2 major risk factors in USA: Tobacco and alcohol abuse
 of the distal esophagus with an irregular surface and luminal narrowing. This was a squamous cell carcinoma.
of the distal esophagus with an irregular surface and luminal narrowing. This was a squamous cell carcinoma.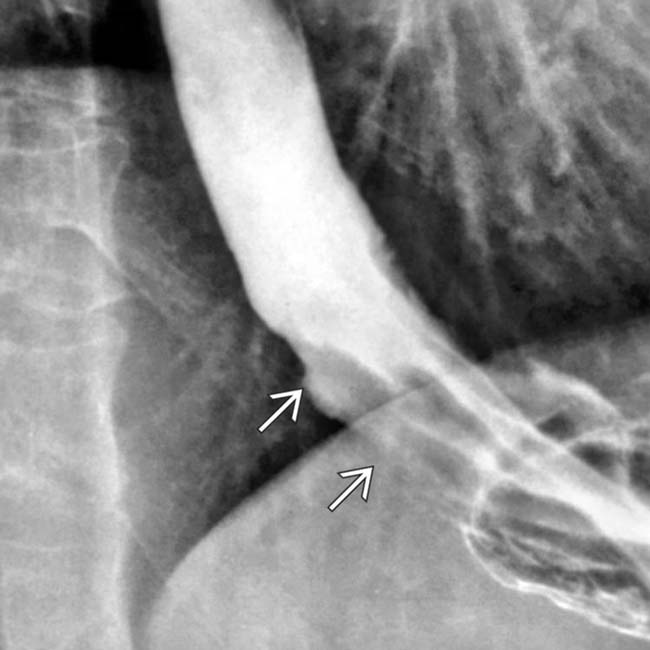
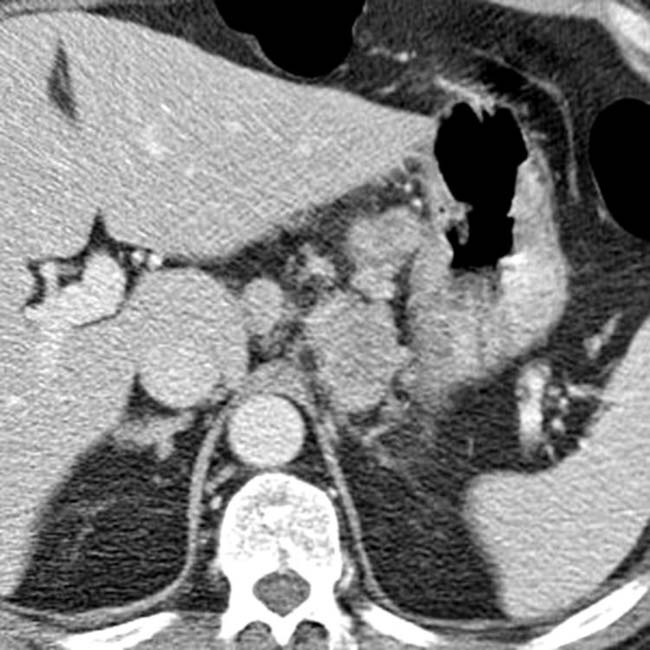
 in the distal esophagus.
in the distal esophagus.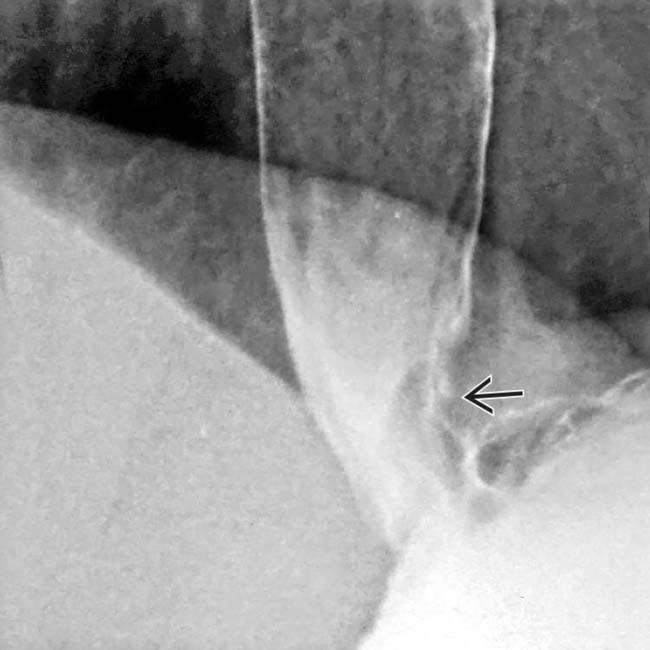
 and luminal narrowing in the distal esophagus. Biopsy confirmed adenocarcinoma.
