Objectives
• Identify the components of a gastrointestinal history.
• Discuss the nursing management of a patient undergoing a gastrointestinal diagnostic procedure.
![]()
Be sure to check out the bonus material, including free self-assessment exercises, on the Evolve web site at http://evolve.elsevier.com/Urden/priorities/.
Assessment of the critically ill patient with gastrointestinal dysfunction includes a review of the patient’s history, a thorough physical examination, and analysis of the patient’s laboratory data. Numerous invasive and noninvasive diagnostic procedures may also be performed to help identify the disorder.
Clinical Assessment
A thorough clinical assessment of the patient with gastrointestinal dysfunction is imperative for the early identification and treatment of gastrointestinal disorders. The completed assessment serves as the foundation for developing the management plan for the patient. The assessment process can be brief or can involve a detailed history and examination, depending on the nature and immediacy of the patient’s situation.1
History
Taking a thorough and accurate history is extremely important to the assessment process. The patient’s history provides the foundation and direction for the rest of the assessment. The overall goal of the patient interview is to expose key clinical manifestations that will facilitate the identification of the underlying cause of the illness. This information can then assist in the development of an appropriate management plan.2
The initial presentation of the patient determines the rapidity and direction of the interview. For a patient in acute distress, the history should be curtailed to a few questions about the patient’s chief complaint and the precipitating events. For a patient in no obvious distress, the history should focus on four different areas: (1) review of the patient’s present illness; (2) overview of the patient’s general gastrointestinal status including previous GI diagnostic studies or interventional procedures; (3) examination of the patient’s personal and social history, including dietary habits, nutritional status, bowel characteristics (stool descriptions), alcohol intake, and dependence on laxatives or enemas; and (4) survey of the patient’s family history, including metabolic disorders, malabsorption syndromes, and cancer of the GI tract.3,4
Physical Examination
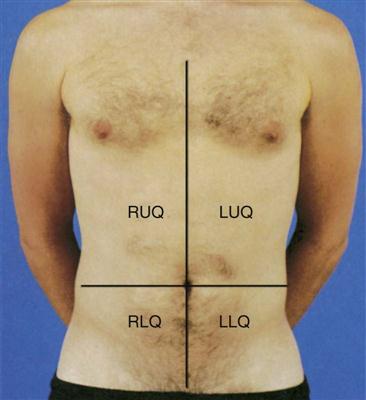
The physical examination helps to establish baseline data about the physical dimensions of the patient’s situation.3 The abdomen is divided into four quadrants (left upper, right upper, left lower, and right lower), with the umbilicus as the middle point, to help specify the location of examination findings (Figure 21-1 and Box 21-1). The assessment should proceed when the patient is as comfortable as possible and in the supine position; however, the position may need readjustment if it elicits pain. To prevent stimulation of gastrointestinal activity, the order for the assessment should be changed to inspection, auscultation, percussion, and palpation.4
Inspection
Inspection of the patient focuses on three priorities: (1) observation of the oral cavity, (2) assessment of the skin over the abdomen, and (3) evaluation of the shape of the abdomen. The examination should be performed in a warm, well-lighted environment with the patient in a comfortable position and with the abdomen exposed.
Observation of the Oral Cavity
Although assessment of the gastrointestinal system classically begins with inspection of the abdomen, the patient’s oral cavity also must be inspected to determine any unusual findings. Abnormal findings of the mouth include joint tenderness, inflammation of the gums, missing teeth, dental caries, ill-fitting dentures, and mouth odor.5
Assessment of the Skin over the Abdomen
Observe the skin for pigmentation, lesions, striae, scars, petechiae, signs of dehydration, and venous pattern. Pigmentation may vary considerably and still be within normal limits because of race and ethnic background, although the abdomen usually is a lighter color than other exposed areas of the skin. Abnormal findings include jaundice, skin lesions, and a tense and glistening appearance of the skin. Old striae (stretch marks) usually are silver, whereas pinkish purple striae may indicate Cushing’s syndrome.4 A bluish discoloration of the umbilicus (Cullen’s sign) and of the flank (Grey Turner’s sign) indicates retroperitoneal bleeding.1
Evaluation of the Shape of the Abdomen
Observe the abdomen for contour, noting whether it is flat, slightly concave, or slightly round; observe for symmetry and for movement. Marked distention is an abnormal finding. In particular, ascites may cause generalized distention and bulging flanks. Asymmetric distention may indicate organ enlargement or a mass. Peristaltic waves should not be visible except in very thin patients. In the case of intestinal obstruction, hyperactive peristaltic waves may be observed. Pulsation in the epigastric area is often a normal finding, but increased pulsation may indicate an aortic aneurysm. Symmetric movement of the abdomen with respirations is usually seen in men.4,5
Auscultation
Auscultation of the patient focuses on two priorities: (1) evaluation of bowels sounds and (2) assessment of bruits. Auscultation of the abdomen provides clinical data regarding the status of the bowel’s motility. Initially, listen with the diaphragm of the stethoscope below and to the right of the umbilicus. The examination proceeds methodically through all four quadrants, lifting and then replacing the diaphragm of the stethoscope lightly against the abdomen (see Figure 21-1).
