Well-defined, smoothly marginated, round/oval submucosal mass with central umbilication
• MR findings: Ectopic pancreas is isointense on all pulse sequences with main pancreas (including DWI/ADC)
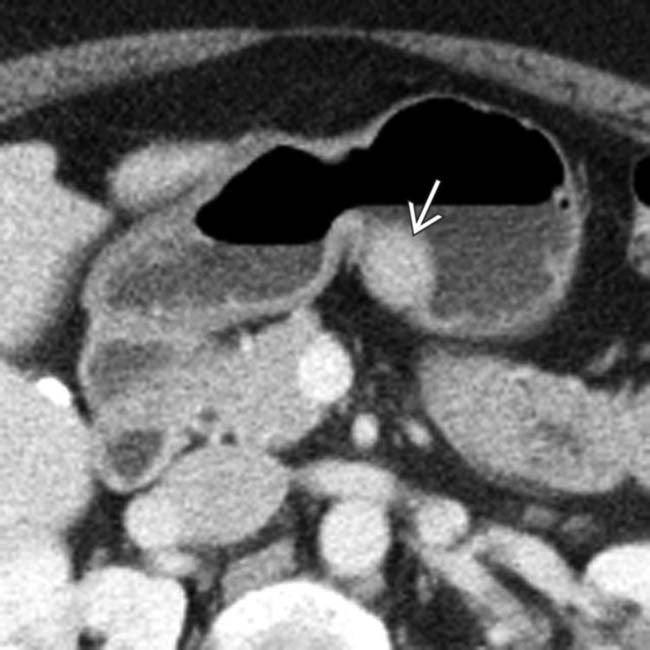
 in the body of the stomach. Note that the mass enhances similarly to the normal pancreas. Endoscopic biopsy revealed ectopic pancreatic tissue.
in the body of the stomach. Note that the mass enhances similarly to the normal pancreas. Endoscopic biopsy revealed ectopic pancreatic tissue.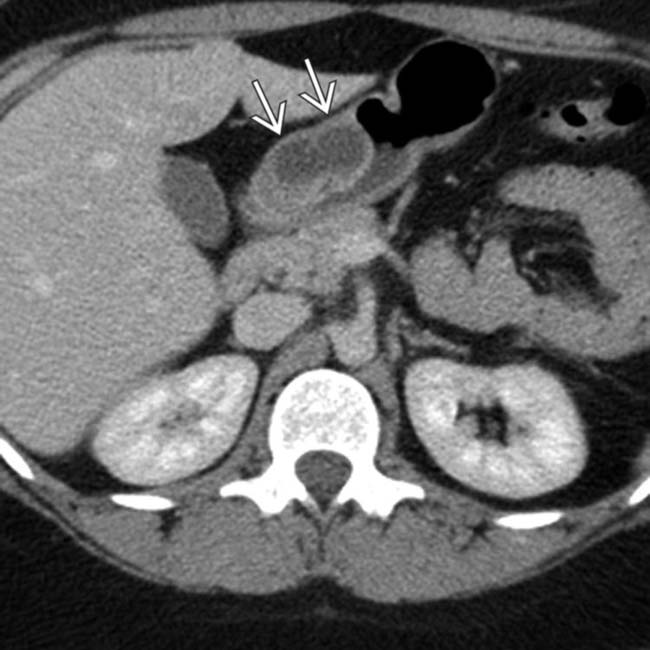
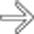
 within the distal stomach, found to represent ectopic pancreas after surgery. Ectopic pancreas can appear homogeneous, heterogeneous, or cystic depending on its internal mixture of acini, ducts, and islet cells.