and luminal narrowing in the distal esophagus. Biopsy confirmed adenocarcinoma.IMAGING
General Features
Radiographic Findings
• Double-contrast esophagography: En face and profile views
 Advanced esophageal squamous cell cancer
Advanced esophageal squamous cell cancer
 Advanced esophageal squamous cell cancer
Advanced esophageal squamous cell cancer
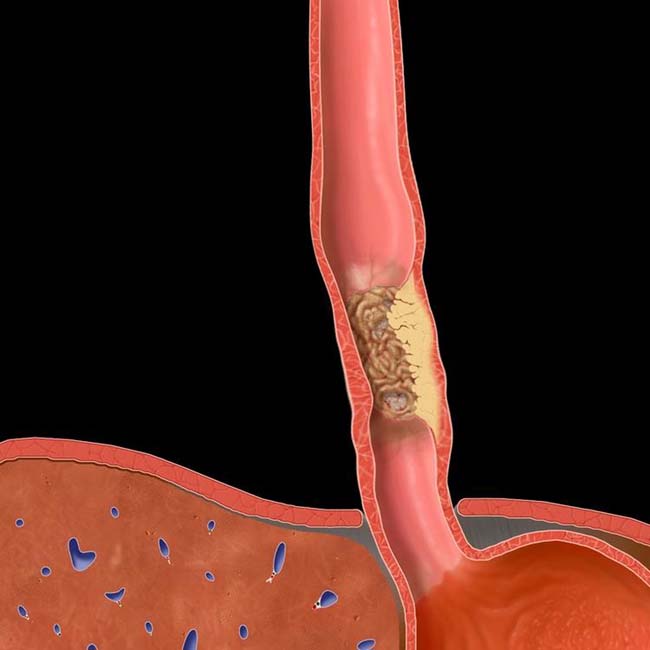
– Infiltrating lesion (most common): Irregular narrowing, luminal constriction (stricture) with nodular or ulcerated mucosa
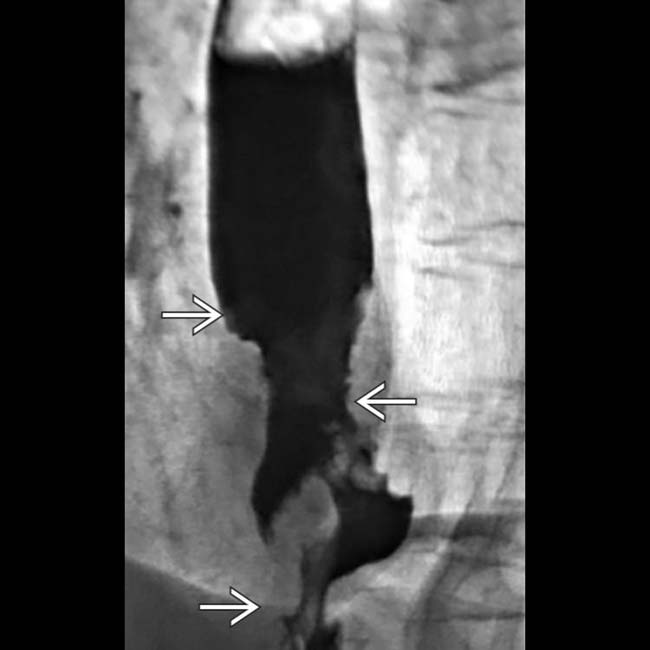
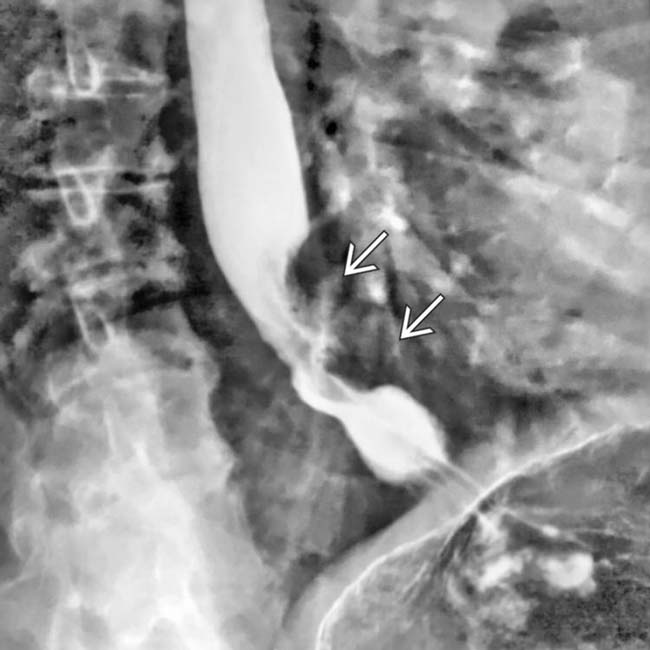
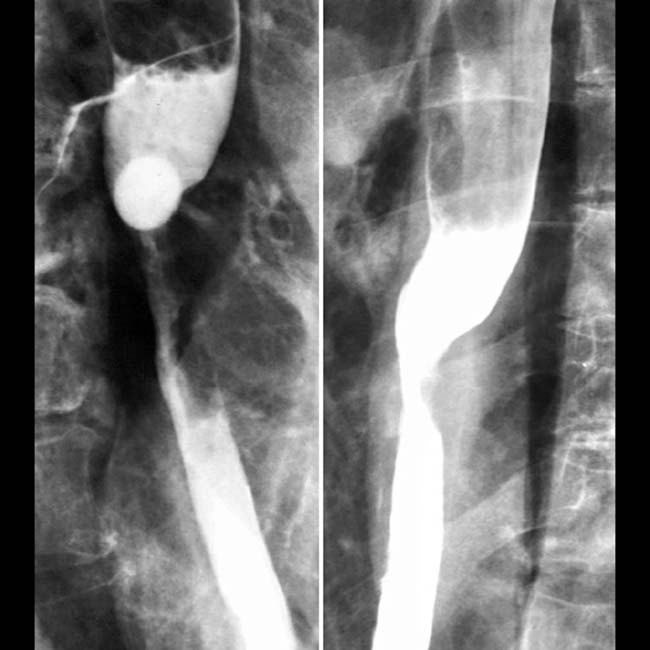
