Elbow and Forearm
A. Bobby Chhabra, Aaron M. Freilich
Regional Anatomy and Surgical Intervals
Regional Anatomy
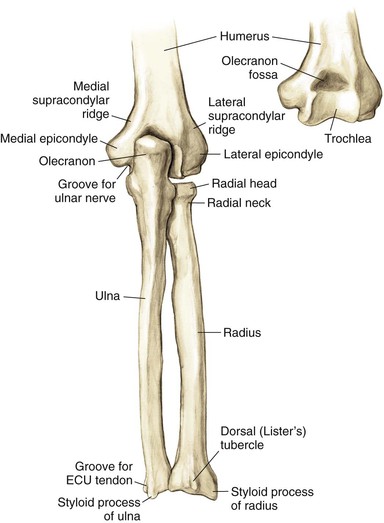
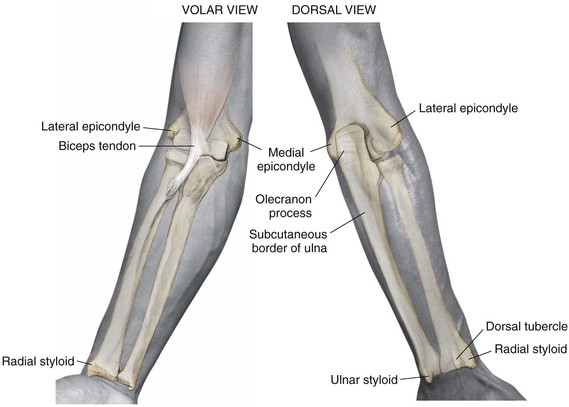
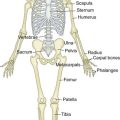
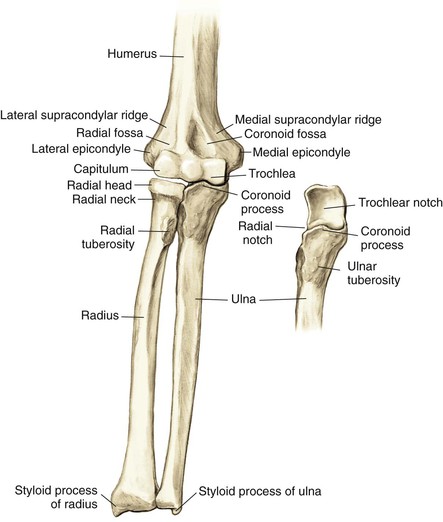
Osteology (Figs. 3-1 and 3-2)
Distal Humerus
Widens and flattens distally into medial and lateral supracondylar ridges, then medial and lateral epicondyles
• The extensor carpi radialis longus (ECRL) originates on the lateral supracondylar ridge
• Common flexor muscles and pronator teres originate on the medial epicondyle
• Common extensor muscles originate on the lateral epicondyle
The capitulum articulates with the radial head laterally
The trochlea articulates with the ulnar trochlear notch medially
The coronoid fossa lies on the anterior humerus
The olecranon fossa lies on the posterior humerus
The radial fossa is anterolateral to accommodate the radial head when the elbow is in flexion
The groove for the ulnar nerve lies between the medial epicondyle and the trochlea
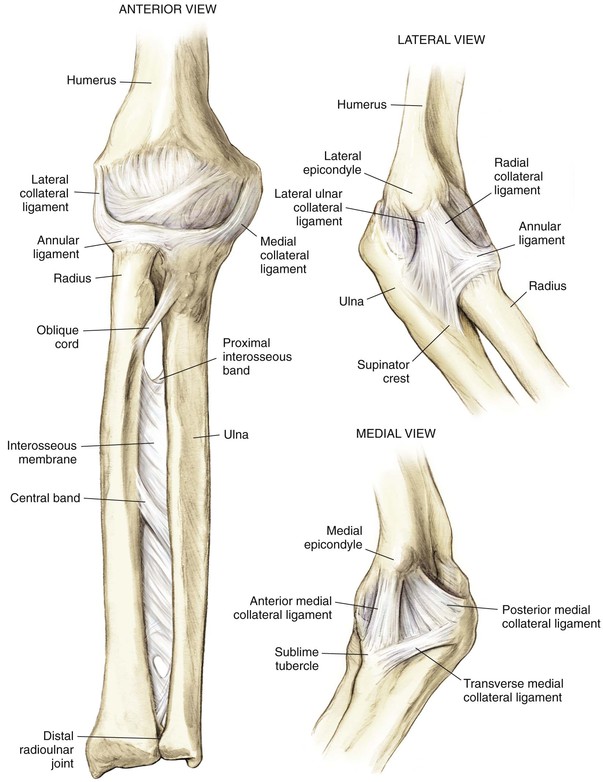
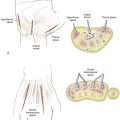
Arthrology (Fig. 3-3)
Elbow Joint
Ligaments
• Annular ligament of the radius
• Lateral ulnar collateral ligament
• From the lateral epicondyle to the ulna supinator crest
• Deficiency leads to posterolateral rotatory instability
• Triangular ligament consisting of three bands
• Anterior band: inferior medial epicondyle to coronoid process
• Posterior band: inferior medial epicondyle to olecranon process
Joint Capsule
Major Stabilizers of the Elbow Joint
Proximal Radioulnar Joint
Middle Radioulnar Joint
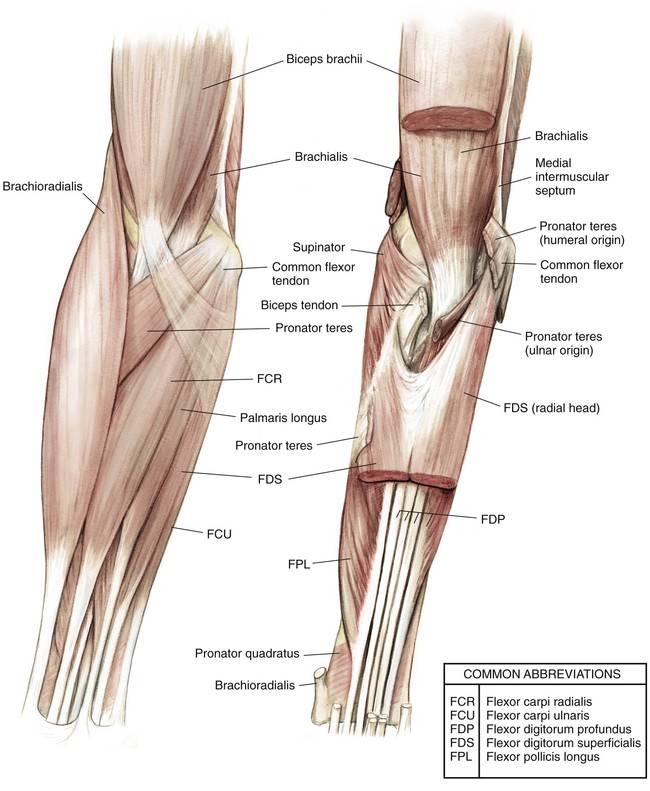
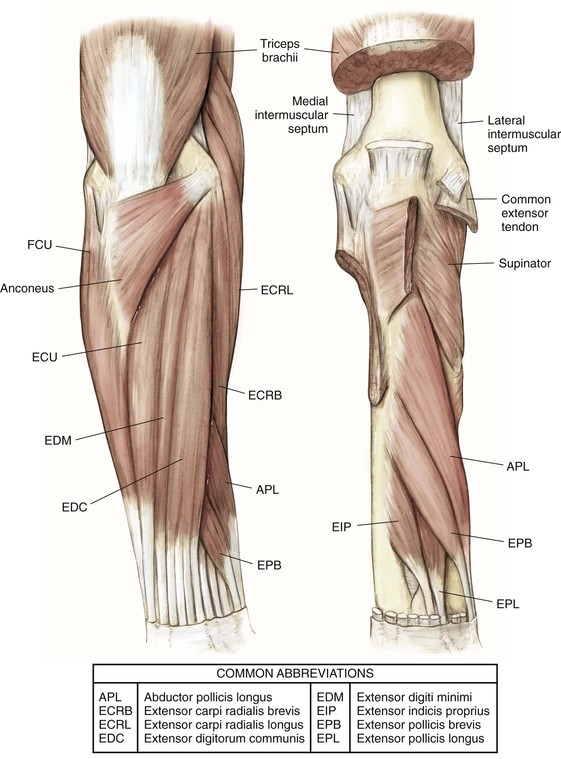
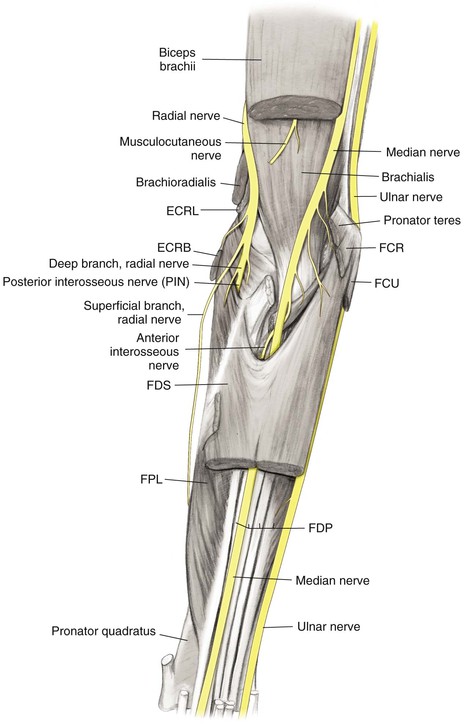
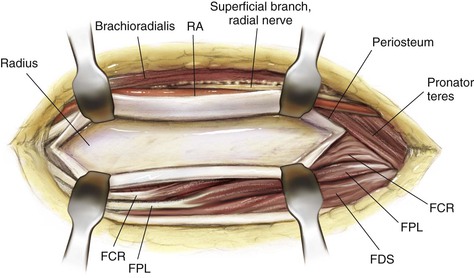
Muscles (Figs. 3-4 and 3-5)
Table 3-1
Compartments and Muscles of the Elbow
| COMPARTMENT | MUSCLE | ORIGIN | INSERTION | INNERVATION | FUNCTION |
| Anterior arm | Biceps brachii | Long head—supraglenoid tubercle | Radial tuberosity | Musculocutaneous nerve | Supination of forearm; flexion of elbow |
| Short head—coracoid process | |||||
| Brachialis | Distal half of anterior humerus | Ulnar tuberosity | Musculocutaneous nerve | Flexion of elbow in pronation | |
| Posterior arm | Triceps brachii | Long head—infraglenoid tubercle | Olecranon process | Radial nerve | Extension of elbow |
| Lateral head—proximal lateral half of humerus | |||||
| Medial head—posterior humerus | |||||
| Superficial forearm flexors | Pronator teres | Medial epicondyle and ulna coronoid process | Lateral middle surface of radius | Median nerve | Forearm pronation |
| Flexor carpi radialis | Medial epicondyle | Base of second and third MC | Median nerve | Flexion of wrist | |
| Palmaris longus | Medial epicondyle | Palmar fascia | Median nerve | Weak flexion of wrist | |