within the distal stomach, found to represent ectopic pancreas after surgery. Ectopic pancreas can appear homogeneous, heterogeneous, or cystic depending on its internal mixture of acini, ducts, and islet cells.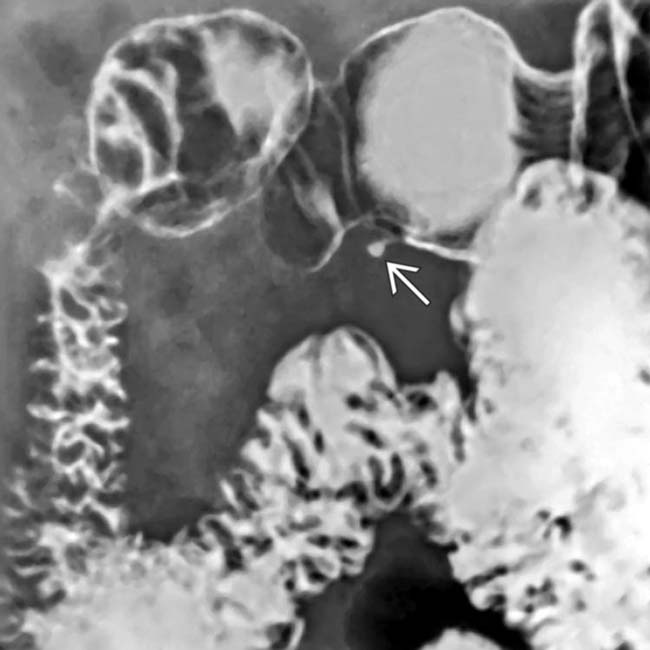
 can be seen filling a rudimentary duct.
can be seen filling a rudimentary duct.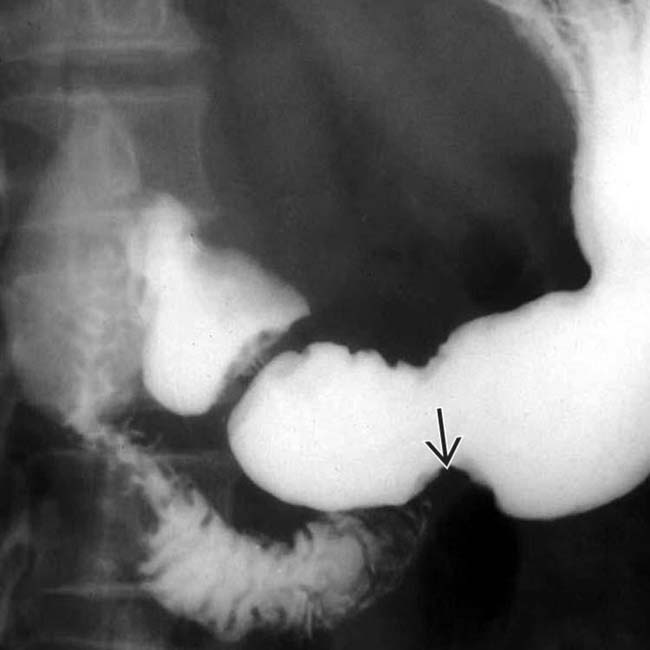
 along the greater curvature of the antrum without central umbilication. Only 45% of patients with ectopic pancreas will have central umbilication on a barium study. In the absence of this sign, it is difficult to distinguish ectopic pancreas from other intramural masses, such as metastasis or GIST.
