Euthyroid sick syndrome
1. What is euthyroid sick syndrome?
Euthyroid sick syndrome refers to changes in serum thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), serum thyroid hormone, and tissue thyroid hormone levels that occur in patients with various nonthyroidal illnesses and starvation. It is not a primary thyroid disorder but instead results from changes in thyroid hormone secretion, transport, and metabolism induced by the nonthyroidal illness.
2. What hormone changes occur in patients with mild to moderate nonthyroidal illnesses?
Serum total triiodothyronine (T3) and free T3 and tissue T3 levels decrease as a result of reduced conversion of thyroxine (T4) to T3 in peripheral tissues, predominantly the liver, where hepatic deiodinase type I (D1) activity is decreased. Serum free T4 and TSH levels usually remain within the reference range in the mildest form of this condition.
3. Describe the hormone changes in patients with moderate to severe nonthyroidal illnesses.
Serum total T3 and free T3 levels decrease further; total T4 also decreases, and the T3 resin uptake (T3RU) increases. The latter changes result from reduced binding of thyroid hormones to their transport proteins because of both impaired protein synthesis and the presence of circulating inhibitors of protein binding. Serum TSH levels remain normal or become decreased at this stage. Free T4 may be normal, decreased, or increased.
4. Describe the hormone changes associated with recovery from nonthyroidal illnesses.
Free T4 decreases, and TSH increases. As hepatic protein synthesis improves and circulating inhibitors of protein binding disappear, serum free T4 levels drop transiently with a compensatory increase in serum TSH levels before complete normalization occurs. Serum T3 levels also eventually normalize.
5. How can euthyroid sick syndrome be distinguished from hypothyroidism?
In euthyroid sick syndrome, serum T3 is decreased proportionately more than T4, the T3RU is high, and TSH is normal or mildly decreased and then mildly increased during recovery. In primary hypothyroidism, serum T4 is reduced proportionately more than T3, the T3RU is low, and TSH is increased. Other tests may also be helpful. In euthyroid sick syndrome, free T4 is usually normal and reverse T3 (rT3) is increased; in hypothyroidism, both free T4 and rT3 are decreased.
6. What causes euthyroid sick syndrome?
Euthyroid sick syndrome is believed to be caused by increased circulating cytokines and other inflammation mediators resulting from the underlying nonthyroidal illness. These mediators inhibit the thyroid axis at multiple levels, including the pituitary (decreased TSH secretion), the thyroid (decreased T4 and T3 responses to TSH), transport proteins (decreased thyroid hormone binding), and peripheral tissues (decreased conversion of T4 to T3).
7. What is the function of the deiodinase enzymes?
Deiodinases are selenocysteine enzymes that activate and deactivate thyroid hormones by removing iodine molecules. Deiodinase enzymes have three known subtypes: D1, deiodinase 2 (D2), and deiodinase 3 (D3) (Table 39-1 and Fig. 39-1). D1 converts T4 to T3 in the liver and kidneys, thus producing the majority of circulating T3, and converts reverse T3 (rT3) to diiodothyronine (T2); D1 has a higher affinity for rT3 than for T4. D2 converts T4 to T3 in the brain and pituitary gland, thus producing the majority of cellular T3 in these tissues; D2 has a higher affinity for T4 than for rT3. D3 converts T4 to rT3 and T3 to T2.
TABLE 39-1.
DEIODINASE ENZYMES: SELENOCYSTEINE ENZYMES THAT DEIODINATE THYROID HORMONES
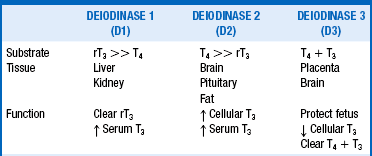
rT3, Reverse triiodothyronine; T3, triiodothyronine; T4, thyroxine.
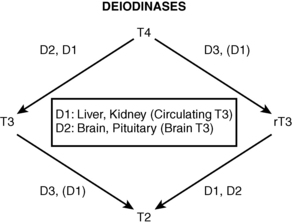
Figure 39-1. Deiodinase function.
8. What changes in deiodinase function are seen in euthyroid sick syndrome?
D1 activity is significantly reduced and D3 activity is enhanced in euthyroid sick syndrome. These changes are responsible for the low serum T3 and high serum rT3 levels that are characteristic of this condition.
9. Is euthyroid sick syndrome an adaptive mechanism, or is it harmful?
Many experts consider euthyroid sick syndrome to be an adaptive mechanism that may reduce peripheral tissue energy expenditure during the nonthyroidal illness. Conversely, other experts argue that the alterations in circulating thyroid hormone levels may be harmful and may accentuate the effects of the nonthyroidal illness. This issue is likely to remain controversial for years to come.
