3 Embryology / Pathology
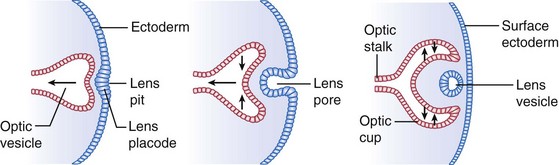
Optic vesicle
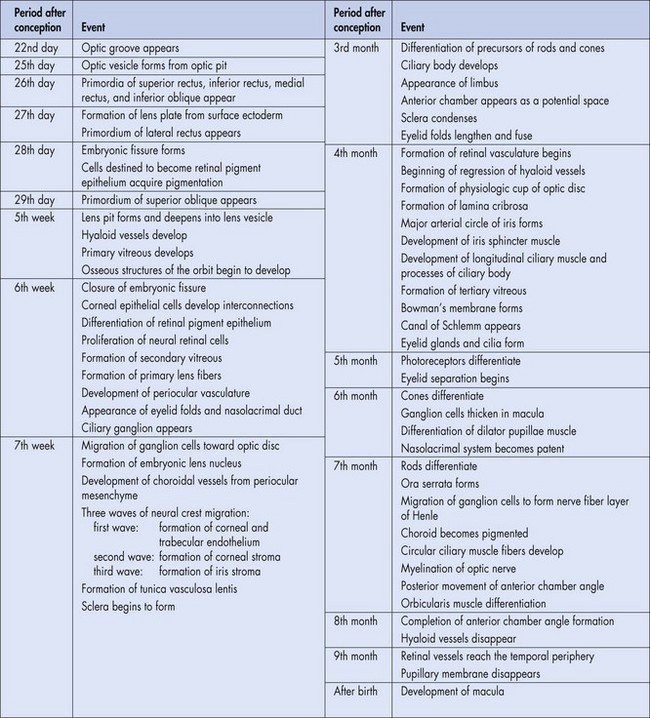
anterolateral outpouching of primitive brain stem; evaginates on day 25 and becomes the globe
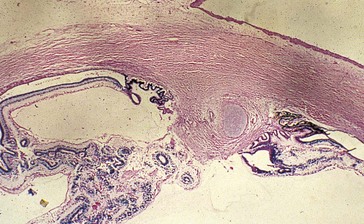
Optic cup (Figure 3.2)
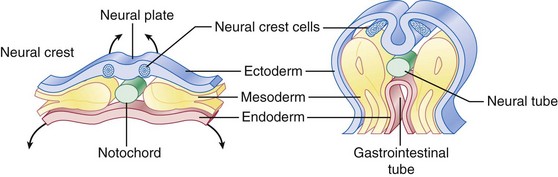
develops embryologically as an anterolateral evagination of the forebrain
Embryonic fissure
on undersurface of optic cups; closes on day 33 allowing pressurization of globe
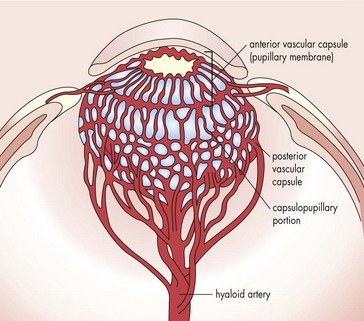
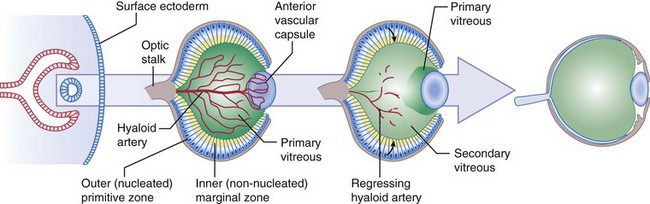
Hyaloid artery (Figure 3-3)
enters through embryonic fissure and forms vasa hyaloidea propria (blood supply to primary vitreous)
Primitive epithelial papillae
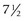 months and lamina cribrosa at birth; complete approximately 1 month after birth
months and lamina cribrosa at birth; complete approximately 1 month after birthVitreous
produced by lens, retina, and walls of hyaloid artery; contains mesenchymal cells
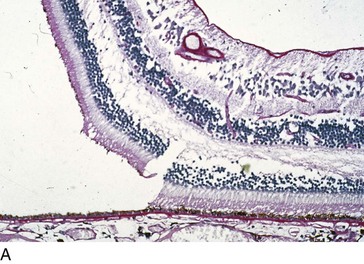
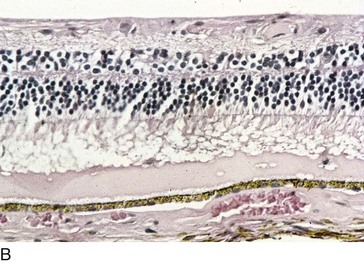
Retina
Cornea
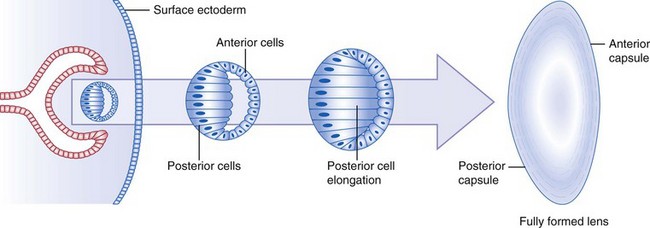
Lens
at 27 days, surface ectoderm adjacent to optic vesicle enlarges to form lens placode (lens plate)
Iris
rim of optic cup grows around lens and forms iris
Ciliary body (CB)
formation begins in 3rd month; fold in optic cup becomes epithelial layers of ciliary processes
Nasolacrimal system
at 6 weeks, surface ectoderm is buried in mesoderm, between maxillary and lateral nasal processes
Embryologic tissues and their components
Fixation artifacts
Hla (human leukocyte antigen) system
Major histocompatibility complex (MHC) proteins found on surfaces of all nucleated cells
In humans, MHC proteins are the HLA molecules
| Uveitis | |
| A29 | Birdshot retinochoroidopathy (90%) |
| B7, DR2 | Presumed ocular histoplasmosis syndrome (80%) |
| B8, B13 | Sarcoidosis |
| B8, B51, DR2, DR15 | Intermediate uveitis |
| B27 (1-5% of population) | Adult iridocyclitis (usually unilateral): Reiter’s syndrome (75%), ankylosing spondylitis (90%), inflammatory bowel disease (90%), psoriatic arthritis, juvenile rheumatoid arthritis (JRA) (subtype V) |
| B51 | Behçet’s disease (70%) |
| DR4 | Sympathetic ophthalmia, Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada syndrome |
| DR15 | Pars planitis |
| DQ7 | Acute retinal necrosis (50%) |
| External disease | |