| Flexor carpi ulnaris | Medial epicondyle and proximal posterior shaft and olecranon process of ulna | Fifth MC, pisiform, and hamate | Ulnar nerve | Wrist flexion and ulnar deviation | |
| Flexor digitorum superficialis | Medial epicondyle, ulna coronoid process, and anterior oblique line of radius | Splits at level of proximal phalanx and inserts onto volar middle phalanx | Median nerve | Finger flexion at PIP joints | |
| Deep forearm flexors | Flexor digitorum profundus | Proximal interosseous membrane and anterior ulna | Volar aspect of distal phalanges | Lateral half—AINMedial half—ulnar nerve | Finger flexion at DIP joints |
| Flexor pollicis longus | Anterior shaft of radius and interosseous membrane | Volar aspect of thumb distal phalanx | AIN | Flexion of thumb IP joint | |
| Pronator quadratus | Distal anterior ulna | Distal anterior radius | AIN | Forearm pronation | |
| Superficial forearm extensors | Brachioradialis | Lateral supracondylar ridge | Radial styloid process | Radial nerve | Flexion of elbow |
| Extensor carpi radialis longus | Lateral supracondylar ridge of humerus and lateral epicondyle | Dorsal base of second MC | Radial nerve | Wrist extension and some radial deviation | |
| Extensor carpi radialis brevis | Lateral epicondyle | Dorsal base of third MC | PIN/radial nerve | Wrist extension and some radial deviation | |
| Extensor digitorum | Lateral epicondyle | Extensor hood of digits 2-5 | PIN | Finger extension | |
| Extensor digiti minimi | Lateral epicondyle | Extensor hood of fifth digit | PIN | Fifth finger extension | |
| Extensor carpi ulnaris | Lateral epicondyle | Dorsal fifth MC | PIN | Wrist extension and ulnar deviation; stabilizes wrist in grip | |
| Anconeus | Posterior lateral epicondyle | Lateral olecranon process and posterior ulna shaft | Radial nerve | Weakly extends elbow | |
| Deep forearm extensors | Supinator | Lateral epicondyle and proximal ulna | Proximal lateral radius | PIN | Forearm supination |
| Abductor pollicis longus | Posterior ulna shaft and interosseous membrane | Dorsal base of first MC and trapezium | PIN | Thumb abduction | |
| Extensor pollicis brevis | Posterior radial shaft and interosseous membrane | Dorsal proximal phalanx of thumb | PIN | Extends thumb at MC joint | |
| Extensor pollicis longus | Posterior ulnar shaft and interosseous membrane | Dorsal distal phalanx of thumb | PIN | Extends thumb at IP joint | |
| Extensor indicis | Posterior ulnar shaft and interosseous membrane | Ulnar side of extensor digitorum communis tendon to second digit at level of MCP joint | PIN | Assists in extension of second digit |
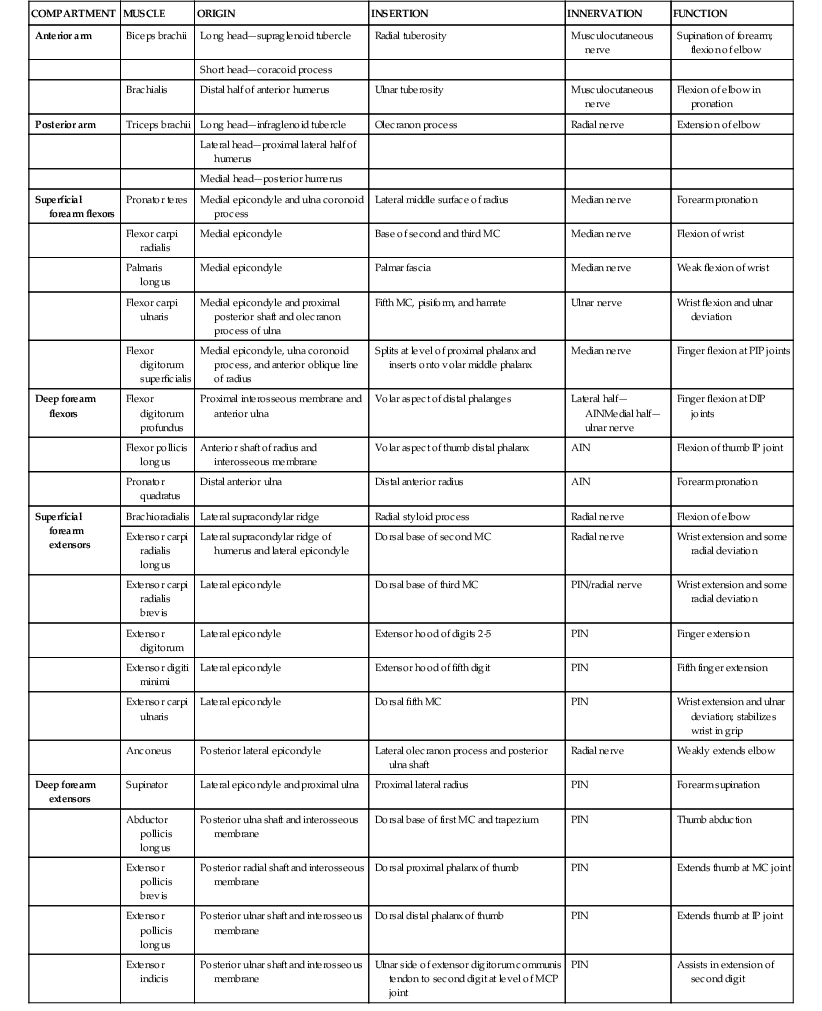
AIN, Anterior interosseous nerve; DIP, distal interphalangeal; IP, interphalangeal; MC, metacarpal; MCP, metacarpophalangeal; PIN, posterior interosseous nerve; PIP, proximal interphalangeal.