10. Should patients with euthyroid sick syndrome be treated with thyroid hormones?
Management of euthyroid sick syndrome is also controversial. Liothyronine (LT3) therapy was shown in a randomized controlled trial to improve ventricular performance and the neuroendocrine profile in patients with chronic heart failure. Interventional studies have not yielded other consistent or convincing evidence of benefit from treating euthyroid sick syndrome patients with either LT3 or levothyroxine (LT4). Experts agree that large, prospective studies in a variety of settings are needed. Therefore, thyroid hormone therapy cannot, at present, be generally recommended for patients with euthyroid sick syndrome, except possibly those with chronic heart failure.
11. Does euthyroid sick syndrome have any prognostic significance?
Low serum T3 levels have significant prognostic value. The degree of reduction of serum T3 has been shown to predict a poor prognosis in patients with ischemic heart disease, heart valve disease, congestive heart failure, meningococcal sepsis, and a variety of illnesses in the intensive care setting. Patients with extremely low serum T3 levels have a high mortality rate.
12. Are levels of thyroid hormone ever elevated in patients with nonthyroid diseases?
The serum T4 may be transiently elevated in patients with acute psychiatric illnesses and various acute medical illnesses. The mechanisms underlying such elevations of T4 are not well understood but may be mediated by alterations in neurotransmitters or cytokines. This condition must be distinguished from true thyrotoxicosis.
Adler, SM, Wartofsky, L. The nonthyroidal illness syndrome. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2007;36:657–672.
Debaveye, Y, Ellger, B, Mebis, L, et al. Regulation of tissue iodothyronine deiodinase activity in a model of prolonged critical illness. Thyroid. 2008;18:551–560.
DeGroot, LJ, Dangerous dogmas in medicine. the nonthyroidal illness syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1999;84:151–164.
den Brinker, M, Joosten, KF, Visser, TJ, et al, Euthyroid sick syndrome in meningococcal sepsis. the impact of peripheral thyroid hormone metabolism and binding proteins. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2005;90:5613–5620.
Huang, SA, Bianco, AC. Reawakened interest in type III iodothyronine deiodinase in critical illness and injury. Nat Clin Pract Endocrinol Metab. 2008;4:148–154.
Iervasi, G, Pingitore, A, Landi, P, et al. Low serum free triiodothyronine values predict mortality in patients with cardiac disease. Circulation. 2003;107:708–711.
Kimura, T, Kanda, T, Kotajima, N, et al. Involvement of circulating interleukin-6 and its receptor in the development of euthyroid sick syndrome in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Eur J Endocrinol. 2000;143:179–184.
Nagaya, T, Fujieda, M, Otsuka, G, et al. A potential role of activated NF-kappa B in the pathogenesis of euthyroid sick syndrome. J Clin Invest. 2000;106:393–402.
Peeters, RP, Kester, MH, Wouters, PJ, et al. Increased thyroxine sulfate levels in critically ill patients as a result of a decreased hepatic type I deiodinase activity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2005;90:6460–6465.
Peeters, RP, van der Geyten, S, Wouters, PJ, et al. Tissue thyroid hormone levels in critical illness. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2005;90:6498–6507.
Peeters, RP, Wouters, PJ, Kaptein, E, et al. Reduced activation and increased inactivation of thyroid hormone in tissues of critically ill patients. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2003;88:3202–3211.
Peeters, RP, Wouters, PJ, van Toor, H, et al. Serum 3, 3’, 5’-triiodothyronine and 3, 5, 3’-triiodothyronine/rT3 are prognostic markers in critically ill patients and are associated with tissue deiodinase activities. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2005;90:4559–4565.
Pingitore, A, Galli, E, Barison, A, et al, Acute effects of triiodothyronine (T3) replacement therapy in patients with chronic heart failure and low-T3 syndrome. a randomized, placebo controlled study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2008;93:1351–1358.
Pingitore, A, Landi, P, Taddei, MC, et al. Triiodothyronine levels for risk stratification of patients with chronic heart failure. Am J Med. 2005;118:132–136.
Plikat, K, Langgartner, J, Buettner, R, et al. Increasing thyroid dysfunction is correlated with degree of illness and mortality in intensive care unit patients. Metabolism. 2007;56:239–244.
Spratt, DI, Frohnauer, M, Cyr-Alves, H, et al. Triiodothyronine replacement does not alter the hemodynamic, metabolic, and hormonal responses to coronary artery surgery. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2007;293:E310–E315.
Vanhorebeek, I, Langouche, L, Van den Berghe, G. Endocrine aspects of acute and prolonged critical illness. Nat Clin Pract Endocrinol Metab. 2006;2:20–31.