along the greater curvature of the antrum without central umbilication. Only 45% of patients with ectopic pancreas will have central umbilication on a barium study. In the absence of this sign, it is difficult to distinguish ectopic pancreas from other intramural masses, such as metastasis or GIST.IMAGING
General Features
Radiographic Findings
• Well-defined, smoothly marginated, round or oval submucosal mass with central umbilication
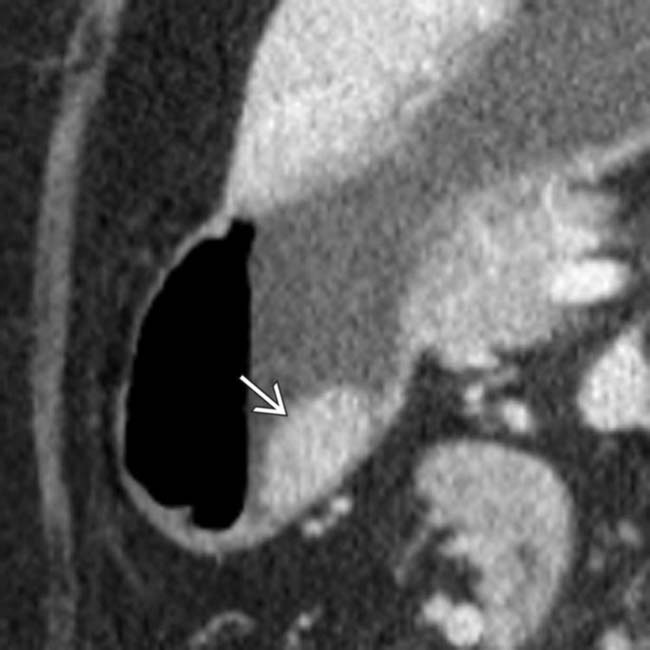
 to have broad base of attachment to the gastric wall and to have obtuse angles with the gastric lumen, suggesting a likely submucosal location for the mass. Endoscopic biopsy revealed ectopic pancreatic tissue.
to have broad base of attachment to the gastric wall and to have obtuse angles with the gastric lumen, suggesting a likely submucosal location for the mass. Endoscopic biopsy revealed ectopic pancreatic tissue.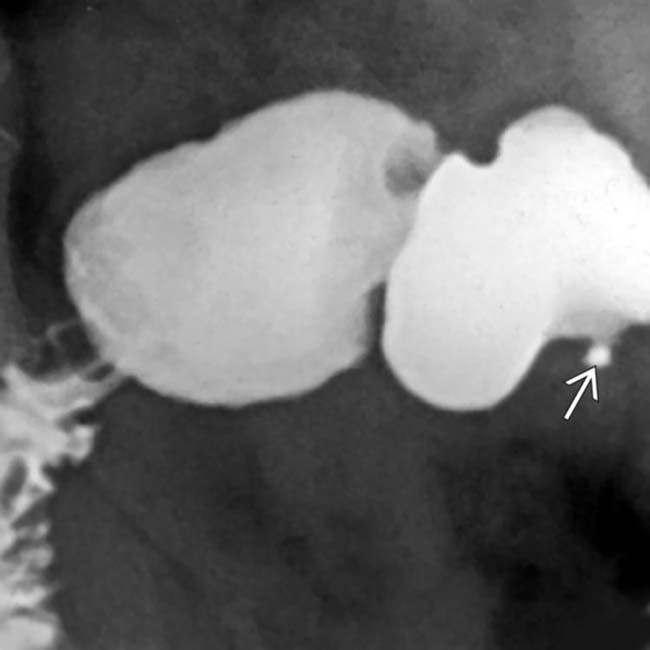
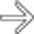
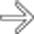
 , which is essentially diagnostic of ectopic pancreatic tissue. The central barium collection represents the rudimentary pancreatic duct.
, which is essentially diagnostic of ectopic pancreatic tissue. The central barium collection represents the rudimentary pancreatic duct.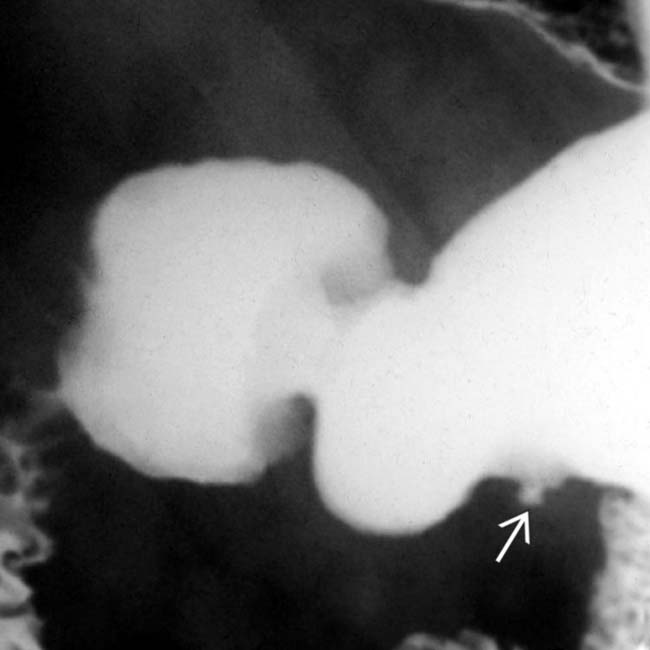
 , which is essentially diagnostic of ectopic pancreatic tissue. The central barium collection represents the rudimentary pancreatic duct.