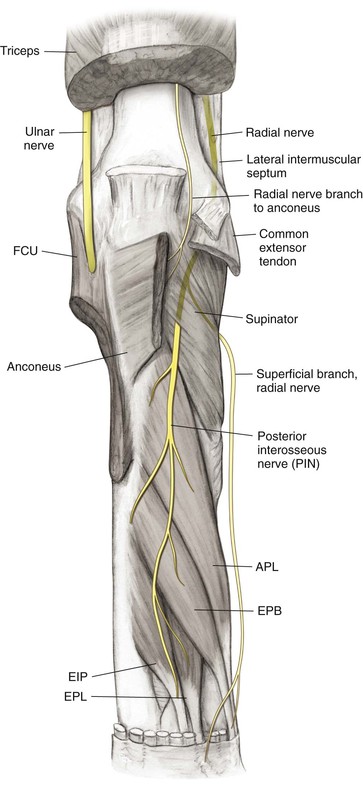
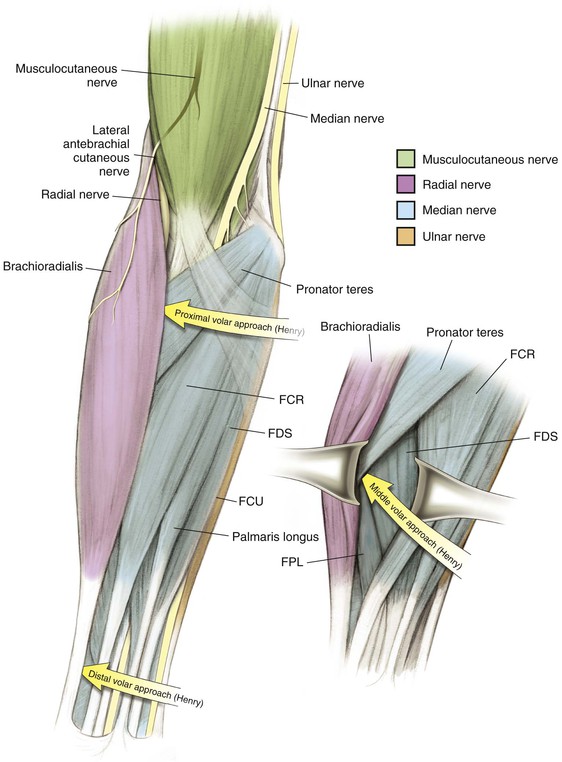
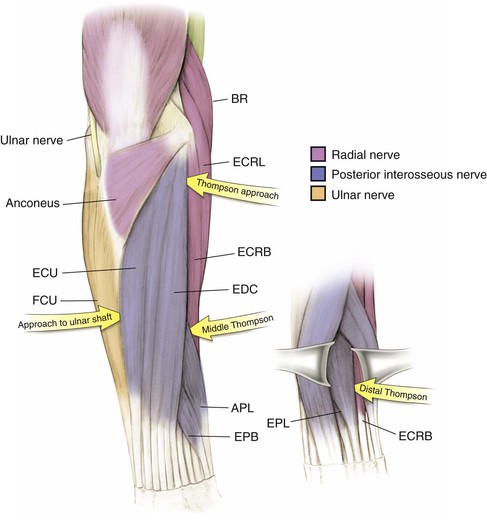
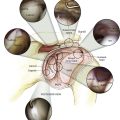
Nerves (Figs. 3-6 and 3-7)
Musculocutaneous Nerve C5, C6, C7
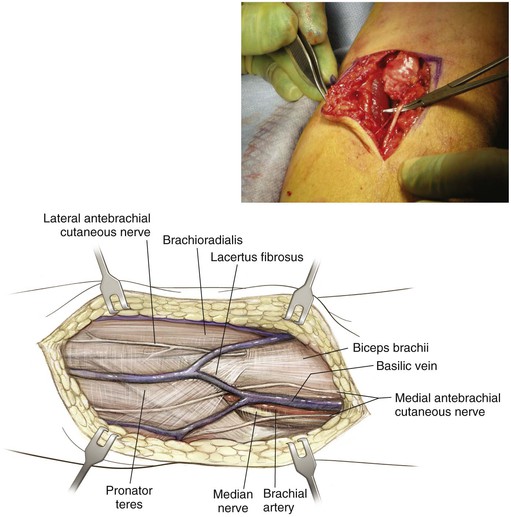
Lies between the biceps brachii and brachialis in the arm
Emerges from beneath the biceps brachii on the lateral side of the biceps tendon
Radial Nerve C5, C6, C7, C8 (T1)
Ulnar Nerve C7, C8 (T1)
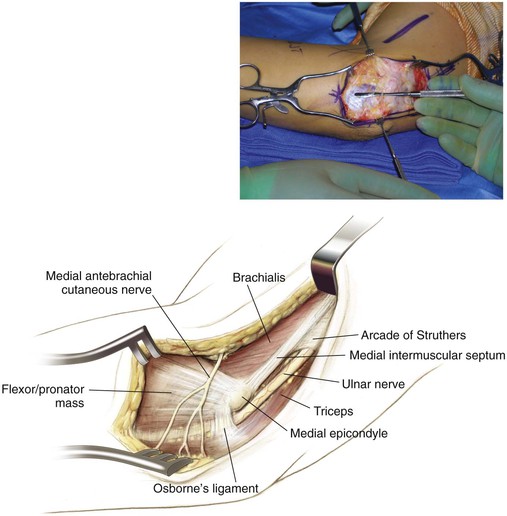
Approaches the elbow posteromedially, travels in the medial intermuscular septum of the triceps, and travels beneath the arcade of Struthers
• Crosses the elbow in the cubital tunnel posterior to the medial epicondyle
Travels distally in the forearm between the FCU and the ulnar side of the FDP, supplying both
Surgical Intervals
Commonly between internervous planes, allowing for the safest exposure of desired structures; the internervous planes for common approaches to the elbow and forearm are depicted in Figures 3-8 through 3-11
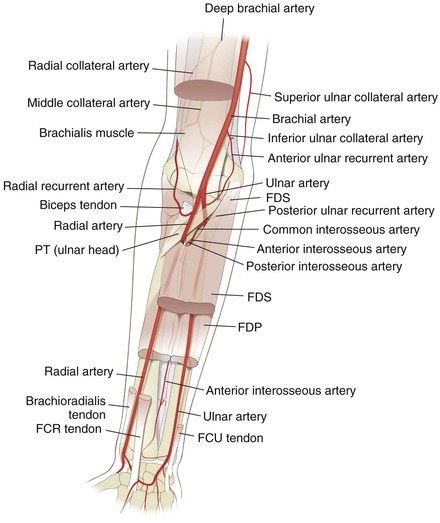
Vascular (Fig. 3-12)
Brachial Artery
The artery branches at approximately the level of the radial neck
• Passes under the bicipital aponeurosis