Evaluation of Bowel Sounds
Normal bowel sounds include high-pitched, gurgling sounds that occur approximately every 5 to 15 seconds or at a rate of 5 to 34 times per minute. Colonic sounds are low-pitched and have a rumbling quality. A venous hum may be audible sometimes.6,7 Table 21-1 provides a list of abnormal abdominal sounds.
TABLE 21-1
| SOUND | CAUSE |
| Hyperactive bowel sounds (borborygmi), loud and prolonged | Hunger, gastroenteritis, or early intestinal obstruction |
| High-pitched, tinkling sounds | Intestinal air and fluid under pressure; characteristic of early intestinal obstruction |
| Decreased (hypoactive) bowel sounds, infrequent and abnormally faint sounds | Possible peritonitis or ileus |
| Absence of bowel sounds (confirmed only after auscultation of all four quadrants and continuous auscultation for 5 min) | Temporary loss of intestinal motility, as occurs with complete ileus |
| Friction rubs, high-pitched sounds heard over liver and spleen (RUQ and LUQ), synchronous with respiration | Pathological conditions such as tumors or infection that cause inflammation of organ’s peritoneal covering |
| Bruits, audible swishing sounds that may be heard over aortic, iliac, renal, and femoral arteries | Abnormality of blood flow (requires additional evaluation to determine specific disorder) |
| Venous hum, low-pitched, continuous sound | Increased collateral circulation between portal and systemic venous systems |
LUQ, left upper quadrant; RUQ, right upper quadrant.
From Doughty DB, Jackson DB: Gastrointestinal disorders, St Louis, 1993, Mosby.
Abnormal findings include the absence of bowel sounds throughout a 5-minute period, extremely soft and widely separated sounds, and increased sounds with a high-pitched, loud rushing sound (peristaltic rush). Absent bowel sounds may result from inflammation, ileus, electrolyte disturbances, and ischemia. Bowels sounds may be increased with diarrhea and early intestinal obstruction.6,7
Assessment of Bruits
The abdomen should be auscultated for the presence of bruits, using the bell of the stethoscope. Bruits are created by turbulent flow over a partially obstructed artery and are always considered an abnormal finding. The aorta, the right and left renal arteries, and the iliac arteries should be auscultated.5–7
Percussion
Percussion of the patient focuses on one priority: (1) assessment of the deep organs. Percussion is used to elicit information about deep organs, such as the liver, spleen, and pancreas. Because the abdomen is a sensitive area, muscle tension may interfere with this part of the assessment. Percussion often helps relax tense muscles, and it is performed before palpation. Percussion in the absence of disease helps to delineate the position and size of the liver and spleen, and it assists in the detection of fluid, gaseous distention, and masses in the abdomen.5
Assessment of Deep Organs
Percussion should proceed systematically and lightly in all four quadrants. Normal findings include tympany over the stomach when empty, tympany or hyperresonance over the intestine, and dullness over the liver and spleen. Abnormal areas of dullness may indicate an underlying mass. Solid masses, enlarged organs, and a distended bladder also produce areas of dullness. Dullness over both flanks may indicate ascites and necessitates further assessment.6
Palpation
Palpation of the patient focuses on one priority: (1) detection of abdominal pathological conditions. Both light and deep palpation of each organ and quadrant should be completed. Light palpation, which has a palpation depth of approximately 1 cm, assesses to the depth of the skin and fascia. Deep palpation assesses the rectus abdominis muscle and is performed bimanually to a depth of 4 to 5 cm. Deep palpation is most helpful in detecting abdominal masses. Areas in which the patient complains of tenderness should be palpated last.6
Detection of Abdominal Pathological Conditions
Normal findings include no areas of tenderness or pain, no masses, and no hardened areas. Persistent involuntary guarding may indicate peritoneal inflammation, particularly if it continues even after relaxation techniques are used. Rebound tenderness, in which pain increases with quick release of a palpated area, indicates an inflamed peritoneum.4
Laboratory Studies
The value of various laboratory studies used to diagnose and treat diseases of the gastrointestinal system has been emphasized often. However, no single study provides an overall picture of the various organs’ functional state, and no single value is predictive by itself. Laboratory studies used in the assessment of gastrointestinal function, liver function, and pancreatic function are found in Tables 21-2, 21-3, and 21-4, respectively.