, which is essentially diagnostic of ectopic pancreatic tissue. The central barium collection represents the rudimentary pancreatic duct.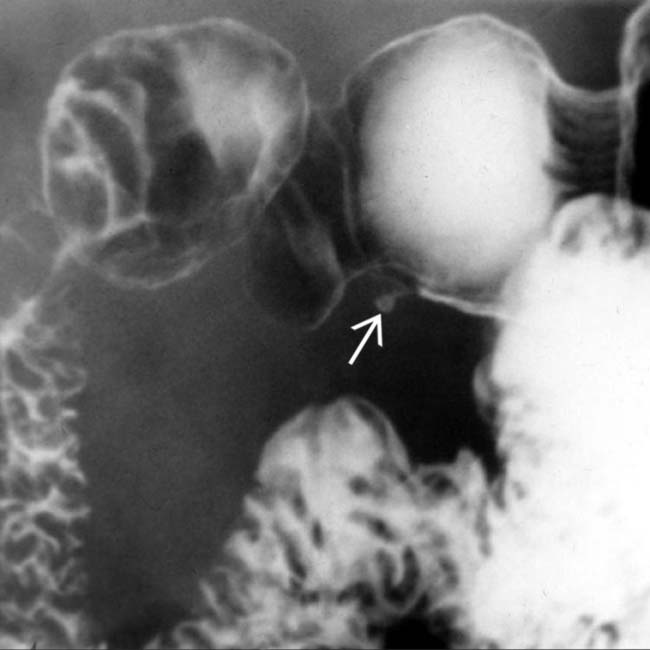
 , which is essentially diagnostic of ectopic pancreatic tissue. The central barium collection represents the rudimentary pancreatic duct
, which is essentially diagnostic of ectopic pancreatic tissue. The central barium collection represents the rudimentary pancreatic duct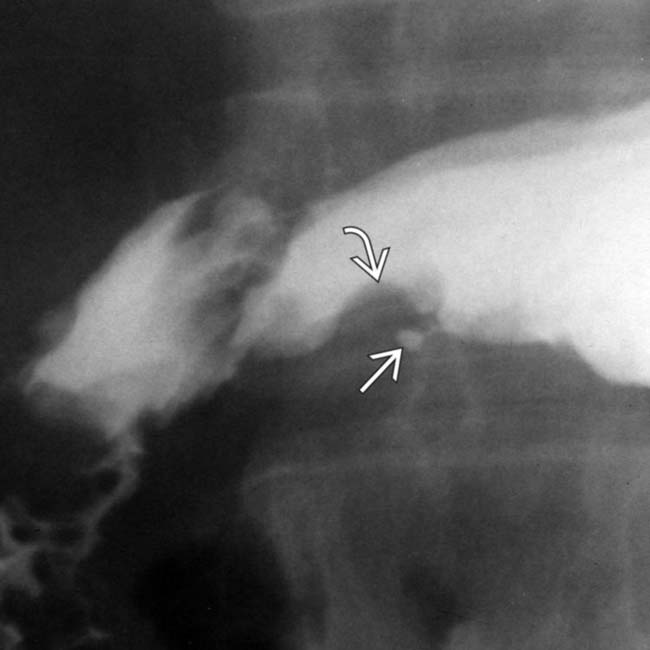
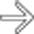
 along the greater curvature of the antrum. The mass has almost right angle interface with the gastric wall and smooth overlying mucosa, characteristic of an intramural mass. Note the central tract of barium
along the greater curvature of the antrum. The mass has almost right angle interface with the gastric wall and smooth overlying mucosa, characteristic of an intramural mass. Note the central tract of barium 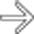 filling the rudimentary pancreatic duct, establishing the diagnosis of ectopic pancreas.