• Gives off the radial recurrent artery as the first branch
• Gives off the ulnar anterior or posterior recurrent artery, or both, as the first branch
• The common interosseous artery branches at a level just distal to the radial tuberosity, then divides into
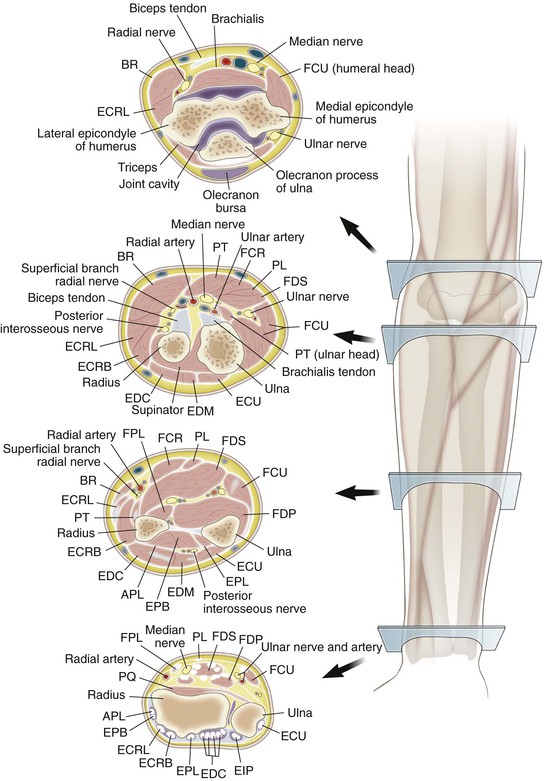
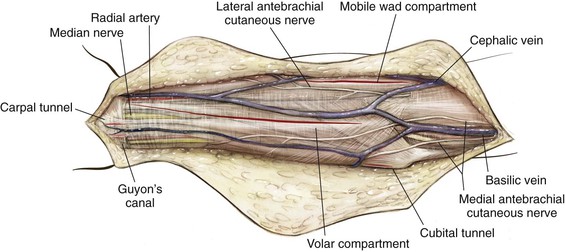
Cross-Sectional Anatomy (Fig. 3-13)
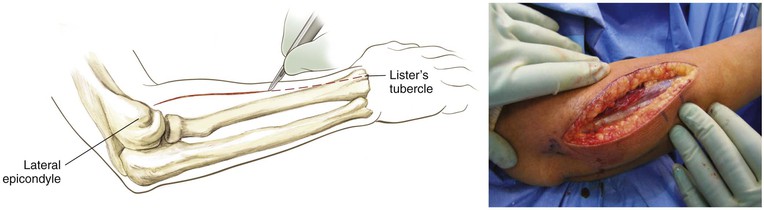
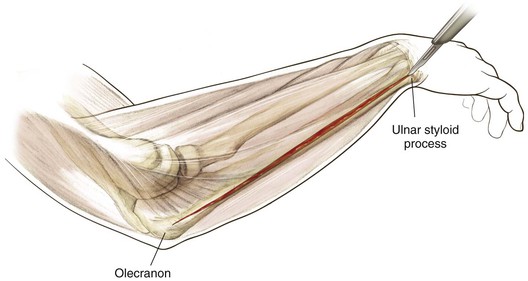
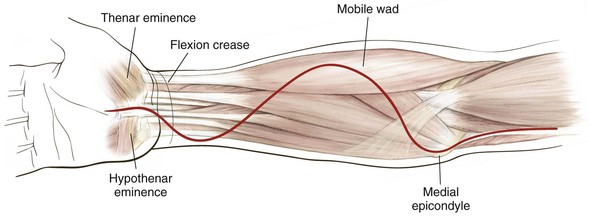
Palpable Anatomic Landmarks for Surgical Incisions and Approaches (Fig. 3-14)
Hazards
Nerves
Radial Nerve
Surgical Approaches to the Elbow
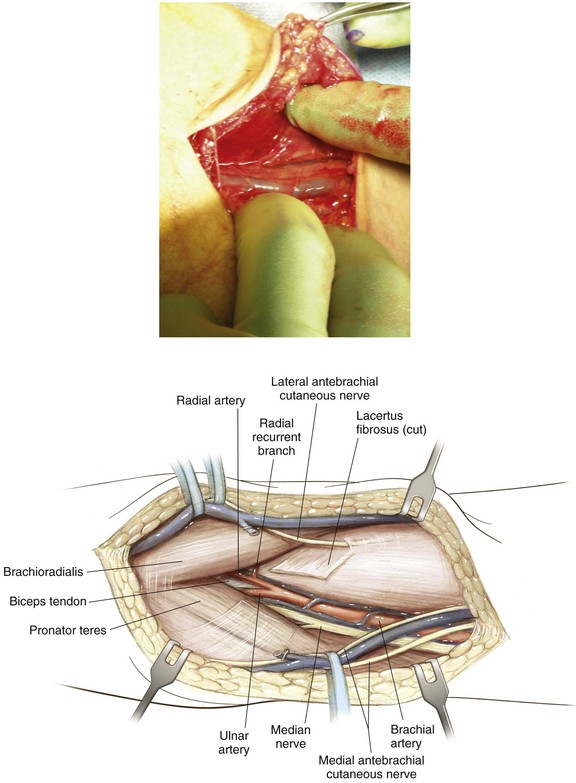
Anterior Approach to the Elbow (Antecubital Fossa)
Indications
Superficial Dissection (Figs. 3-17 and 3-18)
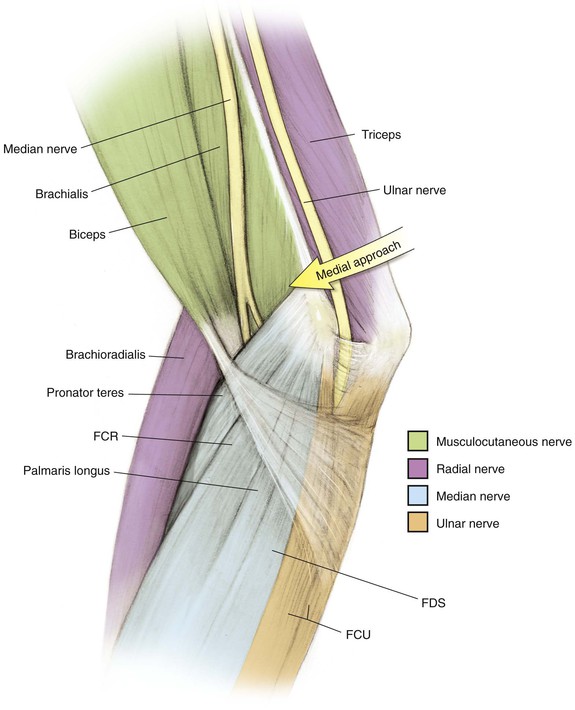
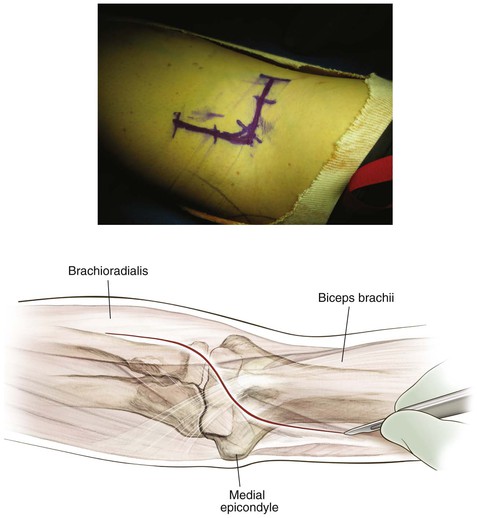
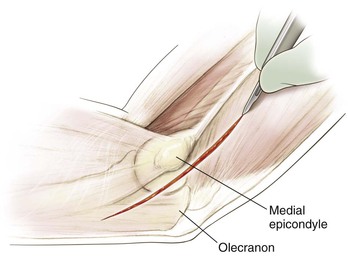
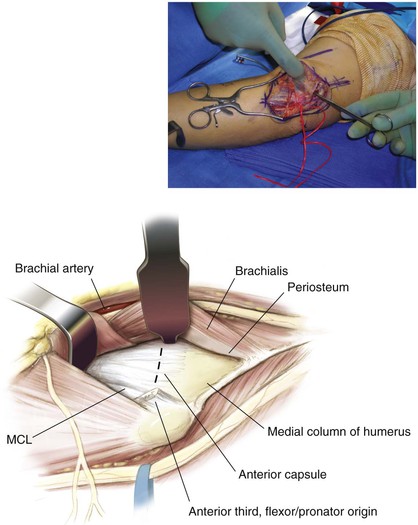
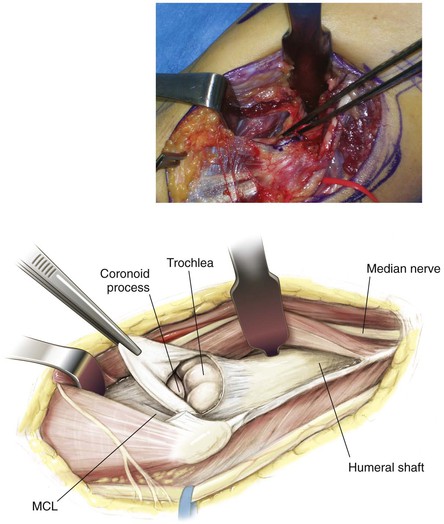
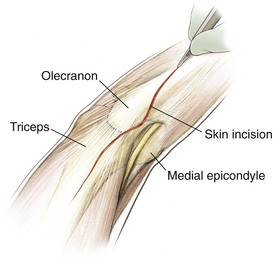
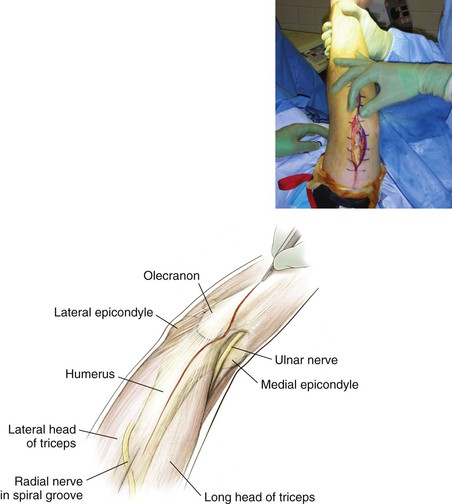
Medial Approach to the Elbow and Humerus (Video 3-1)
Indications
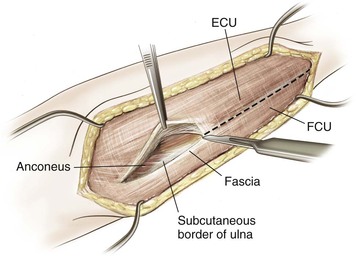