TABLE 21-2
SELECTED LABORATORY STUDIES OF GASTROINTESTINAL FUNCTION
| TEST | NORMAL FINDINGS | CLINICAL SIGNIFICANCE OF ABNORMAL FINDINGS |
| Stool studies | Resident microorganisms: clostridia, enterococci, Pseudomonas, a few yeasts | Detection of Salmonella typhi (typhoid fever), Shigella (dysentery), Vibrio cholerae (cholera), Yersinia (enterocolitis), Escherichia coli (gastroenteritis), Staphylococcus aureus (food poisoning), Clostridium botulinum (food poisoning), Clostridium perfringens (food poisoning), Aeromonas (gastroenteritis) |
| Fat: 2-6 g/24 hr | Steatorrhea (increased values) can result from intestinal malabsorption or pancreatic insufficiency. | |
| Pus: none | Large amounts of pus are associated with chronic ulcerative colitis, abscesses, and anorectal fistula. | |
| Occult blood: none (ortho-toluidine or guaiac test) | Positive test results associated with bleeding | |
| Ova and parasites: none | Detection of Entamoeba histolytica (amebiasis), Giardia lamblia (giardiasis), and worms | |
| D-Xylose absorption | 5-hr urinary excretion: 4.5 g/L | Differentiation of pancreatic steatorrhea (normal D-xylose absorption) from intestinal steatorrhea (impaired D-xylose absorption) |
| Peak blood level: >30 mg/dL | ||
| Gastric acid stimulation | 11-20 mEq/hr after stimulation | Detection of duodenal ulcers, Zollinger-Ellison syndrome (increased values), gastric atrophy, gastric carcinoma (decreased values) |
| Manometry* | Values vary at different levels of the intestine | Inadequate swallowing, motility, sphincter function |
| Culture and sensitivity of duodenal contents | No pathogens | Detection of Salmonella typhi (typhoid fever) |
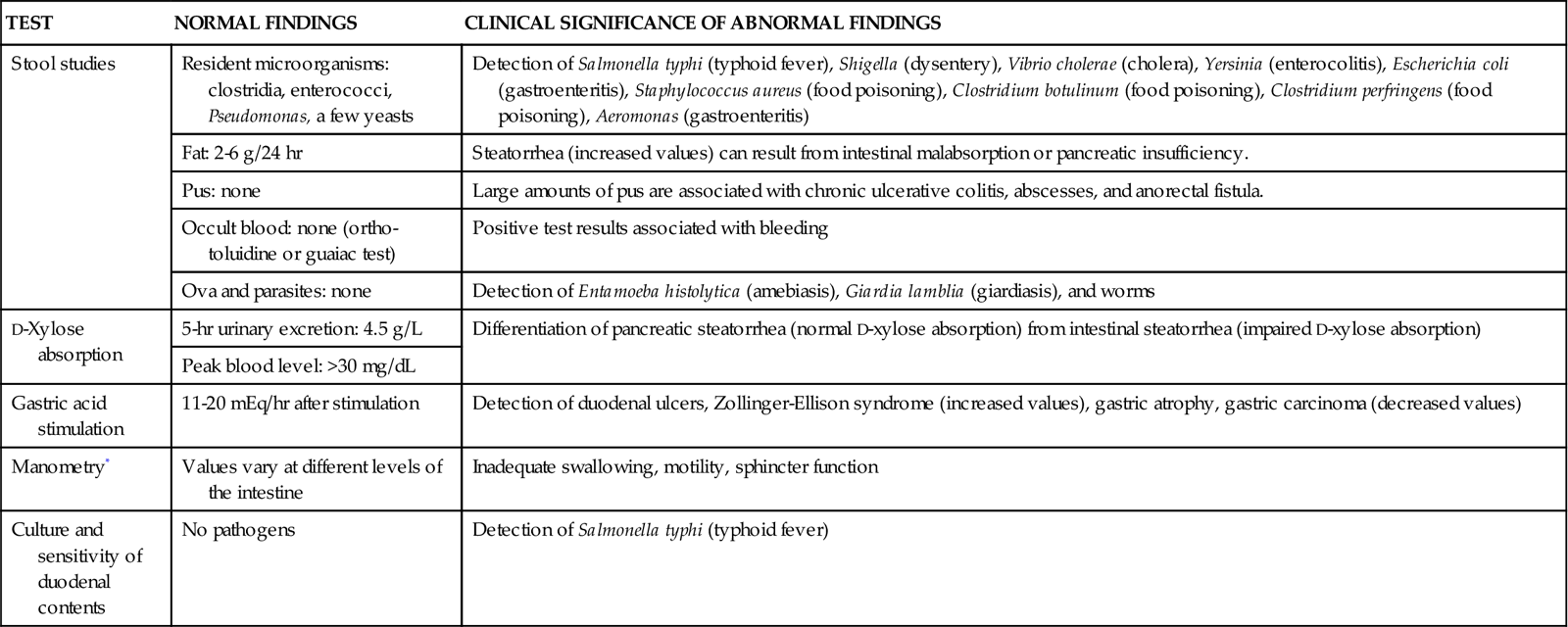
*Use of water-filled catheters connected to pressure transducers passed into the esophagus, stomach, colon, or rectum to evaluate contractility.
From McCance KL, et al, editors: Pathophysiology: The biologic basis for disease in adults and children, ed 6, St Louis, 2010, Mosby.
TABLE 21-3
COMMON LABORATORY STUDIES OF LIVER FUNCTION
| TEST | NORMAL VALUE | INTERPRETATION |
| Serum Enzymes | ||