 of the distal esophagus. There is an abrupt transition, or shoulder, at the proximal end of the tumor as it abuts the normal esophagus. The mucosa through the tumor is destroyed with nodular contours.
of the distal esophagus. There is an abrupt transition, or shoulder, at the proximal end of the tumor as it abuts the normal esophagus. The mucosa through the tumor is destroyed with nodular contours.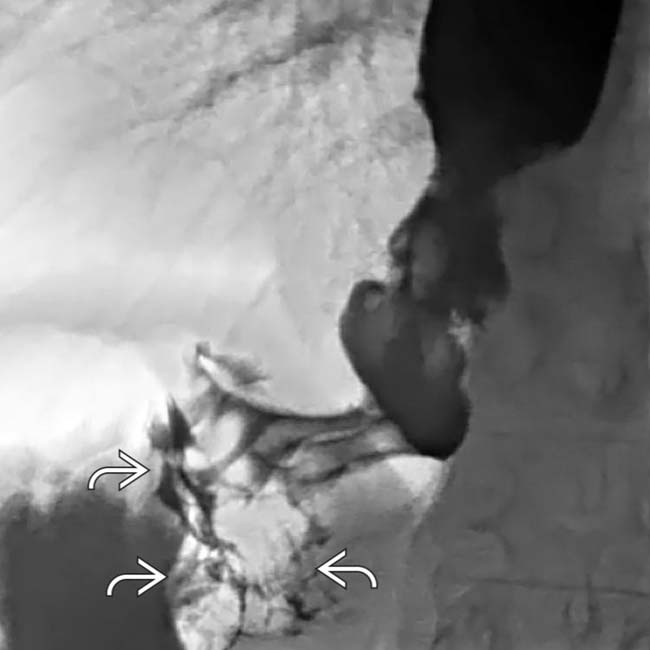
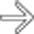
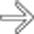
 in the gastric cardia as well, strongly suggesting gastric extension of the tumor. Alternatively, gastric carcinoma may invade the distal esophagus.