Superficial Dissection (Figs. 3-23, 3-24, and 3-25)
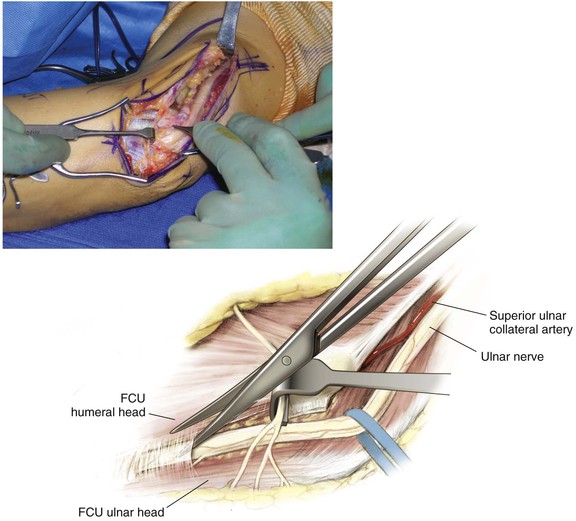
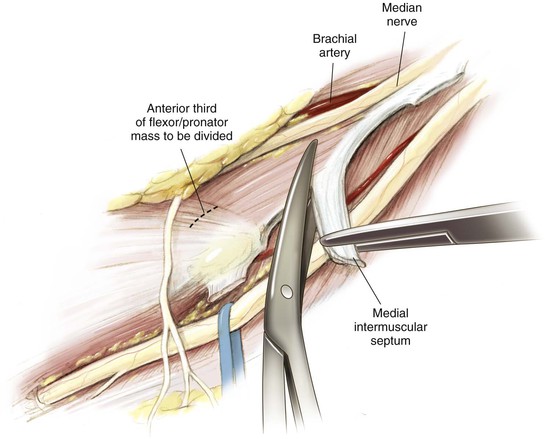
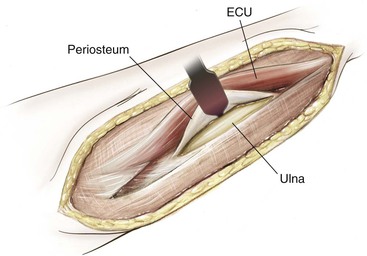
Deep Dissection (Figs. 3-26 and 3-27)
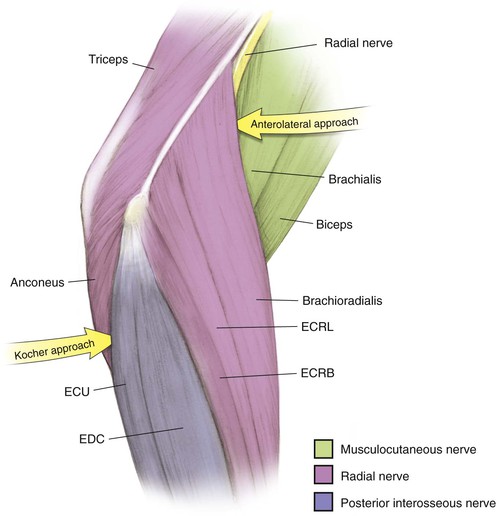
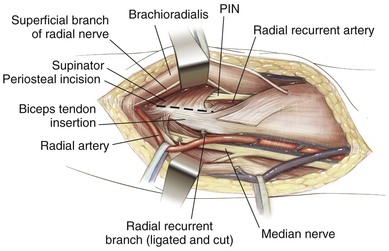
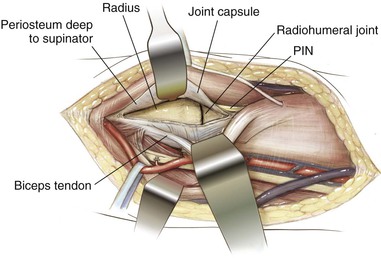
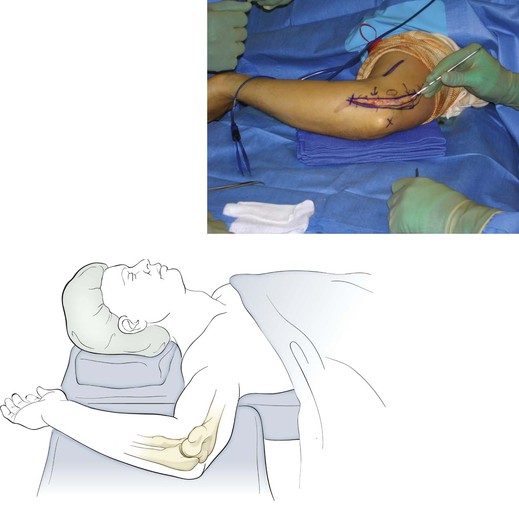
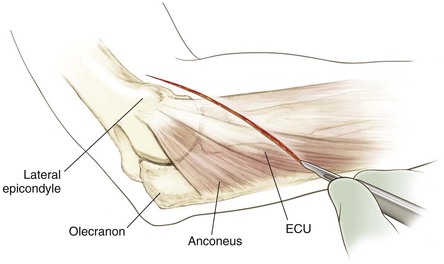
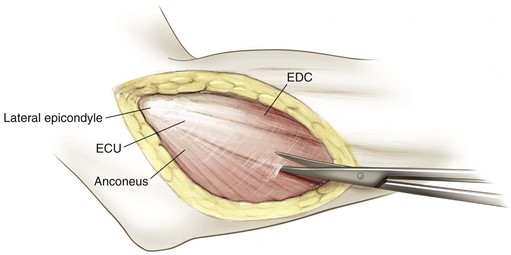
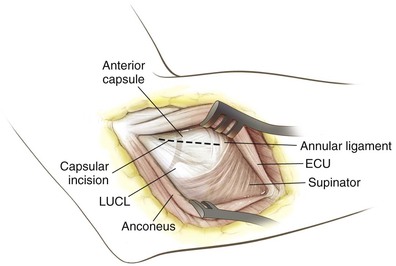
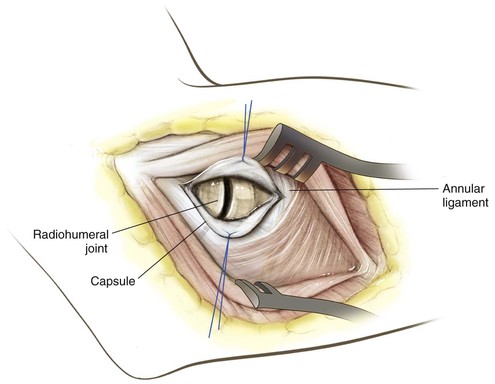
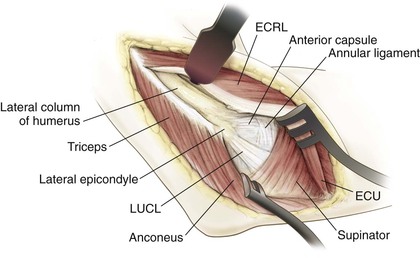
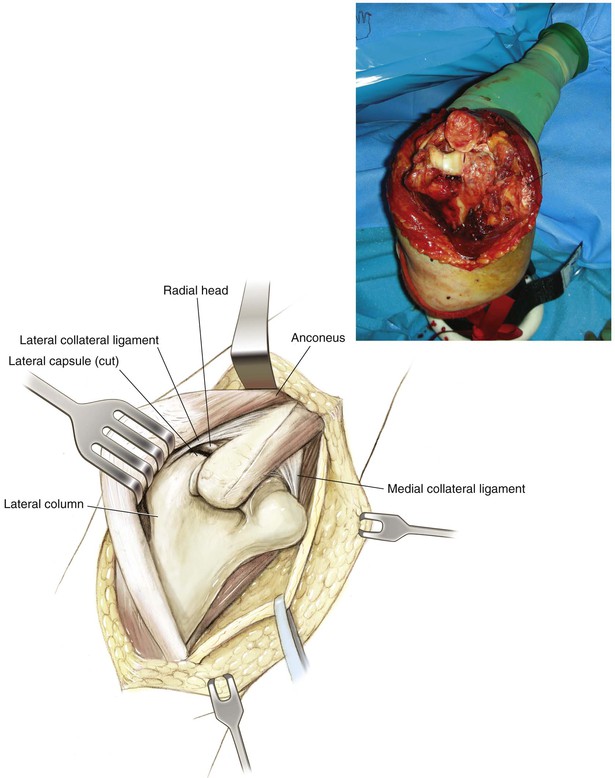
Kocher Approach (Lateral Elbow)
Indications
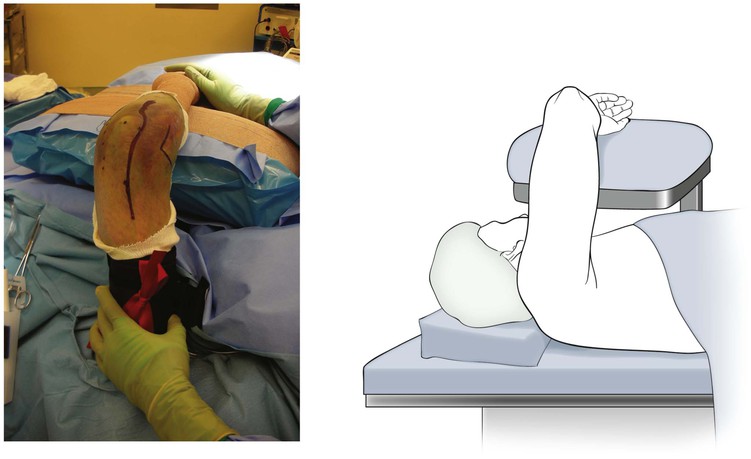
Positioning (Fig. 3-28)
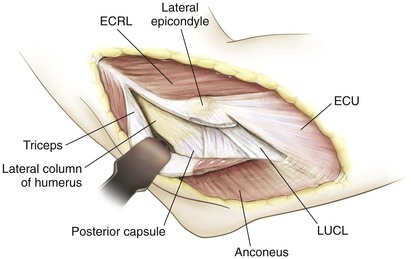
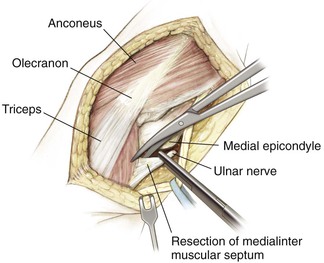
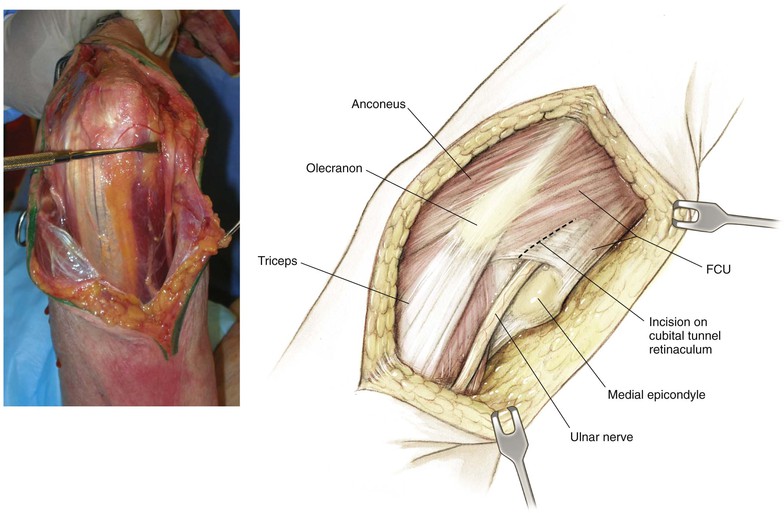
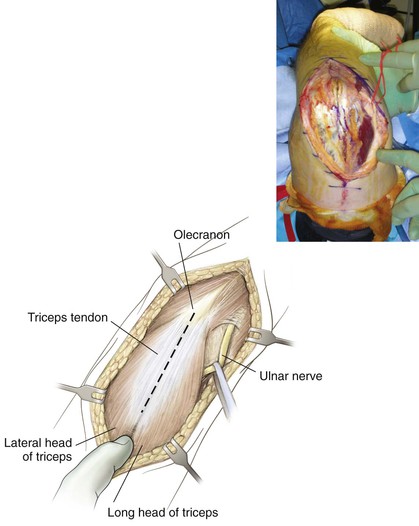
Bryan-Morrey (Triceps-Sparing) Approach
Indications
Superficial Dissection (Figs. 3-38 and 3-39)
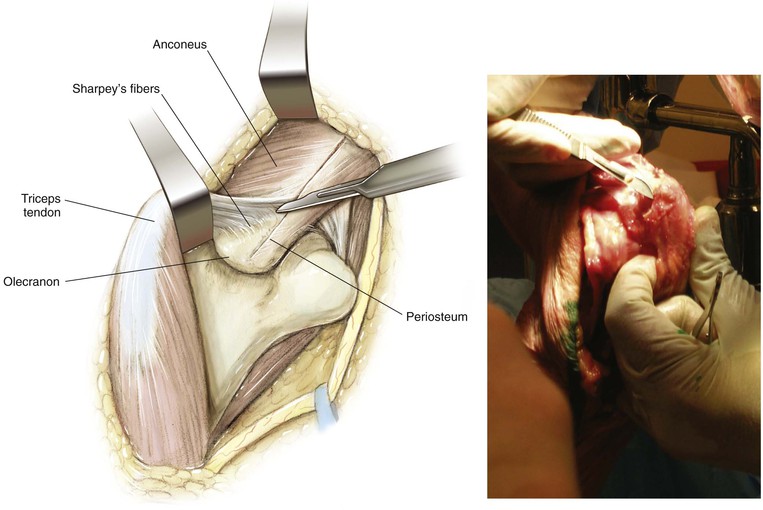
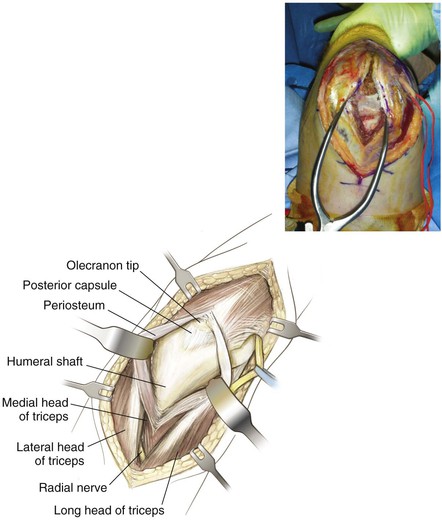
Deep Dissection (Figs. 3-40 and 3-41)
Triceps-Splitting Approach (Video 3-2)
Indications
Deep Dissection (Fig. 3-45)
Hazards
The radial nerve in the spiral groove of the humerus during exposure