| B5, DR3, DR4 | HSV keratitis |
| B8, DR3 | Sjögren’s syndrome |
| B12 | Ocular cicatricial pemphigoid |
| B15 | Scleritis |
| DR3 | Thygeson’s superficial punctate keratitis (SPK) |
| Neuro-ophthalmology | |
| A1, B8, DR3 | Myasthenia gravis (MG) |
| B7, DR2 | Multiple sclerosis (MS) |
| DR3 | Graves’ disease |
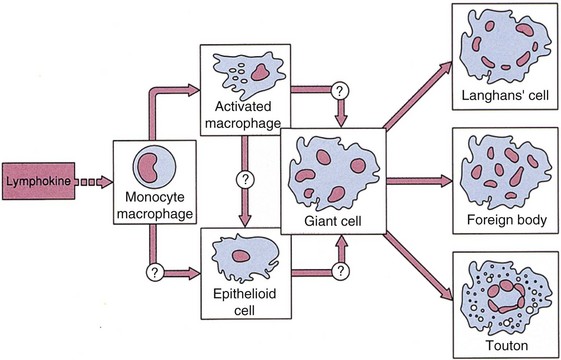
Tissue infiltration by inflammatory cells
Types of Inflammatory Cells
Eosinophils
Macrophages
Types of Inflammation
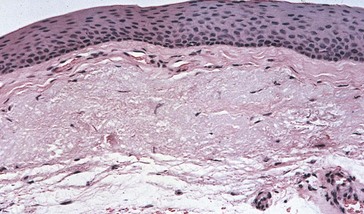
Chronic
Example: sympathetic ophthalmia, fungal infection, JXG, lepromatous leprosy
Sequelae of Inflammation
Cornea
Lens
Hyperkeratosis
thickening of the keratin layer; clinically appears as white, flaky lesion (leukoplakia)
Anaplasia
cytologic malignancy with pleomorphism, anisocytosis, abnormal nuclei, and mitotic figures
Wound Complications
Hemorrhage
Blunt Trauma
Descemet’s rupture
causes acute edema (hydrops); due to minor trauma (keratoconus) or major trauma (forceps injury)
Sequelae of Trauma
Phthisis bulbi
Infection (Table 3-2)
| Endophthalmitis: | |
| Acute postoperative (<6 weeks) | Coagulase-negative Staphylococcus, Staphylococcus aureus |
| Delayed postoperative | Propionibacterium acnes, coagulase-negative Staphylococcus |
| From filtering bleb | Streptococcus pneumoniae, Staphylococcus, Haemophilus influenzae |
| Post-traumatic | Staphylococcus species, Bacillus cereus, Gram-negative organisms |
| Endogenous (IVDA) | Candida |
| Dacryocystitis | S. pneumoniae, Staphylococcus |
| Dacryadenitis | Staphylococcus |
| Canaliculitis | Actinomyces |
| Orbital cellulitis (children) | S. aureus |
| Preseptal cellulites | S. aureus |
| Angular blepharitis | Staphylococcus, Moraxella |
Review Questions (Answers start on page 358)
Apple DJ. Ocular Pathology: Clinical Applications and Self-Assessment, 5th edn. St Louis: Mosby; 1998.
Char PH. Tumors of the Eye and Ocular Adnexa. Hamilton, Ontario, Canada: BC Decker; 2001.
Eagle RC. Eye Pathology: An Atlas and Basic Text, 2nd edn. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2011.
Spencer WH. Ophthalmic Pathology: An Atlas and Textbook, 4th edn. Philadelphia: WB Saunders; 1996.
Yanoff M, Sassani JW. Ocular Pathology, 6th edn. Philadelphia: Mosby; 2008.

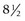 months; intraneural portion becomes central retinal artery
months; intraneural portion becomes central retinal artery