in the gastric cardia as well, strongly suggesting gastric extension of the tumor. Alternatively, gastric carcinoma may invade the distal esophagus.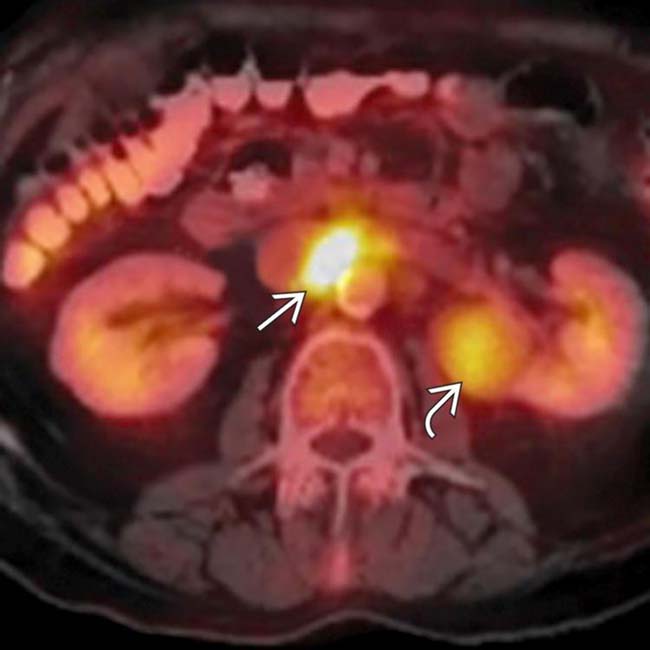
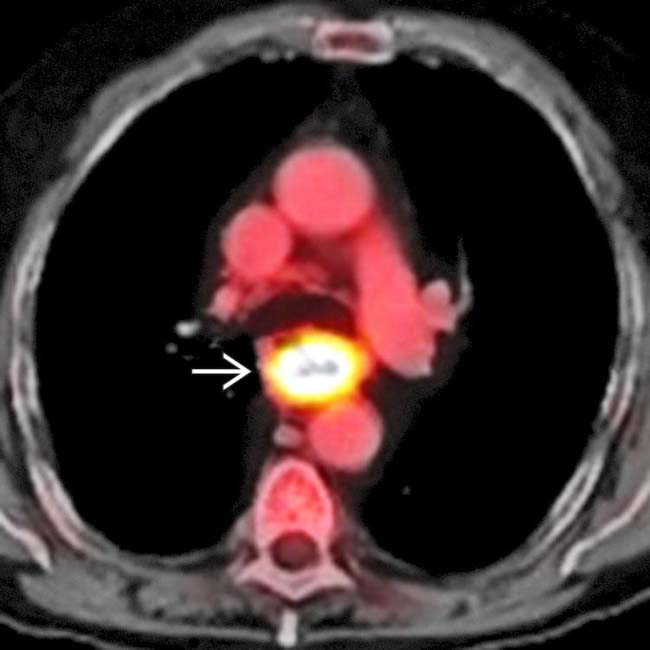
 , indicating metastases to the upper abdomen. There is also abnormal uptake within a left renal mass
, indicating metastases to the upper abdomen. There is also abnormal uptake within a left renal mass 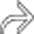 , which proved to be an unrelated primary renal cell carcinoma. PET/CT is the most effective means of evaluation for the total extent of disease and often affects management decisions.
, which proved to be an unrelated primary renal cell carcinoma. PET/CT is the most effective means of evaluation for the total extent of disease and often affects management decisions.