• The nerve crosses the spiral groove approximately 12 to 14 cm above the lateral epicondyle
• Pierces the lateral intermuscular septum approximately 8 to 10 cm above the lateral epicondyle
Ulnar nerve during superficial dissection
Proximal dissection is limited by the radial nerve
Distal dissection is limited to triceps insertion on the olecranon tip
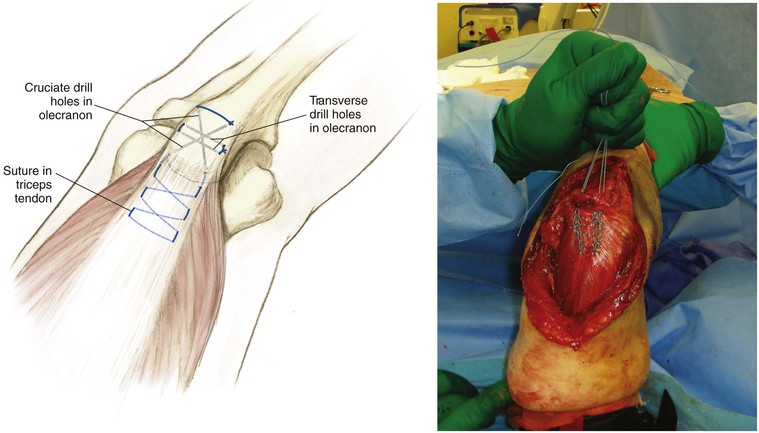
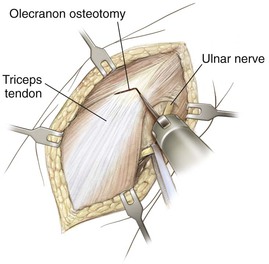
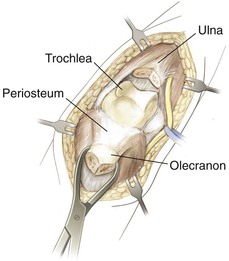
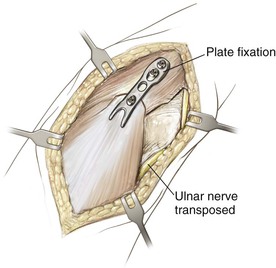
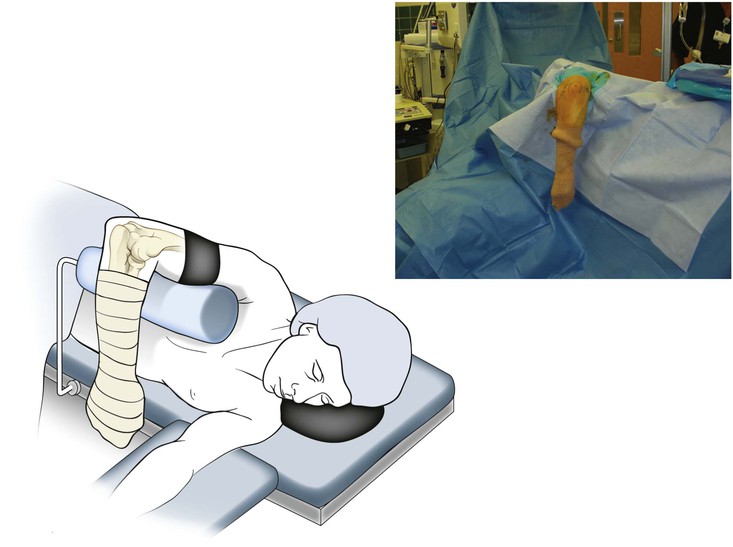
Olecranon Osteotomy
Indication
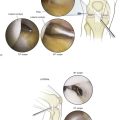
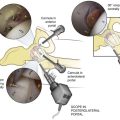
Elbow Arthroscopy
Indications
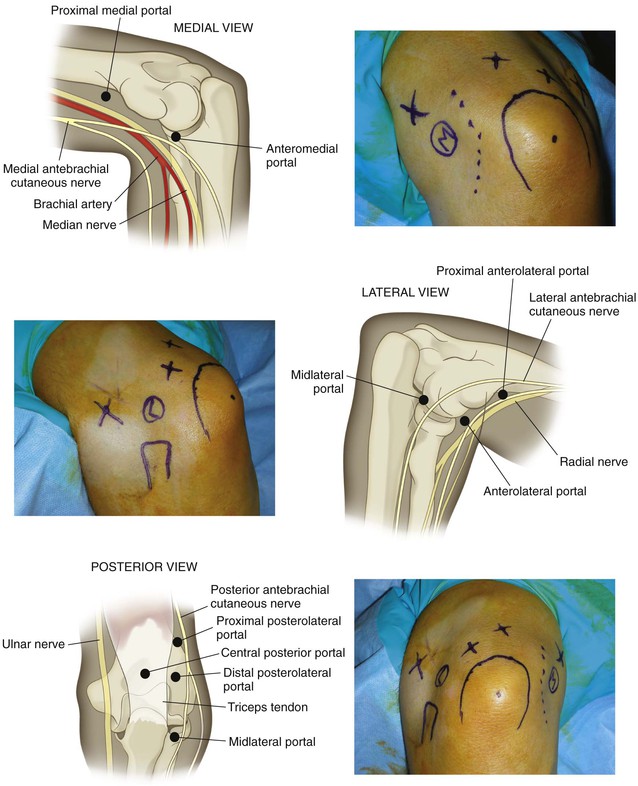
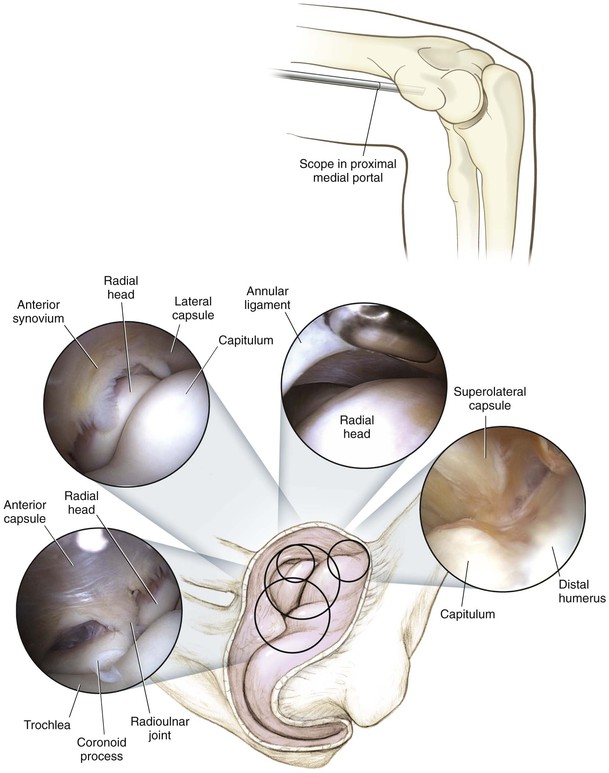
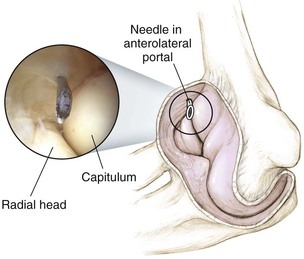
Portals (Fig. 3-50)
Proximal Anterolateral Portal
2 cm proximal and 1 cm anterior to the lateral epicondyle
• The lateral gutter, capitulum, coronoid, trochlea, and radial head are visualized
Proximal Anteromedial Portal
Proximal Posterolateral Portal
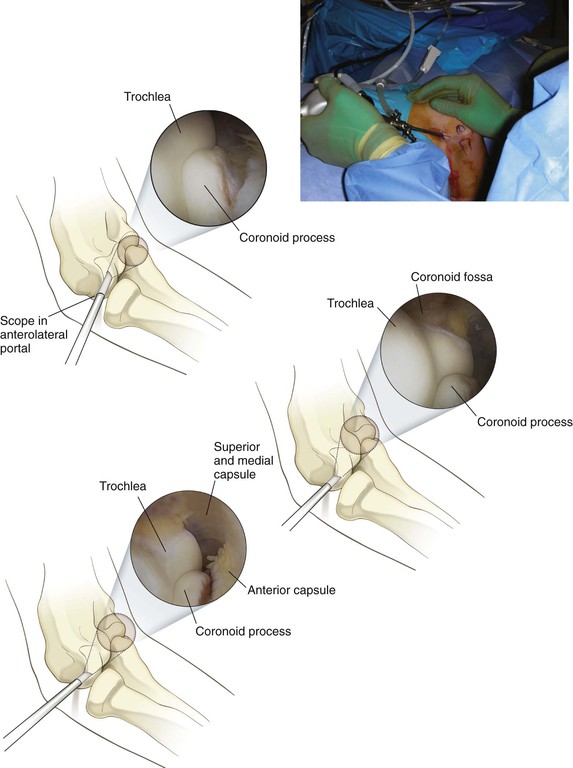
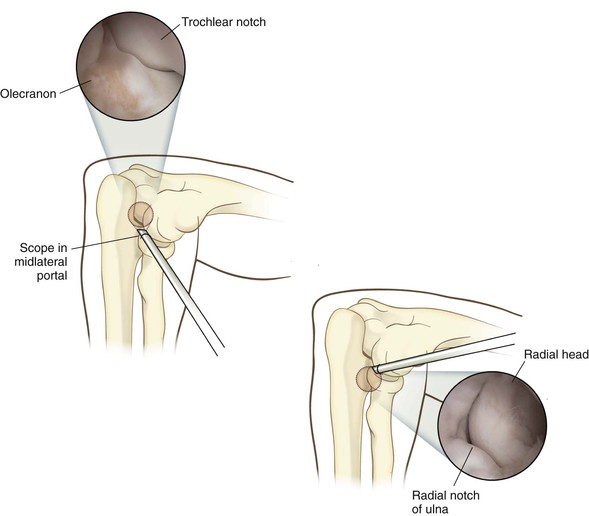
Technique (Figs. 3-51 through 3-56)