| Alkaline phosphatase | 13-39 units/mL | Increases with biliary obstruction and cholestatic hepatitis |
| Aspartate aminotransferase (AST; formerly serum glutamate oxaloacetate transaminase [SGOT]) | 5-40 units/mL | Increases with hepatocellular injury |
| Alanine aminotransferase (ALT; formerly serum glutamate pyruvate transaminase [SGPT]) | 5-35 units/mL | Increases with hepatocellular injury |
| Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) | 200-500 units/mL | Isoenzyme LD5 is elevated with hypoxic and primary liver injury |
| 5′-Nucleotidase | 2-11 units/mL | Increases with increase in alkaline phosphatase and cholestatic disorders |
| Bilirubin Metabolism | ||
| Serum bilirubin | ||
| •Indirect (unconjugated) | <0.8 mg/dL | Increases with hemolysis (lysis of red blood cells) |
| •Direct (conjugated) | 0.2-0.4 mg/dL | Increases with hepatocellular injury or obstruction |
| Total | <1.0 mg/dL | Increases with biliary obstruction |
| Urine bilirubin | 0 | Decreases with biliary obstruction |
| Urine urobilinogen | 0-4 mg/24 hr | Increases with hemolysis or shunting or portal blood flow |
| Serum Proteins | ||
| Albumin | 3.3-5.5 g/dL | Reduced with hepatocellular injury |
| Globulin | 2.5-3.5 g/dL | Increases with hepatitis |
| Total | 6-7 g/dL | |
| Albumin-to-globulin (A/G) ratio | 1.5-2.5 : 1 | Ratio reverses with chronic hepatitis or other chronic liver disease |
| Transferrin | 250-300 µg/dL | Liver damage with decreased values, iron deficiency with increased values |
| Alpha-fetoprotein | 6-20 ng/mL | Elevated values in primary hepatocellular carcinoma |
| Blood Clotting Functions | ||
| Prothrombin time | 11.5-14 sec or 90%-100% of control | Increases with chronic liver disease (cirrhosis) or vitamin K deficiency |
| Partial thromboplastin time | 25-40 sec | Increases with severe liver disease or heparin therapy |
| Bromsulphalein (BSP) excretion | <6% retention in 45 min | Increased retention with hepatocellular injury |
From McCance KL, et al, editors: Pathophysiology: The biologic basis for disease in adults and children, ed 6, St Louis, 2010, Mosby.