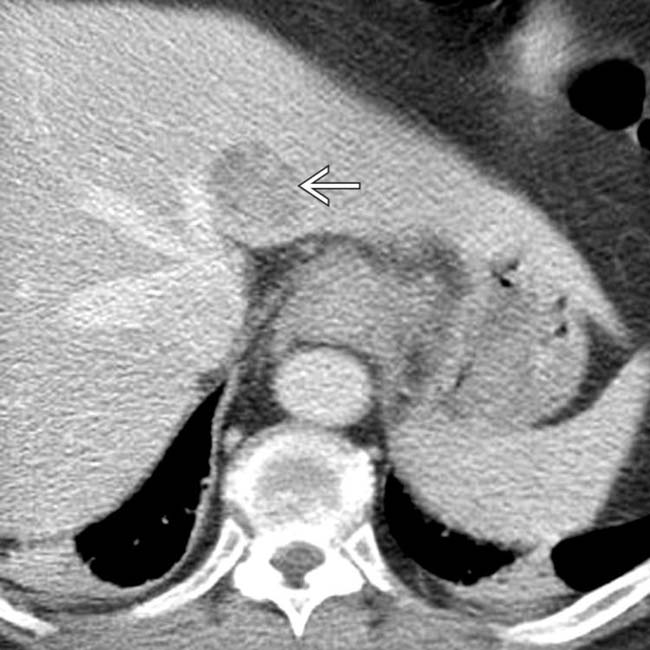
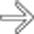 that does not penetrate the muscularis propria (T1a adenocarcinoma). Endoluminal sonography is the best method for determining the depth of tumor invasion.
that does not penetrate the muscularis propria (T1a adenocarcinoma). Endoluminal sonography is the best method for determining the depth of tumor invasion.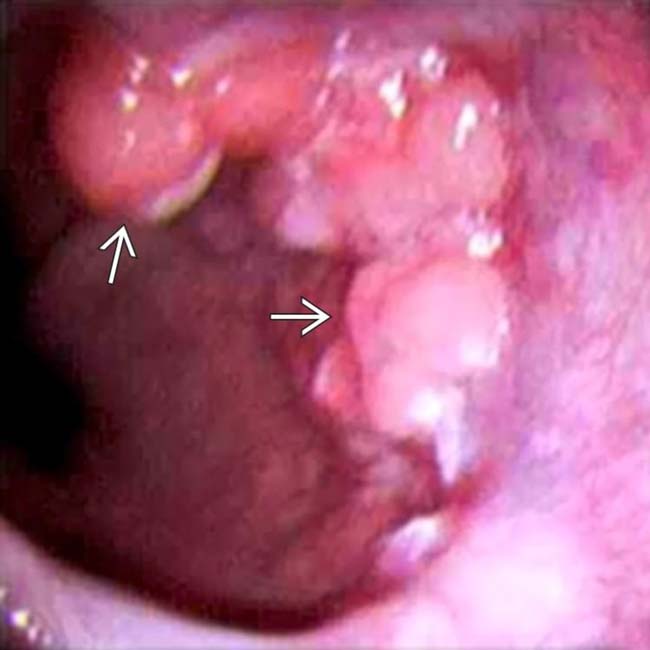
 in the distal esophagus. This adenocarcinoma was treated by esophagectomy with gastric interposition in the chest.
in the distal esophagus. This adenocarcinoma was treated by esophagectomy with gastric interposition in the chest.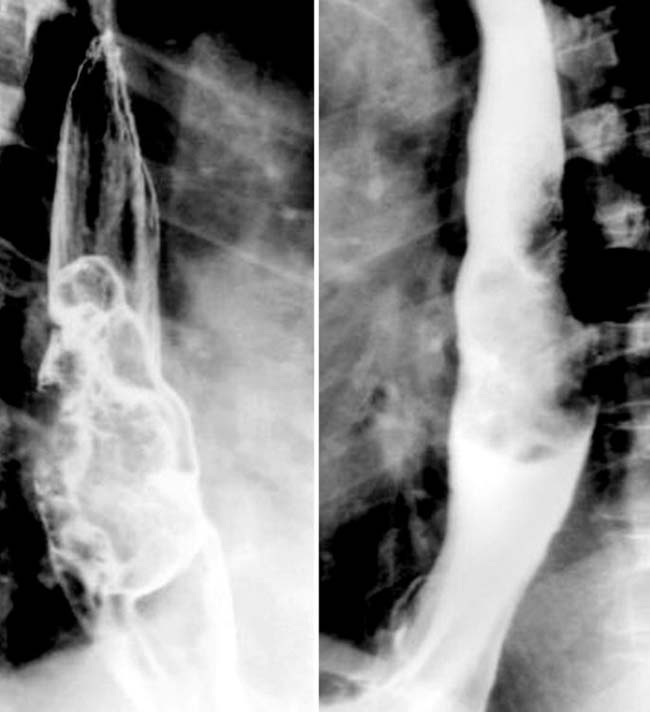


























































 .
.
 .
.