The patient is positioned and anatomic landmarks are drawn
• Beware of subluxating the ulnar nerve
• A sterile tourniquet is applied to the arm, and the patient is prepared and draped
The proximal anteromedial portal is identified, and skin and subcutaneous tissues are incised with a No. 11 blade
• An arthroscope is introduced into the joint via a blunt trocar
• Gravity inflow is established
The proximal posterolateral portal is established next, and the posterior compartment is evaluated
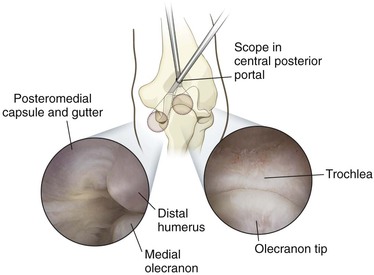
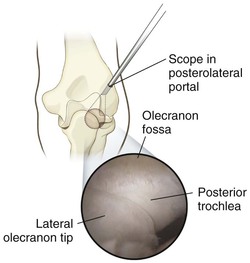
Surgical Approaches to the Forearm
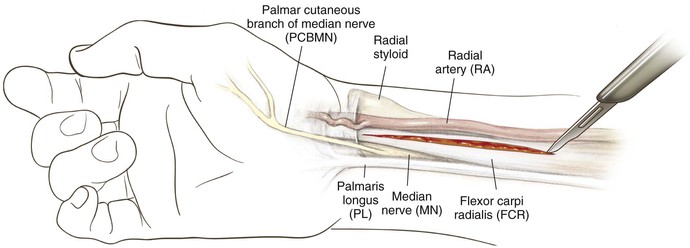
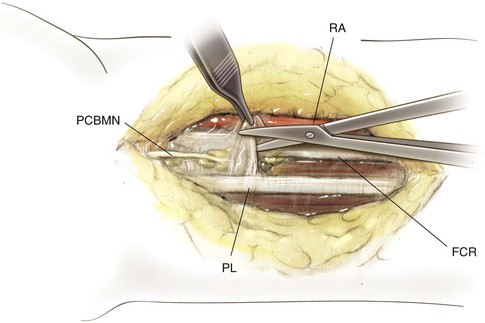
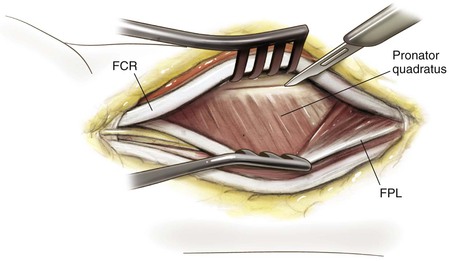
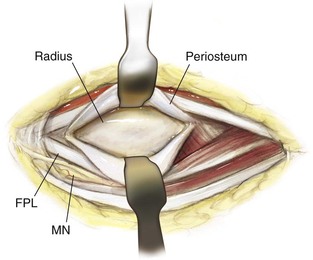
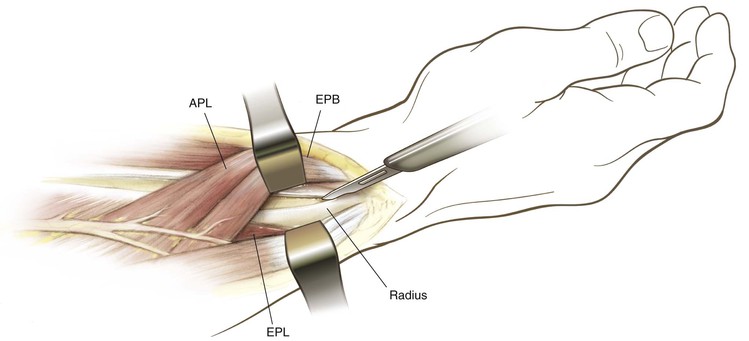
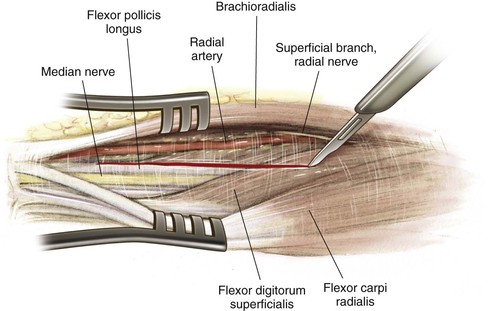
Henry Approach (the Volar Approach to the Forearm)
Indications
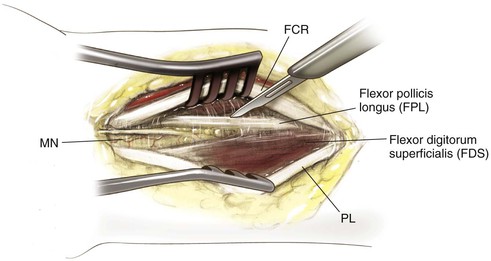
Middle Approach
Deep Dissection (Fig. 3-62)
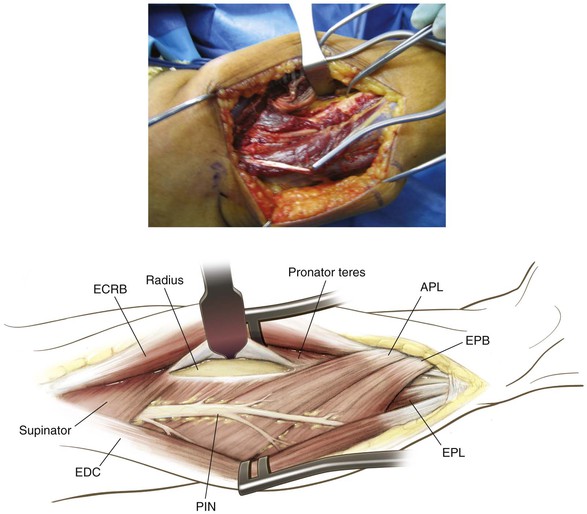
Identify the pronator teres and pronate the forearm to identify its insertion onto the lateral aspect of the radius