filling the rudimentary pancreatic duct, establishing the diagnosis of ectopic pancreas.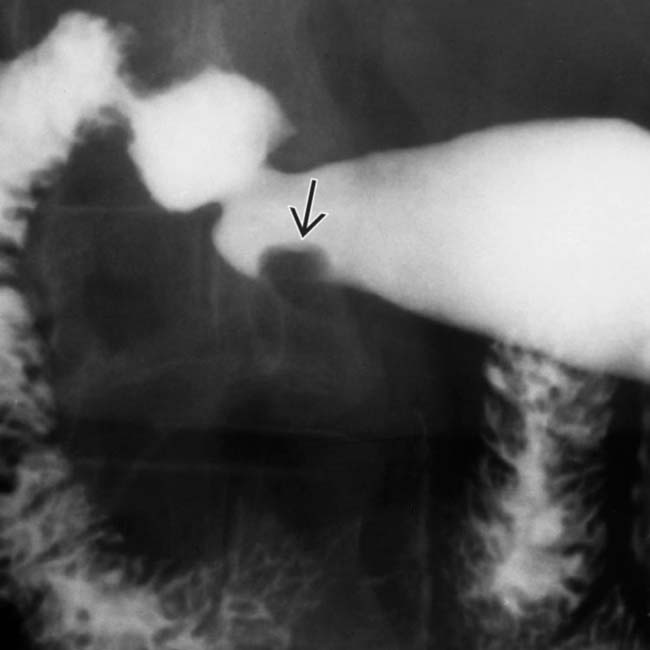
 along the greater curve of the stomach. The overlying mucosa is smooth. The size, location, and appearance of this lesion are typical of ectopic pancreas.
along the greater curve of the stomach. The overlying mucosa is smooth. The size, location, and appearance of this lesion are typical of ectopic pancreas.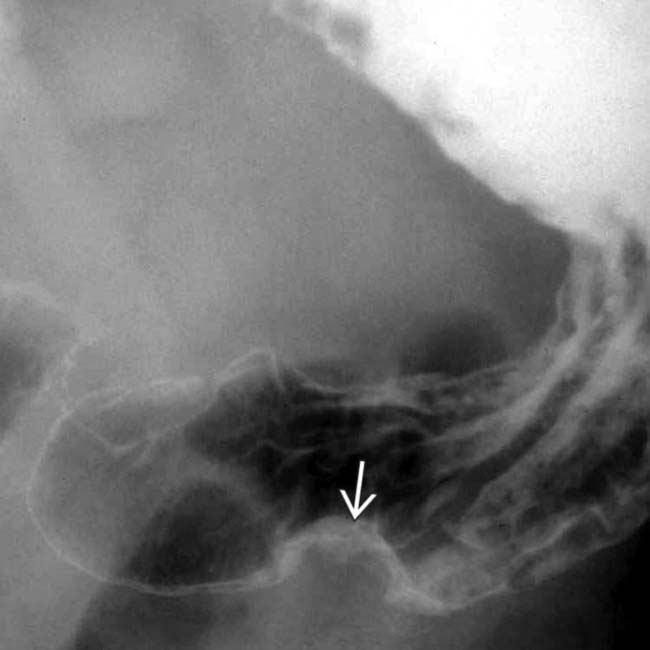
 along the greater curvature of the antrum. No central umbilication is noted. Only 45% of patients with ectopic pancreas will have a central umbilication demonstrated on a barium study. In the absence of this sign, it is difficult to distinguish ectopic pancreas from other types of intramural masses, such as metastasis or a primary stromal tumor.