TABLE 21-4
COMMON LABORATORY STUDIES OF PANCREATIC FUNCTION
| TEST | NORMAL VALUE | CLINICAL SIGNIFICANCE |
| Serum amylase | 60-180 Somogyi units/mL | Elevated levels with pancreatic inflammation |
| Serum lipase | 1.5 Somogyi units/mL | Elevated levels with pancreatic inflammation (may be elevated with other conditions; differentiates with amylase, isoenzyme study) |
| Urine amylase | 35-260 Somogyi units/hr | Elevated levels with pancreatic inflammation |
| Secretin test | Volume 1.8 mL/kg/hr | Decreased volume with pancreatic disease because secretin stimulates pancreatic secretion |
| Bicarbonate concentration: >80 mEq/L | ||
| Bicarbonate output: >10 mEq/L/30 sec | ||
| Stool fat | 2-5 g/25 hr | Measures fatty acids: decreased pancreatic lipase increases stool fat |
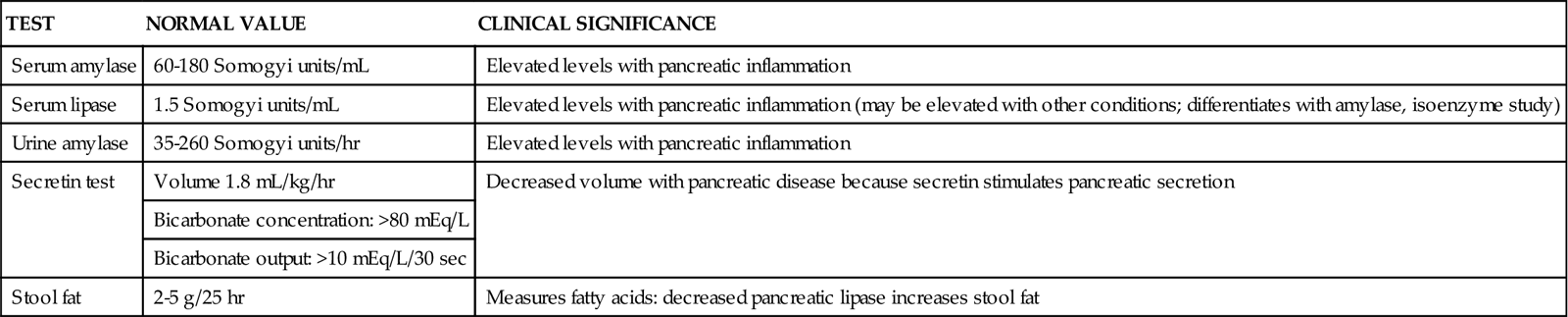
From McCance KL, et al, editors: Pathophysiology: The biologic basis for disease in adults and children, ed 6, St Louis, 2010, Mosby.
Diagnostic Procedures
Table 21-5 presents an overview of the various diagnostic procedures used to evaluate the patient with GI dysfunction.