• The origin of the FDS also can be identified just anterior to this area on the radius
Incise the insertion point of the pronator teres subperiosteally
• Part of the FDS muscle origin also is incised
• Retract the pronator teres radially to expose the middle third of the radial shaft
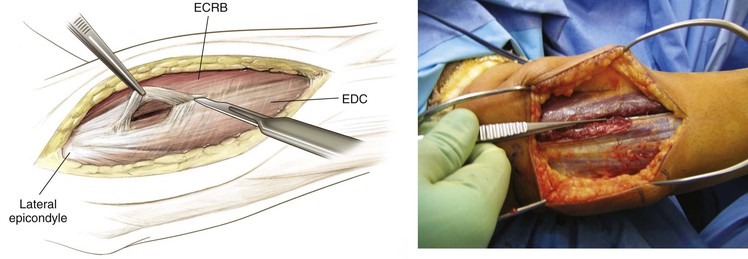
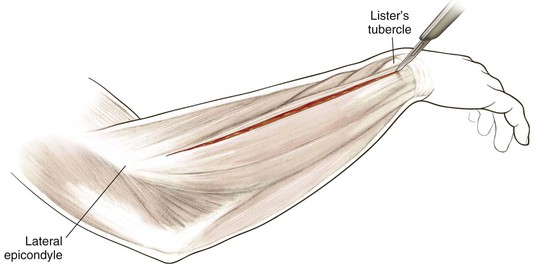
Thompson Approach (the Dorsal Approach to the Forearm)
Indications
Proximal Dorsal Approach
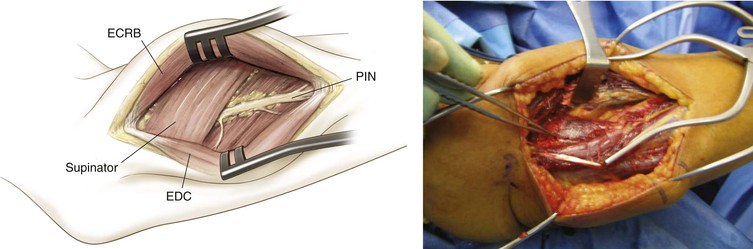
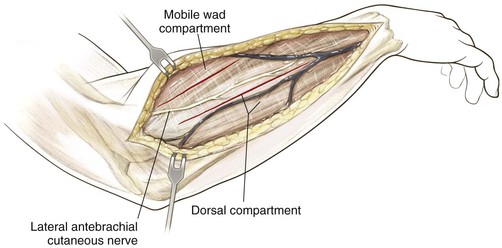
Deep Dissection (Figs. 3-65 and 3-66)
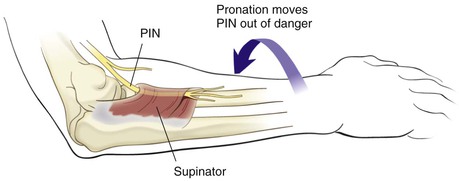
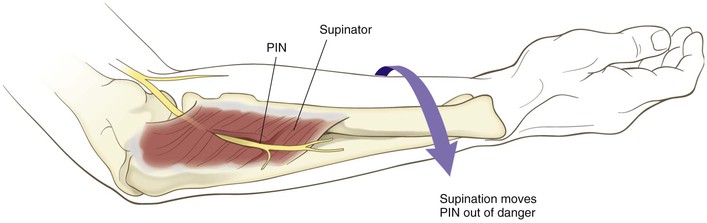
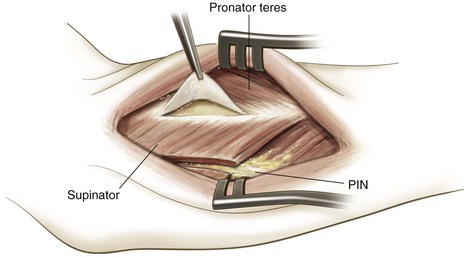
Identify the PIN as it exits the supinator (1 cm distal to the muscle belly) and carefully divide the supinator from distal to proximal, carefully visualizing and protecting the PIN at all times
• Be careful to identify distal branches, and visualize and protect these branches at all times
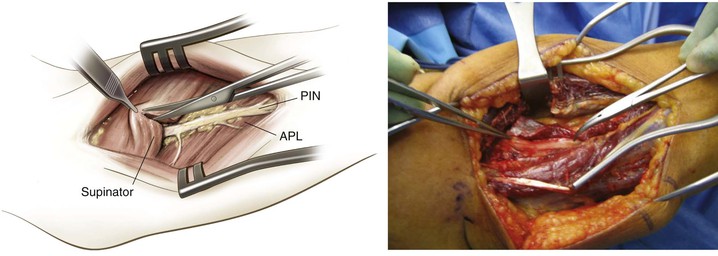
Fully supinate the forearm and identify the supinator on the anterior surface of the radius (Fig. 3-67)
Subperiosteally strip the supinator muscle from the radius and reflect it to expose the proximal radius (Fig. 3-68)