Janssen L.W., et al. Prospective assessment of interobserver agreement for defecography in fecal incontinence. Am. J. Roentgenol.. 2005;185(5):1166-1172.
Jones H.J., Swift R.I., Blake H. A prospective audit of the usefulness of evacuating proctography. Ann. R. Coll. Surg. Engl.. 1998;80(1):40-45.
Kelvin F.M., Maglinte D.D., Hornback J.A., et al. Pelvic prolapse: assessment with evacuation proctography (defecography). Radiology. 1992;184:547-551.
Coeliac Axis, Superior Mesenteric and Inferior Mesenteric Arteriography
Technique
Late-phase visceral arteriography
N.B. If splenic vein opacification is required, then a late-phase splenic arteriogram is necessary.
ULTRASOUND OF THE GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT
ENDOLUMINAL EXAMINATION OF THE OESOPHAGUS AND STOMACH
Indications
Technique
Monitoring with a pulse oximeter is recommended. If the stomach is to be examined, this may be filled with de-aerated water through the working channel before the patient is examined in a left lateral decubitus position. The echo-endoscope is passed during endoscopy, either combined with direct vision or blind by an experienced endoscopist. A 360° rotary transducer will provide transverse scans with respect to the long axis of the tube.
Transabdominal Examination of the Lower Oesophagus and Stomach
HYPERTROPHIC PYLORIC STENOSIS
The typical patient is a 6-week-old male infant with non-bilious projectile vomiting.
Technique
Small Bowel
Indications
Large Bowel
CT of the Gastrointestinal Tract
Boudiaf M., Soyer P., Terem C., et al. CT evaluation of small bowel obstruction. Radiographics. 2001;21(3):613-624.
Domjan J., Blaquiere R., Odurny A. Is minimal preparation CT comparable with barium enema in elderly patients with colonic symptoms. Clin. Radiol.. 1998;53:894-898.
Peck J.J., Milleson T., Phelan J. The role of computed tomography with contrast and small bowel follow-through in the management of small bowel obstruction. Am. J. Surg.. 1999;177:375-378.
Rao P.M., Boland G.W. Imaging of acute right lower abdominal quadrant pain. Clin. Radiol.. 1998;53:639-649.
Wittenberg J., Harisinghani M.G., Jhaveri K., et al. Algorithmic approach to CT diagnosis of the abnormal bowel wall. Radiographics. 2002;22(5):1093-1107.
Computed Tomographic Colonography
Indications
Technique
Aschoff A.J., Ernst A.S., Brambs H.J. CT colonography: an update. Eur. Radiol.. 2008;18(3):429-437.
Blachar A., Sosna J. CT colonography (virtual colonoscopy): technique, indications and performance. Digestion. 2007;76(1):34-41.
Geenen R.W., Hussain S.M., Cademartiri F., et al. CT and MR colonography: scanning techniques, post processing, and emphasis on polyp detection. Radiographics. 2004;24(1):e18.
Mang T., Maier A., Plank C., et al. Pitfalls in multi-detector row CT colonography: a systematic approach. Radiographics. 2007;27(2):431-454.
Tolan D.J., Armstrong E.M., Chapman A.H. Replacing barium enema with CT colonography in patients older than 70 years: the importance of detecting extracolonic abnormalities. Am. J. Roentgenol.. 2007;189(5):1104-1111.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Gastrointestinal Tract
Small-bowel magnetic resonance enteroclysis
Berman L., Israel G.M., McCarthy S.M., et al. Utility of magnetic resonance imaging in anorectal disease. World J. Gastroenterol.. 2007;13(23):3153-3158.
Buchanan G.N., Halligan S., Bartram C.I., et al. Clinical examination, endosonography, and MR imaging in preoperative assessment of fistula in ano: comparison with outcome-based reference standard. Radiology. 2004;233:674-681.
Fidler J. MR imaging of the small bowel. Radiol. Clin. North Am.. 2007;45(2):317-331.
Halligan S., Stoker J. Imaging of fistula in ano. Radiology. 2006;239:18-33.
Schreyer A.G., Geissler A., Albrich H., et al. Abdominal MRI after enteroclysis or with oral contrast in patients with suspected or proven Crohn’s disease. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol.. 2004;2(6):491-497.
Radionuclide Gastro-Oesophageal Reflux Study
Radiopharmaceuticals
Technique
Physiological test1 – adults and older children
Milk scan1 – infants and younger children
1 Guillet J., Basse-Cathalinat B., Christophe E., et al. Routine studies of swallowed radionuclide transit in paediatrics: experience with 400 patients. Eur. J. Nucl. Med.. 1984;9:86-90.
2 Martins J.C., Isaacs P.E., Sladen G.E., et al. Gastro-oesophageal reflux scintigraphy compared with pH probe monitoring. Nucl. Med. Commun.. 1984;5:201-204.
Radionuclide Gastric-Emptying Study
Radiopharmaceuticals
Many radiolabelled meals have been designed for gastric-emptying studies, but as yet no standard has emerged. Emptying rate measured by radiolabelling is influenced by many factors, for example meal bulk, fat content, calorie content, patient position during imaging and labelling stability in vivo. For this reason, so-called ‘normal’ emptying times need to be taken in the context of the particular meal and protocol used to generate them. It is important that the meal used is physiological and reproducible. For centres new to the technique it is better to use a meal for which published data exist, rather than create yet another formulation with inherently different behaviour.
Both liquid and solid studies may be performed, separately or simultaneously, as a dual isotope study. Liquids have generally shorter emptying times than solids, and tend to follow an exponential emptying pattern. Solids tend to empty linearly after a lag phase. Prolonged solid emptying is highly correlated with prolonged liquid emptying, and there is debate, therefore, as to whether both studies are routinely necessary.1 Examples of meals used are:
Technique
Imaging from a single projection can cause significant errors due to movement of the meal anteriorly as it transfers to the antrum, thereby altering the amount of tissue attenuation of gamma-photons. The problem is likely to be exacerbated in obese patients. This can largely be overcome by taking pairs of opposing views and calculating the geometric, mean stomach activity in each pair:
Analysis
Additional techniques
Radionuclide Meckel’s Diverticulum Scan
Contraindications
Elsayes K.M., Menias C.O., Harvin H.J., et al. Imaging manifestations of Meckel’s diverticulum. Am. J. Roentgenol.. 2007;189:81-88.
Ford P.V., Bartold S.P., Fink-Bennett D.M., et al. Procedure guidelines for gastrointestinal bleeding and Meckel’s diverticulum scintigraphy. J. Nucl. Med.. 1999;40:1226-1232.
Radionuclide Imaging of Gastrointestinal Bleeding
Radiopharmaceuticals
Patient preparation
Technique
1 Chaudhuri T.K. Radionuclide methods of detecting acute gastrointestinal bleeding. Int. J. Rad. Appl. Instrum.. 1991;18(Part B):655-661.
2 Bunker S.R., Lull R.J., Tanasescu D.E., et al. Scintigraphy of gastrointestinal hemorrhage: superiority of 99mTc red blood cells over 99mTc sulfur colloid. Am. J. Roentgenol.. 1984;143:543-548.
3 Maurer A.H. Gastrointestinal bleeding and cine-scintigraphy. Semin. Nucl. Med.. 1996;26:43-50.
4 Laing C.J., Tobias T., Rosenblum D.I., et al. Acute gastrointestinal bleeding: emerging role of multidetector CT angiography and review of current imaging techniques. Radiographics. 2007;27:1055-1070.

 = Barium
= Barium