TABLE 21-5
GASTROINTESTINAL DIAGNOSTIC STUDIES
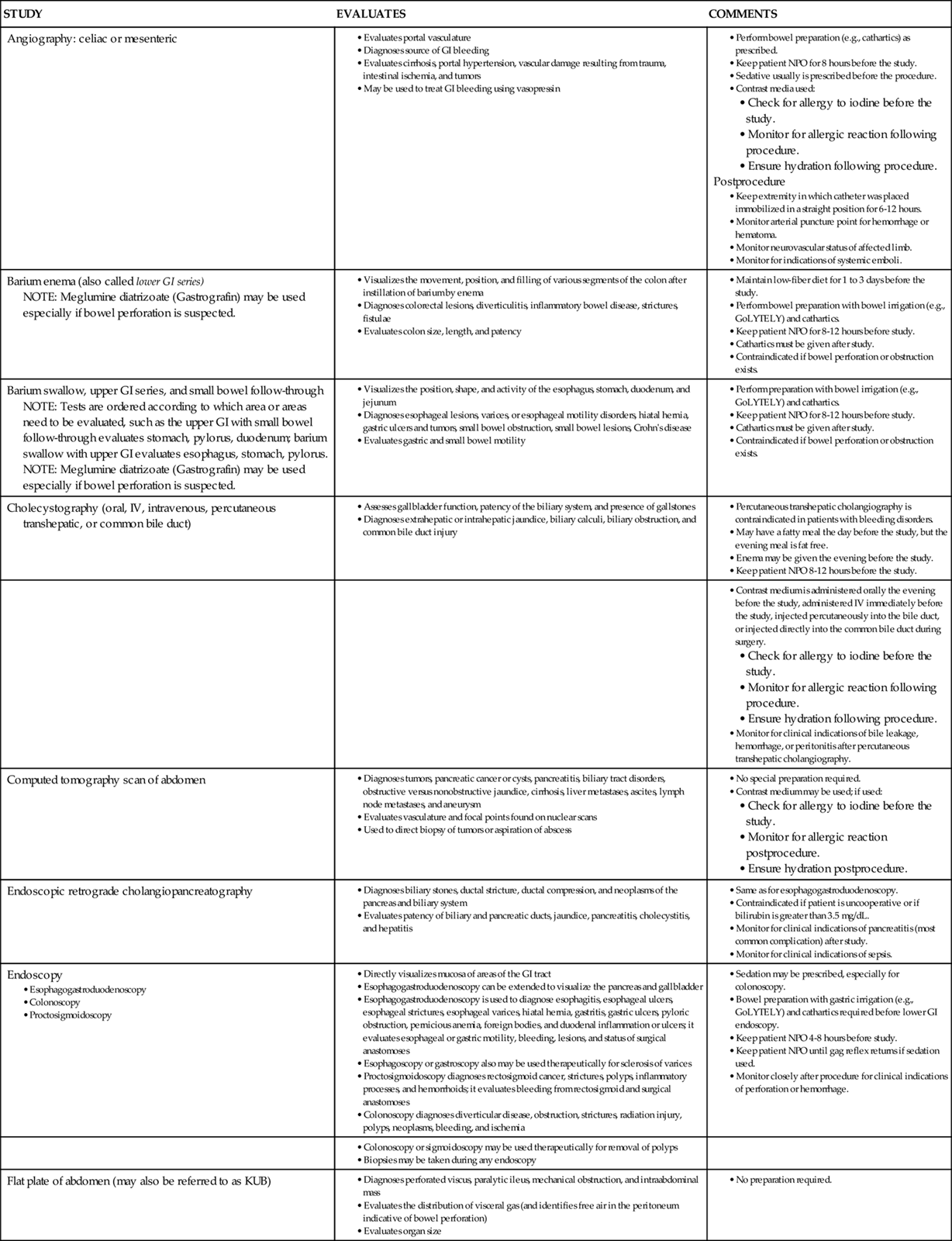
GI, Gastrointestinal; IV, intravenous; NPO, nothing by mouth.
From Dennison RD: Pass CCRN!, ed 3, St Louis, 2007, Mosby.
Nursing Management
The nursing management of a patient undergoing a diagnostic procedure involves a variety of interventions. Nursing priorities include (1) preparing the patient psychologically and physically for the procedure, (2) monitoring the patient’s responses to the procedure, and (3) assessing the patient after the procedure. Preparing the patient includes teaching the patient about the procedure, answering any questions, and transporting and positioning the patient for the procedure. Monitoring the patient’s responses to the procedure includes observing the patient for signs of pain, anxiety, or hemorrhage and monitoring vital signs. Assessing the patient after the procedure includes observing for complications of the procedure and medicating the patient for any postprocedural discomfort. Any evidence of gastrointestinal bleeding should be immediately reported to the physician, and emergency measures to maintain circulation must be initiated.8