along the greater curvature of the antrum. No central umbilication is noted. Only 45% of patients with ectopic pancreas will have a central umbilication demonstrated on a barium study. In the absence of this sign, it is difficult to distinguish ectopic pancreas from other types of intramural masses, such as metastasis or a primary stromal tumor.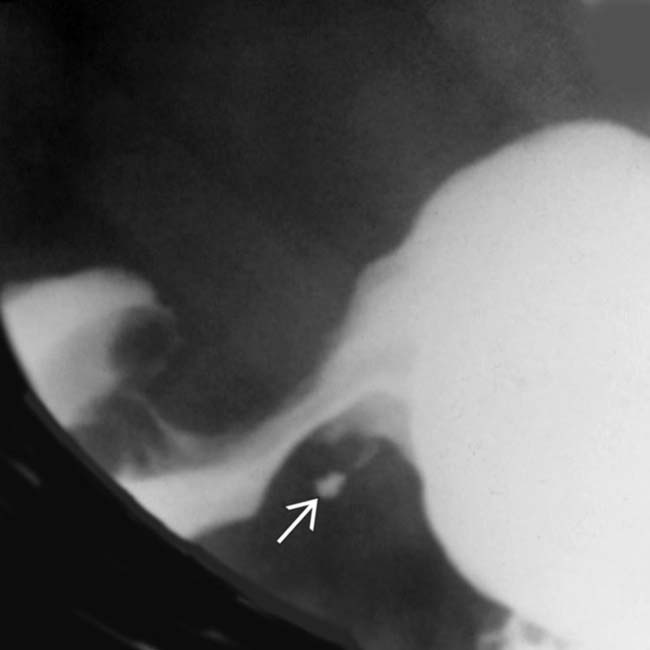
 filling the rudimentary pancreatic duct, establishing the diagnosis of ectopic pancreas.
filling the rudimentary pancreatic duct, establishing the diagnosis of ectopic pancreas.




























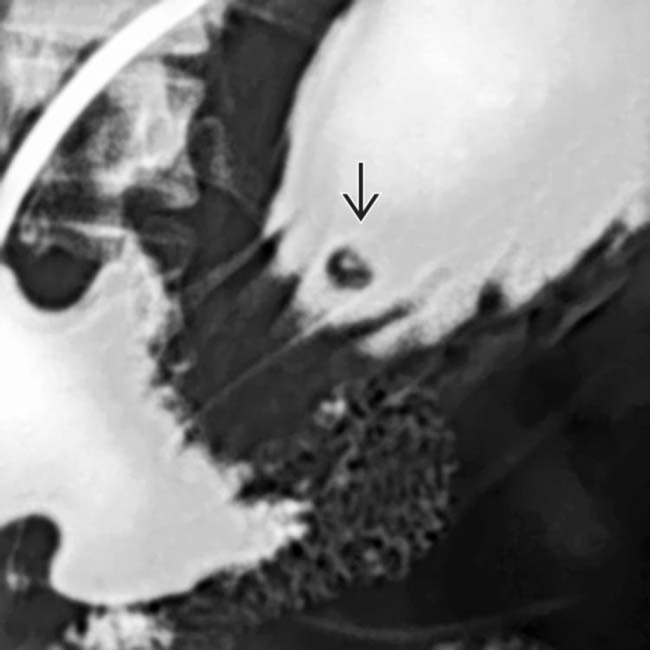
 . This is an unusual location for an ectopic pancreas. A “bull’s-eye” lesion of this type and location would raise concern for a metastatic lesion, Kaposi sarcoma, or lymphoma.
. This is an unusual location for an ectopic pancreas. A “bull’s-eye” lesion of this type and location would raise concern for a metastatic lesion, Kaposi sarcoma, or lymphoma.


